|
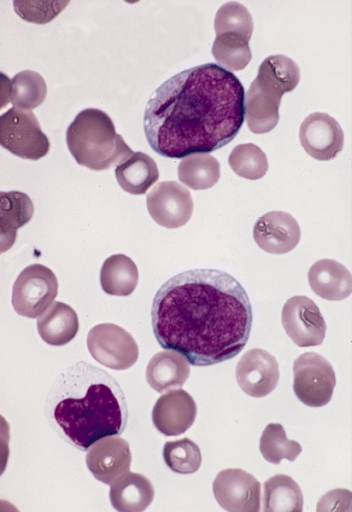
Acute Erythroid Leukemia
Acute erythrocyte leukemia is a rare form of acute myeloid leukemia (less than 5% of AML cases) where the myeloproliferation is of erythrocytic precursors. It is defined as type "M6" under the FAB classification. Signs and symptoms The most common symptoms of AEL are related to pancytopenia (a shortage of all types of blood cells), including fatigue, infections, and mucocutaneous bleeding. Almost half of people with AEL exhibit weight loss, fever and night sweats at the time of diagnosis. Almost all people with AEL are anemic, and 77% have a hemoglobin level under 10.0 g/dl. Signs of thrombocytopenia are found in about half of people with AEL. Causes The causes of AEL are unknown. Prior to a 2008 reclassification by the World Health Organization, cases that evolved from myelodysplastic syndromes, myeloproliferative neoplasms, chemotherapy for other cancers or exposure to toxins were defined as ''secondary AEL''. These cases are now likely to instead be classified as ''acute my ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematology
Hematology ( always spelled haematology in British English) is the branch of medicine concerned with the study of the cause, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases related to blood. It involves treating diseases that affect the production of blood and its components, such as blood cells, hemoglobin, blood proteins, bone marrow, platelets, blood vessels, spleen, and the mechanism of coagulation. Such diseases might include hemophilia, blood clots ( thrombus), other bleeding disorders, and blood cancers such as leukemia, multiple myeloma, and lymphoma. The laboratory analysis of blood is frequently performed by a medical technologist or medical laboratory scientist. Specialization Physicians specialized in hematology are known as hematologists or haematologists. Their routine work mainly includes the care and treatment of patients with hematological diseases, although some may also work at the hematology laboratory viewing blood films and bone marrow slides unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of platelets, also known as thrombocytes, in the blood. It is the most common coagulation disorder among intensive care patients and is seen in a fifth of medical patients and a third of surgical patients. A normal human platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets/microliter (μl) of blood. Values outside this range do not necessarily indicate disease. One common definition of thrombocytopenia requiring emergency treatment is a platelet count below 50,000/μl. Thrombocytopenia can be contrasted with the conditions associated with an abnormally ''high'' level of platelets in the blood - thrombocythemia (when the cause is unknown), and thrombocytosis (when the cause is known). Signs and symptoms Thrombocytopenia usually has no symptoms and is picked up on a routine complete blood count. Some individuals with thrombocytopenia may experience external bleeding, such as nosebleeds or bleeding gum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) is the transplantation of multipotent hematopoietic stem cells, usually derived from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood in order to replicate inside of a patient and to produce additional normal blood cells. It may be autologous (the patient's own stem cells are used), allogeneic (the stem cells come from a donor) or syngeneic (from an identical twin). It is most often performed for patients with certain cancers of the blood or bone marrow, such as multiple myeloma or leukemia. In these cases, the recipient's immune system is usually destroyed with radiation or chemotherapy before the transplantation. Infection and graft-versus-host disease are major complications of allogeneic HSCT. HSCT remains a dangerous procedure with many possible complications; it is reserved for patients with life-threatening diseases. As survival following the procedure has increased, its use has expanded beyond cancer to autoimmune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idarubicin
Idarubicin or 4-demethoxydaunorubicin is an anthracycline antileukemic drug. It inserts itself into DNA and prevents DNA unwinding by interfering with the enzyme topoisomerase II. It is an analog of daunorubicin, but the absence of a methoxy group increases its fat solubility and cellular uptake. Similar to other anthracyclines, it also induces histone eviction from chromatin. It belongs to the family of drugs called antitumor antibiotics. It is currently combined with cytosine arabinoside as a first line treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. It is used for treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis. It is distributed under the trade names Zavedos (UK) and Idamycin (USA). Side effects Diarrhea, stomach cramps, nausea and vomiting Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose. Vomiting can be the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daunorubicin
Daunorubicin, also known as daunomycin, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat cancer. Specifically it is used for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and Kaposi's sarcoma. It is administered by injection into a vein. A liposomal formulation known as liposomal daunorubicin also exists. Common side effects include hair loss, vomiting, bone marrow suppression, and inflammation of the inside of the mouth. Other severe side effects include heart disease and tissue death at the site of injection. Use in pregnancy may harm the fetus. Daunorubicin is in the anthracycline family of medication. It works in part by blocking the function of topoisomerase II. Daunorubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1979. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It was originally isolated from bacteria of the ''Streptomyces'' type. Medical uses It slows or stops the growth o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytarabine
Cytarabine, also known as cytosine arabinoside (ara-C), is a chemotherapy medication used to treat acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL), chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML), and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is given by injection into a vein, under the skin, or into the cerebrospinal fluid. There is a liposomal formulation for which there is tentative evidence of better outcomes in lymphoma involving the meninges. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, vomiting, diarrhea, liver problems, rash, ulcer formation in the mouth, and bleeding. Other serious side effects include loss of consciousness, lung disease, and allergic reactions. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Cytarabine is in the antimetabolite and nucleoside analog families of medication. It works by blocking the function of DNA polymerase. Cytarabine was patented in 1960 and approved for medical use in 1969. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proerythroblast
A proerythroblast (or rubriblast, or pronormoblast) is the earliest of four stages in development of the normoblast. In histology, it is very difficult to distinguish it from the other "-blast" cells (lymphoblast, myeloblast, monoblast, and megakaryoblast). The cytoplasm is blue in an H&E stain, indicating that it is basophilic. Proerythroblasts arise from the CFU-e (colony-forming unit erythroid) cells, and give rise to basophilic erythroblasts. In the mouse, proerythroblasts are large committed progenitors that express high levels of transferrin receptor (iron acquisition receptor), the erythropoietin receptor (EpoR), some c-Kit (stem cell factor receptor), and are Ter119 (cell surface molecule)-positive. Their proliferative capacity is more limited compared to the preceding stage, the CFU-e. In vivo, starting with the proerythroblast stage, erythroid cells undergo several more cell divisions while at the same time upregulating survival genes such as Bcl-xL, acquiring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ''leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia— acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myeloblast
The myeloblast is a unipotent stem cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival. Structure Myeloblasts reside extravascularly in the bone marrow. Hematopoiesis takes place in the extravascular cavities between the sinuses of the marrow. The wall of the sinuses is composed of two different types of cells, endothelial cells and adventitial reticular cells. The hemopoietic cells are aligned in cords or wedges between these sinuses, with myeloblasts and other granular progenitors concentrated in the subcortical regions of these hemopoietic cords. Myeloblasts are rather small cells with a diameter between 14 and 18μm. The major part is occupied by a large oval nucleus composed of very fine nonaggregated chromatin and possessing 3 or more nucleoli. The cytoplasm has a basophilic character and is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyserythropoiesis
Dyserythropoiesis refers to the defective development of red blood cells, also called erythrocytes. This problem can be congenital, acquired, or inherited. Some red blood cells may be destroyed within the bone marrow during the maturation process, whereas others can enter the circulation with abnormalities. These abnormalities can be functional and/or morphological, which can lead to anemia since there may be increased turnover of red blood cells. There are a number of diseases that cause dyserythropoiesis. Congenital/inherited causes include congenital dyserythropoietic anemia, thalassemia, pyruvate kinase deficiency, hereditary pyropoikilocytosis, and abetalipoproteinemia. Acquired causes include nutrient deficiency/malnutrition (e.g. cobalamine, folate, and iron), myelodysplasia, HIV infection, and certain medications (e.g. zidovudine). See also * Erythropoiesis * Erythrocyte * Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia (CDA) is a rare blood di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythroblast
A nucleated red blood cell (NRBC), also known by several other names, is a red blood cell that contains a cell nucleus. Almost all vertebrate organisms have hemoglobin-containing cells in their blood, and with the exception of mammals, all of these red blood cells are nucleated. In mammals, NRBCs occur in normal development as precursors to mature red blood cells in erythropoiesis, the process by which the body produces red blood cells. NRBCs are normally found in the bone marrow of humans of all ages and in the blood of fetuses and newborn infants. After infancy, RBCs normally contain a nucleus only during the very early stages of the cell's life, and the nucleus is ejected as a normal part of cellular differentiation before the cell is released into the bloodstream. Thus, if NRBCs are identified on an adult's complete blood count or peripheral blood smear, it suggests that there is a very high demand for the bone marrow to produce RBCs, and immature RBCs are being relea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals ( signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |