|
Action Of 10 November 1808
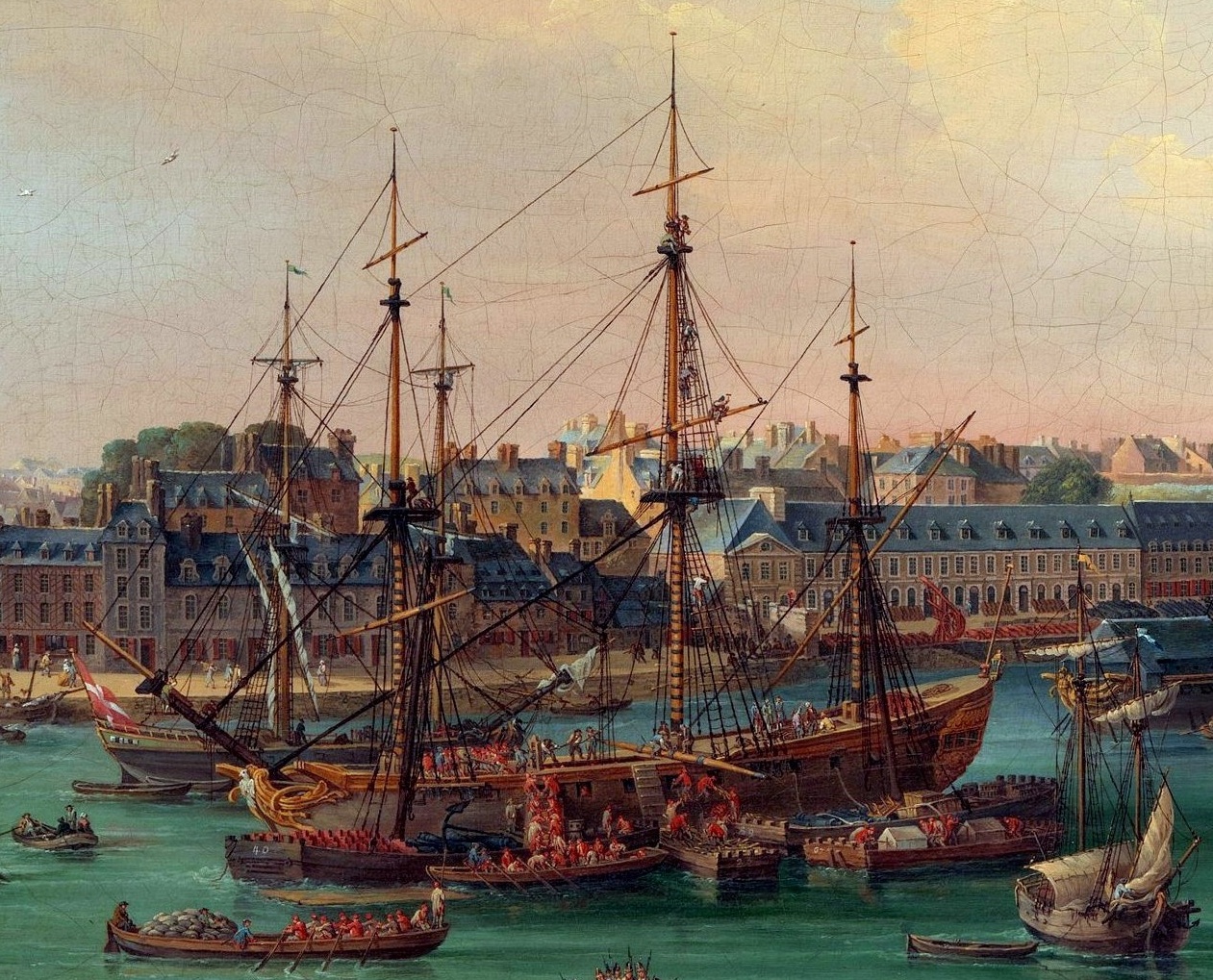
The action of 10 November 1808 was a minor naval engagement of the Napoleonic Wars, in which a British frigate defeated and captured a French frigate in the Bay of Biscay. The action formed part of the blockade of the French Biscay ports during the war by the British Royal Navy, a strategy designed to prevent ships from entering or leaving French harbours, thus eliminating foreign trade with France and damaging the French economy as well as cutting France off from her overseas colonies. The French ship in the action, '' Thétis'', was destined for the French held West Indian island of Martinique with a cargo of flour and military supplies, including over 100 soldiers to reinforce the island's garrison. ''Thétis'' had not even cleared the French coast when she was discovered by a patrolling British frigate of the inshore squadron, a unit tasked with watching the entrance to the French Biscay ports, principally Brest, and intercepting any ships seeking to enter or leave the harbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of French domination over most of continental Europe. The wars stemmed from the unresolved disputes associated with the French Revolution and the French Revolutionary Wars consisting of the War of the First Coalition (1792–1797) and the War of the Second Coalition (1798–1802). The Napoleonic Wars are often described as five conflicts, each termed after the coalition that fought Napoleon: the Third Coalition (1803–1806), the Fourth (1806–1807), the Fifth (1809), the Sixth (1813–1814), and the Seventh (1815) plus the Peninsular War (1807–1814) and the French invasion of Russia (1812). Napoleon, upon ascending to First Consul of France in 1799, had inherited a republic in chaos; he subsequently created a state with stable financ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Niémen (1808)
HMS ''Niemen'' was a Royal Navy 38-gun fifth-rate Sailing frigate, frigate. She began her career as the ''Niémen'', a 44-gun French Navy frigate, designed by Pierre Rolland. She was only in French service for a few months when in 1809 she encountered some British frigates. The British captured her and she continued in British service as ''Niemen''. In British service she cruised in the Atlantic and North American waters, taking numerous small American prizes, some privateers but mostly merchantmen. She was broken up in 1815, at the end of the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812. Construction and capture Chantier Courau Frères at Bordeaux built ''Niémen'' to a design by Pierre Rolland, carrying 40 guns. She was launched in 1808 but spent only months in French service. She was commissioned at Bordeaux on 22 November 1808, but not completed until January 1809. On 4 April 1809 she sailed under the command of Commandant Jean Dupotet for Mauritius, Fort-de-France with stores an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Masterman Hardy
Vice-Admiral Sir Thomas Masterman Hardy, 1st Baronet, GCB (5 April 1769 – 20 September 1839) was a British Royal Navy officer. He took part in the Battle of Cape St. Vincent in February 1797, the Battle of the Nile in August 1798 and the Battle of Copenhagen in April 1801 during the French Revolutionary Wars. He served as flag captain to Admiral Lord Nelson, and commanded HMS ''Victory'' at the Battle of Trafalgar in October 1805 during the Napoleonic Wars. Nelson was shot as he paced the decks with Hardy, and as he lay dying, Nelson's famous remark of "Kiss me, Hardy" was directed at him. Hardy went on to become First Naval Lord in November 1830 and in that capacity refused to become a Member of Parliament and encouraged the introduction of steam warships. Early life Born the second son of Joseph Hardy and Nanny Hardy (née Masterman) at Kingston Russell House in Long Bredy (or according to some sources in Winterborne St Martin), Hardy joined the navy with his entry ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groix
Groix (; br, Enez Groe) is an island and a commune in the Morbihan department of the region of Brittany in north-western France. Groix lies a few kilometres off the coast of Lorient. Several ferries a day run from Lorient to Groix. There are a few small towns on the island. High cliffs are on its north coast and sandy beaches in secluded coves on the south coast. Groix is also home to a wide variety of sea birds. Groix is also famous for hosting the only convex beach in Europe, which also moves following sea currents. During the last 15 years, the beach moved half a kilometer westbound. The geology of Groix is distinct from that of the nearby continent, and the east and south coasts have been designated a mineral nature reserve since 1982. More than 60 minerals can be found on the island, particularly blue glaucophane (observable on the surface), epidote or garnet. The island mainly consists of schist. A major naval battle between Britain and France took place off Groix in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize Money
Prize money refers in particular to naval prize money, usually arising in naval warfare, but also in other circumstances. It was a monetary reward paid in accordance with the prize law of a belligerent state to the crew of a ship belonging to the state, either a warship of its navy or a privateer vessel commissioned by the state. Prize money was most frequently awarded for the capture of enemy ships or of cargoes belonging to an enemy in time of war, either arrested in port at the outbreak of war or captured during the war in international waters or other waters not the territorial waters of a neutral state. Goods carried in neutral ships that are classed as contraband, being shipped to enemy-controlled territory and liable to be useful to it for making war, were also liable to be taken as prizes, but non-contraband goods belonging to neutrals were not. Claims for the award of prize money were usually heard in a prize court, which had to adjudicate the claim and condemn the pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glorious First Of June
The Glorious First of June (1 June 1794), also known as the Fourth Battle of Ushant, (known in France as the or ) was the first and largest fleet action of the naval conflict between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the First French Republic during the French Revolutionary Wars. The action was the culmination of a campaign that had criss-crossed the Bay of Biscay over the previous month in which both sides had captured numerous merchant ships and minor warships and had engaged in two partial, but inconclusive, fleet actions. The British Channel Fleet under Admiral Lord Howe attempted to prevent the passage of a vital French grain convoy from the United States, which was protected by the French Atlantic Fleet, commanded by Rear-Admiral Villaret-Joyeuse. The two forces clashed in the Atlantic Ocean, some west of the French island of Ushant on 1 June 1794. During the battle, Howe defied naval convention by ordering his fleet to turn towards the French and for each of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Emerald (1795)
HMS ''Emerald'' was a 36-gun ''Amazon''-class fifth rate frigate that Sir William Rule designed in 1794 for the Royal Navy. The Admiralty ordered her construction towards the end of May 1794 and work began the following month at Northfleet dockyard. She was completed on 12 October 1795 and joined Admiral John Jervis's fleet in the Mediterranean. In 1797, ''Emerald'' was one of several vessels sent to hunt down and capture the crippled Santisima Trinidad, which had escaped from the British at the Battle of Cape St Vincent. ''Emerald'' was supposed to have been present at the Battle of the Nile but in May 1798 a storm separated her from Horatio Nelson's squadron and she arrived in Aboukir Bay nine days too late. She was part of Rear-Admiral John Thomas Duckworth's squadron during the action of 7 April 1800 off Cádiz. ''Emerald'' served in the Caribbean throughout 1803 in Samuel Hood's fleet, then took part in the invasion of St Lucia in July, and of Surinam the follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Lewis Maitland (Rear Admiral)
Rear-Admiral Sir Frederick Lewis Maitland (7 September 177730 November 1839) was an officer in the Royal Navy during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. He rose to the rank of rear admiral and held a number of commands. The most famous event of his career occurred when Napoleon Bonaparte surrendered to him aboard , marking the final end of the Napoleonic Wars. Family and early life Maitland was born at Rankeilour, Fife on 7 September 1777, as the third son of Frederick Lewis Maitland (1730–1786), himself a distinguished naval officer. Several other members of Maitland's family were serving officers in the army, including his uncle, General Sir Alexander Maitland, 1st Baronet and his cousin, General Frederick Maitland (1763–1848). Having received an education at the Royal High School, Edinburgh, Maitland followed his father into the Navy, spending his first years aboard the sloop , under Captain George Duff, followed by a period aboard the frigate with R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannon
A cannon is a large- caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during the late 19th century. Cannons vary in gauge, effective range, mobility, rate of fire, angle of fire and firepower; different forms of cannon combine and balance these attributes in varying degrees, depending on their intended use on the battlefield. A cannon is a type of heavy artillery weapon. The word ''cannon'' is derived from several languages, in which the original definition can usually be translated as ''tube'', ''cane'', or ''reed''. In the modern era, the term ''cannon'' has fallen into decline, replaced by ''guns'' or ''artillery'', if not a more specific term such as howitzer or mortar, except for high-caliber automatic weapons firing bigger rounds than machine guns, called autocannons. The earliest known depict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lorient
Lorient (; ) is a town ('' commune'') and seaport in the Morbihan department of Brittany in western France. History Prehistory and classical antiquity Beginning around 3000 BC, settlements in the area of Lorient are attested by the presence of megalithic architecture. Ruins of Roman roads (linking Vannes to Quimper and Port-Louis to Carhaix) confirm Gallo-Roman presence. Founding In 1664, Jean-Baptiste Colbert founded the French East Indies Company. In June 1666, an ordinance of Louis XIV granted lands of Port-Louis to the company, along with Faouédic on the other side of the roadstead. One of its directors, Denis Langlois, bought lands at the confluence of the Scorff and the Blavet rivers, and built slipways. At first, it only served as a subsidiary of Port-Louis, where offices and warehouses were located. The following years, the operation was almost abandoned, but in 1675, during the Franco-Dutch War, the French East Indies Company scrapped its base in Le H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Navy
The French Navy (french: Marine nationale, lit=National Navy), informally , is the maritime arm of the French Armed Forces and one of the five military service branches of France. It is among the largest and most powerful naval forces in the world, ranking seventh in combined fleet tonnage and fifth in number of naval vessels. The French Navy is one of eight naval forces currently operating fixed-wing aircraft carriers,Along with the U.S., U.K., China, Russia, Italy, India and Spain with its flagship being the only nuclear-powered aircraft carrier outside the United States Navy, and one of two non-American vessels to use catapults to launch aircraft. Founded in the 17th century, the French Navy is one of the oldest navies still in continual service, with precursors dating back to the Middle Ages. It has taken part in key events in French history, including the Napoleonic Wars and both world wars, and played a critical role in establishing and securing the French coloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean) and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico and the North American mainland, east of Central America, and north of South America. Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate, the region has more than 700 islands, islets, reefs and cays (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arcs delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea: The Greater Antilles and the Lucayan Archipelago on the north and the Lesser Antilles and the on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles). They form the West Indies with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago (the Bahamas and Turks and Caicos Islands), which are considered to be part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |