|
Acantharea
The Acantharea (Acantharia) are a group of radiolarian protozoa, distinguished mainly by their strontium sulfate skeletons. Acantharians are heterotrophic marine microplankton that range in size from about 200 microns in diameter up to several millimeters. Some acantharians have photosynthetic endosymbionts and hence are considered mixotrophs. Morphology Acantharian skeletons are composed of strontium sulfate, SrSO4, in the form of mineral celestine crystal. Celestine is named for the delicate blue colour of its crystals, and is the heaviest mineral in the ocean. The denseness of their celestite ensures acantharian shells function as mineral ballast, resulting in fast sedimentation to bathypelagic depths. High settling fluxes of acantharian cysts have been observed at times in the Iceland Basin and the Southern Ocean, as much as half of the total gravitational organic carbon flux. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiolaria
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, while the ectopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaeocystis
''Phaeocystis'' is a genus of algae belonging to the Prymnesiophyte class and to the larger division of Haptophyta. It is a widespread marine phytoplankton and can function at a wide range of temperatures ( eurythermal) and salinities (euryhaline). Members of this genus live in the open ocean, as well as in sea ice. It has a polymorphic life cycle, ranging from free-living cells to large colonies. The ability to form a floating colony is one of the unique attributes of ''Phaeocystis'' – hundreds of cells are embedded in a polysaccharide gel matrix, which can increase massively in size during blooms. The largest ''Phaeocystis'' blooms form in the polar seas: ''P. pouchetii'' in the north and ''P. antarctica'' in the south. This intense ''Phaeocystis'' productivity generally persists for about a three-month period, spanning most of the summer in the Southern Hemisphere. ''Phaeocystis''-abundant ecosystems are generally associated with commercially important stocks of crusta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
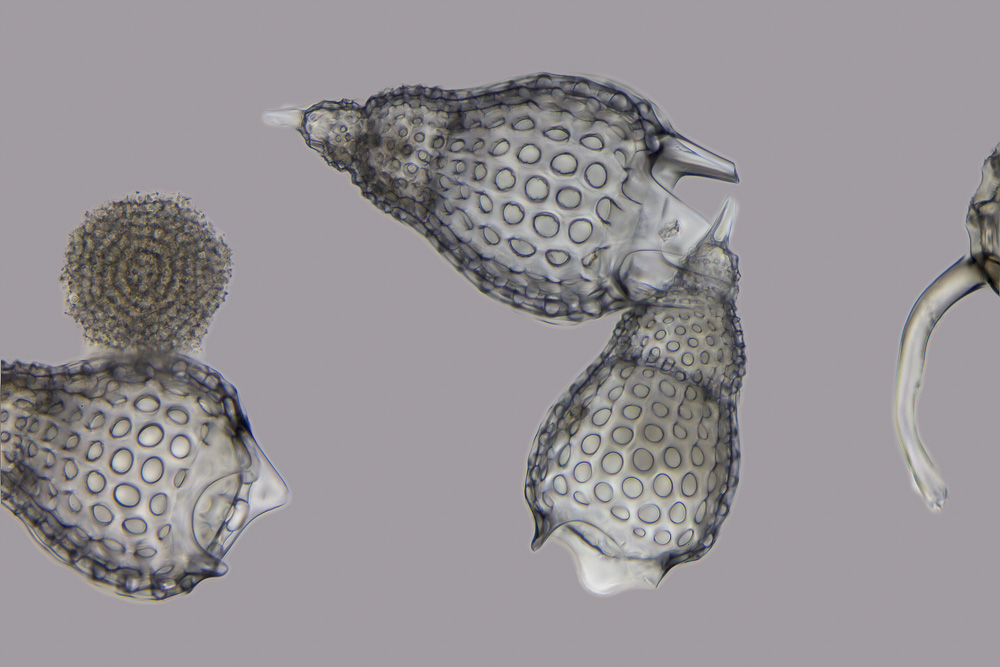
Acanthophractida
Acanthophractida is an order of marine radiolarians in the subclass Acantharia; skeleton includes a latticework shell and skeletal rods. They have a latticework shell, which can be spherical or ovoid and fused with the skeletal rods. The shell is concentric with the central capsule. "The body is usually covered with a single or double gelatinous sheath through which the skeletal rods emerge". References Radiolarian orders {{Radiolarian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthracanthida
Radiolaria (Challenger) Plate. Arthracanthida, a subclass of Acantharea, is a group of marine protozoans. They consist mainly of a gelatinous sheath filled with cytoplasm and a skeleton of up to 20 radially placed spicules made of celestine ( strontium sulfate). While mostly found in the upper areas of the ocean, they are able to move vertically by using microfilaments attached to the spicules to expand and contract the sheath. They are plentiful in the Gulf Stream The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension the North Atlantic Drift, is a warm and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico and flows through the Straits of Florida and up the eastern coastline of the Unit ... during the summer months, but little is known about their overall distribution. References *L. H. Hyman, The Invertebrates, vol. 1, McGraw-Hill, 1940 *T. Cavalier-Smith, Kingdom Protozoa and its 18 phyla, Microbiol. Rev., 57(4):953–994, 1993 *K. Hausmann and N. Hul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acantharia Confocial Micrograph 2
''Acantharia'' is a genus of fungi in the Venturiaceae family. Species * '' Acantharia aterrima'' (Cooke & G. Winter) Arx (1954) * '' Acantharia chaetomoides'' W.H. Hsieh, Chi Y. Chen & Sivan. (1995) * '' Acantharia echinata'' (Ellis & Everh.) Theiss. & Syd. (1918) * '' Acantharia elegans'' (Syd. & P. Syd.) Arx (1954) * '' Acantharia hamata'' (Penz. & Sacc.) Arx (1954) * '' Acantharia quercus-dilatatae'' S.K. Bose & E. Müll. (1965) * '' Acantharia sinensis'' (Petr.) Arx (1954) References Index Fungorum species listing External links *Acantharia' at Index Fungorum ''Index Fungorum'' is an international project to index all formal names (scientific names) in the fungus kingdom. the project is based at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, one of three partners along with Landcare Research and the Institute of M ... Venturiaceae Taxa named by Hans Sydow {{Pleosporales stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestine (mineral)
Celestine (the IMA-accepted name) or celestite is a mineral consisting of strontium sulfate ( Sr S O). The mineral is named for its occasional delicate blue color. Celestine and the carbonate mineral strontianite are the principal sources of the element strontium, commonly used in fireworks and in various metal alloys. Etymology Celestine derives its name from the Latin word ''caelestis'' meaning celestial which in turn is derived from the Latin word ''caelum'' meaning sky or heaven. Occurrence Celestine occurs as crystals, and also in compact massive and fibrous forms. It is mostly found in sedimentary rocks, often associated with the minerals gypsum, anhydrite, and halite. On occasion in some localities, it may also be found with sulfur inclusions. The mineral is found worldwide, usually in small quantities. Pale blue crystal specimens are found in Madagascar. White and orange variants also occurred at Yate, Bristol, UK, where it was extracted for commercial purpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strontium Sulfate
Strontium sulfate (SrSO4) is the sulfate salt of strontium. It is a white crystalline powder and occurs in nature as the mineral celestine. It is poorly soluble in water to the extent of 1 part in 8,800. It is more soluble in dilute HCl and nitric acid and appreciably soluble in alkali chloride solutions (e.g. sodium chloride). Structure Strontium sulfate is a polymeric material, isostructural with barium sulfate. Crystallized strontium sulfate is utilized by a small group of radiolarian protozoa, called the Acantharea, as a main constituent of their skeleton. Applications and chemistry Strontium sulfate is of interest as a naturally occurring precursor to other strontium compounds, which are more useful. In industry it is converted to the carbonate for use as ceramic precursor and the nitrate for use in pyrotechnics. The low aqueous solubility of strontium sulfate can lead to scale formation in processes where these ions meet. For example, it can form on surfaces of equipmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protozoa
Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Historically, protozoans were regarded as "one-celled animals", because they often possess animal-like behaviours, such as motility and predation, and lack a cell wall, as found in plants and many algae. When first introduced by Georg Goldfuss (originally spelled Goldfuß) in 1818, the taxon Protozoa was erected as a class within the Animalia, with the word 'protozoa' meaning "first animals". In later classification schemes it was elevated to a variety of higher ranks, including phylum, subkingdom and kingdom, and sometimes included within Protoctista or Protista. The approach of classifying Protozoa within the context of Animalia was widespread in the 19th and early 20th century, but not universal. By the 1970s, it became usual to require ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates ( Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey ( phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, '' Oodinium'' and '' Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagodinium Béii
''Pelagodinium béii'' is a photosynthetic dinoflagellate that forms a symbiotic relationship with planktonic foraminifera. Discovery and classification ''P. béii'' was originally described as ''Gymnodinium béii'' by marine isotope geochemist Howard Spero in 1987, after being discovered in the eastern Pacific Ocean. It was redefined as ''P. béii'' in 2010 after its Ribosomal RNA was characterized, revealing it to be a relative of the genus ''Symbiodinium : ''This is about the genus sometimes called Zoox. For the company, see Zoox (company)'' ''Symbiodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known. These unicell ...''. ''Symbiodinium'' is a well-studied endosymbiont of deep water invertebrates, protists and foraminifera, found especially alongside reef-dwelling organisms. Ecology The ''P. béii'' contains a single straight elongated apical vesicle with a row of small knobs, eight latitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myonemes
Infusoria are minute freshwater life forms including ciliates, euglenoids, protozoa, unicellular algae and small invertebrates. Some authors (e.g., Bütschli) used the term as a synonym for Ciliophora. In modern formal classifications, the term is considered obsolete; the microorganisms previously included in the Infusoria are mostly assigned to the kingdom Protista. Aquarium use Infusoria are used by owners of aquaria to feed fish fry; because of its small size it can be used to rear newly hatched fry of many common aquarium species. Many home aquaria are unable to naturally supply sufficient infusoria for fish-rearing, so hobbyists may create and maintain their own supply cultures or use one of the many commercial cultures available.Sharpe, Shirlie (December 22, 2018)"How to Culture Your Own Infusoria at Home" The Spruce Pets. Retrieved August 28, 2019. Infusoria can be cultured by soaking any decomposing vegetative matter such as papaya skin in a jar of aged (i.e., chlorine-fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haptophyte
The haptophytes, classified either as the Haptophyta, Haptophytina or Prymnesiophyta (named for '' Prymnesium''), are a clade of algae. The names Haptophyceae or Prymnesiophyceae are sometimes used instead. This ending implies classification at the class rank rather than as a division. Although the phylogenetics of this group has become much better understood in recent years, there remains some dispute over which rank is most appropriate. Characteristics The chloroplasts are pigmented similarly to those of the heterokonts, but the structure of the rest of the cell is different, so it may be that they are a separate line whose chloroplasts are derived from similar red algal endosymbionts. The cells typically have two slightly unequal flagella, both of which are smooth, and a unique organelle called a '' haptonema'', which is superficially similar to a flagellum but differs in the arrangement of microtubules and in its use. The name comes from the Greek ''hapsis'', touch, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |