|
Ablaq
Ablaq ( ar, أبلق; particolored; literally 'piebald') is an architectural technique involving alternating or fluctuating rows of light and dark stone. Records trace the beginnings of this type of masonry technique to the southern parts of Syria. It is associated as an Arabic term, especially as related to Arabic Islamic architectural decoration. The first recorded use of the term ''ablaq'' pertained to repairs of the Great Mosque of Damascus in 1109, but the technique itself was used much earlier. Technique This technique is a feature of Islamic architecture. The ablaq decorative technique is thought to maybe be a derivative from the ancient Byzantine Empire, whose architecture used alternate sequential runs of light colored ashlar stone and darker colored orange brick. The first known use of the term ablaq in building techniques is in masonry work in reconstruction improvements to the walls of the Umayyad Mosque of Damascus. According to records, these reconstruction m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ablaq Design
Ablaq ( ar, أبلق; particolored; literally 'piebald') is an architectural technique involving alternating or fluctuating rows of light and dark stone. Records trace the beginnings of this type of masonry technique to the southern parts of Syria. It is associated as an Arabic term, especially as related to Arabic Islamic architectural decoration. The first recorded use of the term ''ablaq'' pertained to repairs of the Great Mosque of Damascus in 1109, but the technique itself was used much earlier. Technique This technique is a feature of Islamic architecture. The ablaq decorative technique is thought to maybe be a derivative from the ancient Byzantine Empire, whose architecture used alternate sequential runs of light colored ashlar stone and darker colored orange brick. The first known use of the term ablaq in building techniques is in masonry work in reconstruction improvements to the walls of the Umayyad Mosque of Damascus. According to records, these reconstruction mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamluk Architecture
Mamluk architecture was the architectural style under the Mamluk Sultanate (1250–1517), which ruled over Egypt, the Levant, and the Hijaz from their capital, Cairo. Despite their often tumultuous internal politics, the Mamluk sultans were prolific patrons of architecture and contributed enormously to the fabric of historic Cairo. The Mamluk period, particularly in the 14th century, oversaw the peak of Cairo's power and prosperity. Their architecture also appears in cities such as Damascus, Jerusalem, Aleppo, Tripoli, and Medina. Major Mamluk monuments typically consisted of multi-functional complexes which could combine various elements such as a patron's mausoleum, a madrasa, a khanqah ( Sufi lodge), a mosque, a sabil, or other charitable functions found in Islamic architecture. These complexes were built with increasingly complicated floor plans which reflected the need to accommodate limited urban space as well as a desire to visually dominate their urban environment. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Architecture
Islamic architecture comprises the architectural styles of buildings associated with Islam. It encompasses both secular and religious styles from the early history of Islam to the present day. The Islamic world encompasses a wide geographic area historically ranging from western Africa and Europe to eastern Asia. Certain commonalities are shared by Islamic architectural styles across all these regions, but over time different regions developed their own styles according to local materials and techniques, local dynasties and patrons, different regional centers of artistic production, and sometimes different religious affiliations. Early Islamic architecture was influenced by Roman, Byzantine, Iranian, and Mesopotamian architecture and all other lands which the Early Muslim conquests conquered in the seventh and eighth centuries.: "As the Arabs did not have an architectural tradition suited to the needs of a great empire, they adopted the building methods of the defeated Sas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
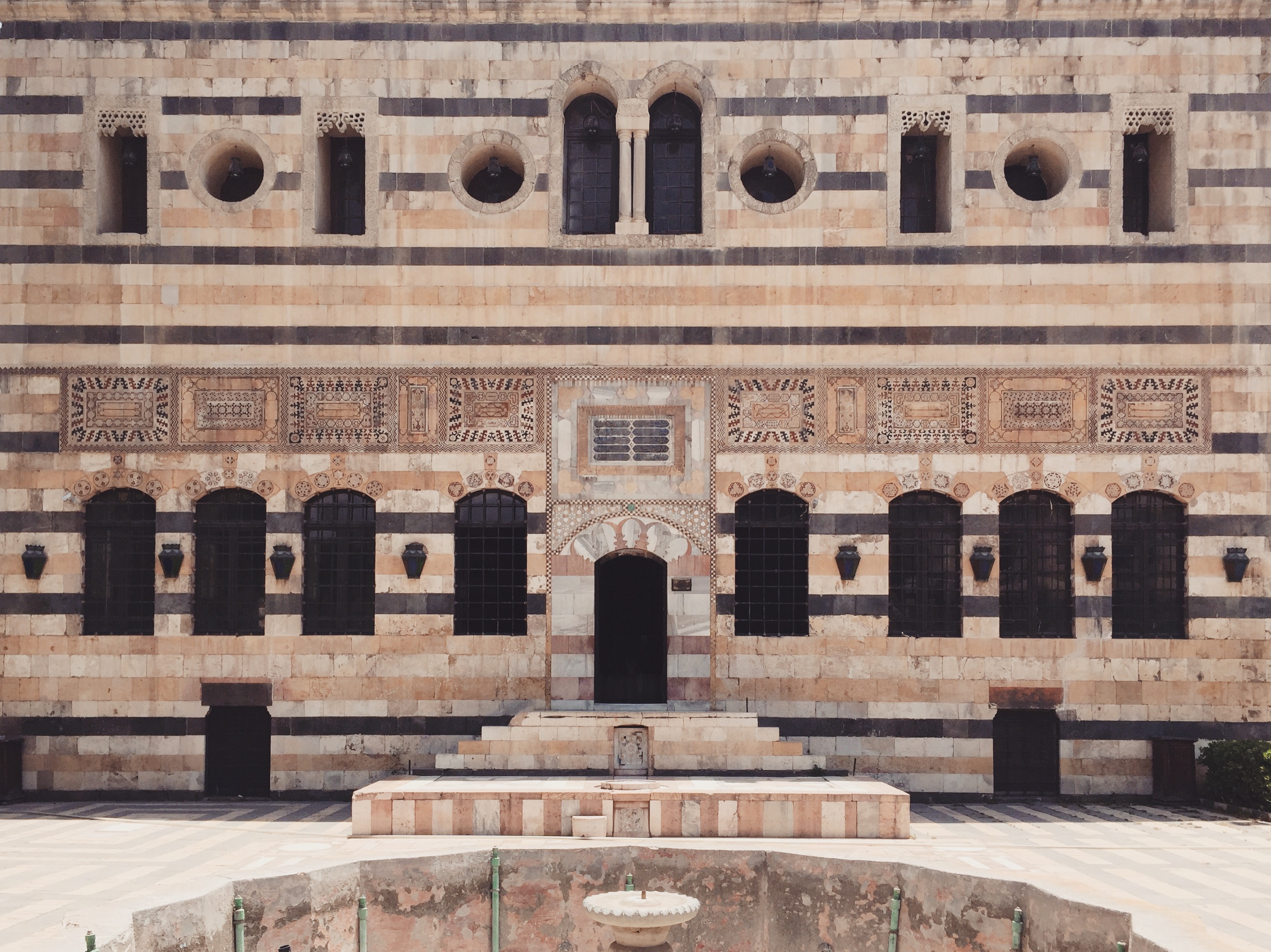
Azm Palace
Al-Azem Palace ( ar, قصر العظم) is a palace in Damascus, Syria, built in 1749. Located north of Al-Buzuriyah Souq in the Ancient City of Damascus, the palace was built in 1749 to be the private residence for As'ad Pasha al-Azem, the governor of Damascus; during the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon, it housed the French Institute. After being purchased by the Syrian government from the Al-Azem family and undergoing several reconstruction works, the palace now houses the Museum of Arts and Popular Traditions. History The palace was built during the Ottoman era over the former site of a Mamluk palace as a residence for the governor of Damascus, As'ad Pasha al-Azem during the reign of Sultan Mahmud I. Serving as a joint residence and guesthouse, the palace was a monument to 18th-century Arab architecture. The palace was built by 800 workers in a span of three years, and the building was decorated with highly sophisticated and expensive decorative elements. A local ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azm Palace - Damascus
Azm, AZM or variants may refer to: People * Al-Azm family, prominent Syrian family ** As'ad Pasha al-Azm (c. 1706 – 1758), governor of Damascus ** Sulayman Pasha al-Azm (died 1743), governor of Damascus ** Ibrahim Pasha al-Azm (died 1746), governor of Tripoli and Sidon ** Haqqi al-Azm (1864–1955), former prime minister of Syria ** Khalid al-Azm (1903–1965), five times prime minister of Syria ** Sadiq Jalal al-Azm (1934–2016), Syrian philosophy professor * AZM (wrestler) (born 2002), Japanese professional wrestler Places * Azm Palace, Damascus, Syria * Azm Palace (Hama), Syria Other uses * Project Azm, a cancelled Pakistani aircraft project * Old Azerbaijani manat, a former currency of Azerbaijan * Ipalapa Amuzgo, ISO 639 language code azm, a dialect of Amuzgo * Azinphos-methyl, an organophosphate insecticide * American Zionist Movement, the American federation of Zionist groups See also * Azem (other) * Azim (other) Azim (''ʿAẓīm'' ) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
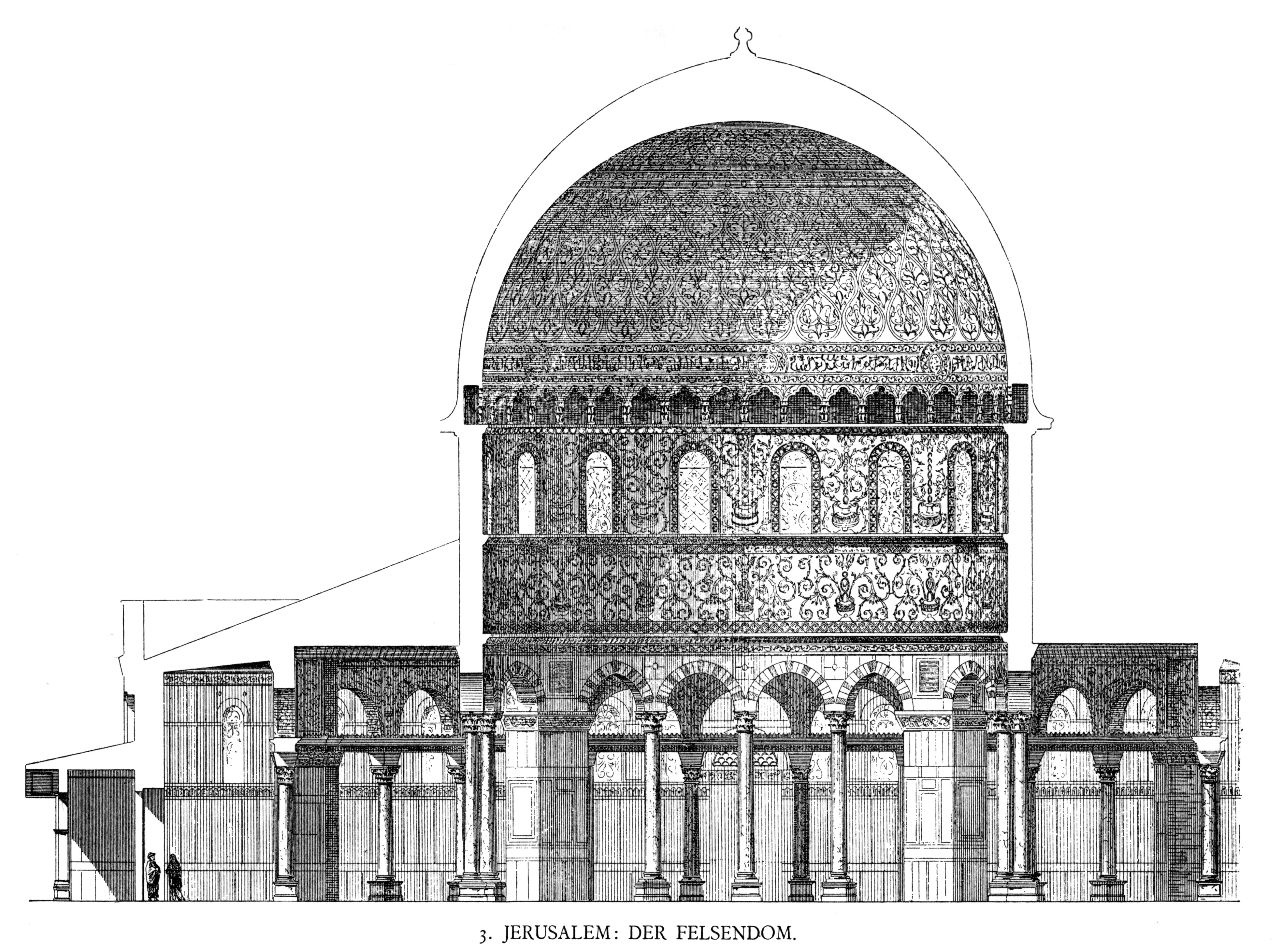
Dome Of The Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial construction was undertaken by the Umayyad Caliphate on the orders of Abd al-Malik during the Second Fitna in 691–692 CE, and it has since been situated on top of the site of the Second Jewish Temple (built in to replace the destroyed Solomon's Temple), which was destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE. The original dome collapsed in 1015 and was rebuilt in 1022–23. The Dome of the Rock is the world's oldest surviving work of Islamic architecture. Its architecture and mosaics were patterned after nearby Byzantine churches and palaces, although its outside appearance was significantly changed during the Ottoman period and again in the modern period, notably with the addition of the gold-plated roof, in 1959–61 and again in 1993. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Wales Lampeter
University of Wales, Lampeter ( cy, Prifysgol Cymru, Llanbedr Pont Steffan) was a university in Lampeter, Wales. Founded in 1822, and incorporated by royal charter in 1828, it was the oldest Academic degree, degree awarding institution in Wales, with limited degree awarding powers since 1852. It was a self-governing college of the University of Wales from 1972 until its merger (under its 1828 charter) with Trinity University College in 2010 to form the University of Wales Trinity Saint David. The university was founded as St David's College (''Coleg Dewi Sant''), becoming St David's University College (''Coleg Prifysgol Dewi Sant'') in 1971, when it became part of the federal University of Wales. With fewer than 2,000 students on campus, it was often claimed to be one of the smallest public university, public universities in Europe. History When Thomas Burgess (bishop, born 1756), Thomas Burgess was appointed Bishop of St David's in 1803, he saw a need for a college in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Archaeology
Islamic archaeology involves the recovery and scientific investigation of the material remains of past cultures that can illuminate the periods and descriptions in the Quran, and early Islam. The science of archaeology grew out of the older multi-disciplinary study known as antiquarianism. The Egyptian " Antiquities Authority" was established in 1858 and remains a government organization which serves to protect and preserve the heritage and ancient history of Egypt. Early pioneers in Islamic archaeology included Eduard Glaser and Alois Musil. Khaled al-Asaad was principal custodian of the Palmyra site from 1963, overseeing its elevation to a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Some of the earliest areas investigated in Saudi Arabia include Al Faw Village and Madain Saleh. Jodi Magness has covered the archaeology of early Islamic settlement in Palestine. The Museum of Islamic Archaeology and Art of Iran was opened in 1972. It houses tools dating back 30,000 to 35,000 years and cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Period
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious". , motto = , image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg , image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg , seal_type = Seal , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Syria#Mediterranean east#Arab world#Asia , pushpin_label_position = right , pushpin_mapsize = , pushpin_map_caption = Location of Damascus within Syria , pushpin_relief = 1 , coordinates = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = Governorate , subdivision_name1 = Damascus Governorate, Capital City , government_footnotes = , government_type = , leader_title = Governor , leader_name = Mohammad Tariq Kreishati , parts_type = Municipalities , parts = 16 , established_title = , established_date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in England that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, Routledge, F1000 (publisher), F1000 Research or Dovepress. It is a division of Informa, Informa plc, a United Kingdom–based publisher and conference company. Overview The company was founded in 1852 when William Francis (chemist), William Francis joined Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor in his publishing business. Taylor had founded his company in 1798. Their subjects covered agriculture, chemistry, education, engineering, geography, law, mathematics, medicine, and social sciences. Francis's son, Richard Taunton Francis (1883–1930), was sole partner in the firm from 1917 to 1930. In 1965, Taylor & Francis launched Wykeham Publications and began book publishing. T&F acquired Hemisphere Publishing in 1988, and the company was renamed Taylor & Francis Group to reflect the growing number of Imprint (trade name), imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baibars
Al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baybars al-Bunduqdari ( ar, الملك الظاهر ركن الدين بيبرس البندقداري, ''al-Malik al-Ẓāhir Rukn al-Dīn Baybars al-Bunduqdārī'') (1223/1228 – 1 July 1277), of Turkic Kipchak origin, commonly known as Baibars or Baybars ( ar, بيبرس, ''Baybars'') – nicknamed Abu al-Futuh (; English: ''Father of Conquests'', referring to his victories) – was the fourth Mamluk sultan of Egypt and Syria in the Bahri dynasty, succeeding Qutuz. He was one of the commanders of the Egyptian forces that inflicted a defeat on the Seventh Crusade of King Louis IX of France. He also led the vanguard of the Egyptian army at the Battle of Ain Jalut in 1260, which marked the first substantial defeat of the Mongol army and is considered a turning point in history. The reign of Baybars marked the start of an age of Mamluk dominance in the Eastern Mediterranean and solidified the durability of their military system. He managed to pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


.jpg)
