|
Automatic Target Recognition
Automatic target recognition (ATR) is the ability for an algorithm or device to recognize targets or other objects based on data obtained from sensors. Target recognition was initially done by using an audible representation of the received signal, where a trained operator who would decipher that sound to classify the target illuminated by the radar. While these trained operators had success, automated methods have been developed and continue to be developed that allow for more accuracy and speed in classification. ATR can be used to identify man-made objects such as ground and air vehicles as well as for biological targets such as animals, humans, and vegetative clutter. This can be useful for everything from recognizing an object on a battlefield to filtering out interference caused by large flocks of birds on Doppler weather radar. Possible military applications include a simple identification system such as an IFF transponder, and is used in other applications such as unmanned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
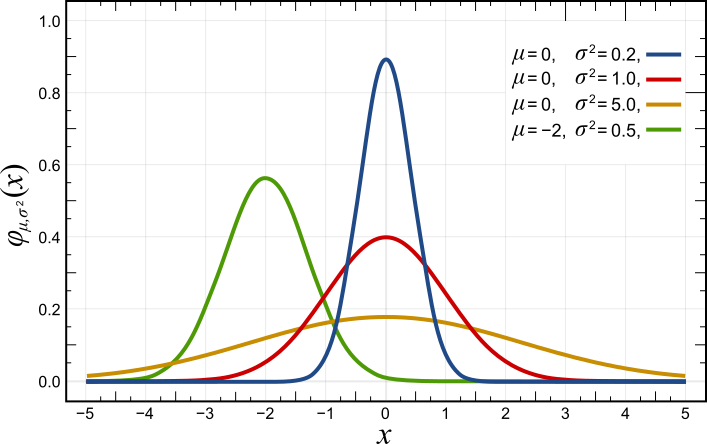
Maximum A Posteriori Estimation
An estimation procedure that is often claimed to be part of Bayesian statistics is the maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimate of an unknown quantity, that equals the mode of the posterior density with respect to some reference measure, typically the Lebesgue measure. The MAP can be used to obtain a point estimate of an unobserved quantity on the basis of empirical data. It is closely related to the method of maximum likelihood (ML) estimation, but employs an augmented optimization objective which incorporates a prior density over the quantity one wants to estimate. MAP estimation is therefore a regularization of maximum likelihood estimation, so is not a well-defined statistic of the Bayesian posterior distribution. Description Assume that we want to estimate an unobserved population parameter \theta on the basis of observations x. Let f be the sampling distribution of x, so that f(x\mid\theta) is the probability of x when the underlying population parameter is \theta. Then t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radar Lock-on
Lock-on is a feature of many radar systems that allow it to automatically follow a selected target. Lock-on was first designed for the AI Mk. IX radar in the UK, where it was known as lock-follow or auto-follow. Its first operational use was in the US ground-based SCR-584 radar, which demonstrated the ability to easily track almost any airborne target, from aircraft to artillery shells. History In the post-WWII era, the term became more widely used in connection to missile guidance concepts. Many modern anti-aircraft missiles use some form of semi-active radar homing, where the missile seeker listens for reflections of the launch platform's main radar. To provide a continuous signal, the radar is locked-onto the target, following it throughout the missile's flight. Ships and surface-to-air missiles often have a dedicated illuminator radar for this purpose. In older radar systems, through the 1980s, lock-on was normally assisted by a change in the radar signal characteristic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is the task of assigning a class to an observation based on patterns extracted from data. While similar, pattern recognition (PR) is not to be confused with pattern machines (PM) which may possess PR capabilities but their primary function is to distinguish and create emergent patterns. PR has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Pattern recognition has its origins in statistics and engineering; some modern approaches to pattern recognition include the use of machine learning, due to the increased availability of big data and a new abundance of processing power. Pattern recognition systems are commonly trained from labeled "training" data. When no labeled data are available, other algorithms can be used to discover previously unknown patterns. KDD and data mining have a larger focus on unsupervised methods and str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Outline Of Robotics
following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to robotics: Robotics is a branch of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering and computer science that deals with the design, construction, operation, and application of robots, as well as computer systems for their control, sensory feedback, and information processing. These technologies deal with automated machines that can take the place of humans in dangerous environments or manufacturing processes, or resemble humans in appearance, behaviour, and or cognition. Many of today's robots are inspired by nature contributing to the field of bio-inspired robotics. The word "robot" was introduced to the public by Czech writer Karel Čapek in his play R.U.R. (Rossum's Universal Robots), published in 1920. The term "robotics" was coined by Isaac Asimov in his 1941 science fiction short-story " Liar!" Nature of robotics Robotics can be described as: * An applied science – scientific knowledge trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Outline Of Artificial Intelligence
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to artificial intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence exhibited by machines or software. It is also the name of the scientific field which studies how to create computers and computer software that are capable of intelligent behavior. AI algorithms and techniques Search * Discrete search algorithms ** Uninformed search *** Brute force search *** Search tree **** Breadth-first search **** Depth-first search *** State space search ** Informed search *** Best-first search *** A* search algorithm *** Heuristics *** Pruning (algorithm) ** Adversarial search *** Minmax algorithm ** Logic as search *** Production system (computer science), Rule based system *** Production rule, Inference rule, Horn clause *** Forward chaining *** Backward chaining ** Planning as search *** State space search *** Means–ends analysis Optimization search * Optimization (mathematics) algorithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Object Recognition
Object recognition – technology in the field of computer vision for finding and identifying objects in an image or video sequence. Humans recognize a multitude of objects in images with little effort, despite the fact that the image of the objects may vary somewhat in different view points, in many different sizes and scales or even when they are translated or rotated. Objects can even be recognized when they are partially obstructed from view. This task is still a challenge for computer vision systems. Many approaches to the task have been implemented over multiple decades. Approaches based on CAD-like object models * Edge detection * Primal sketch * Marr, Mohan and Nevatia * Lowe * Olivier Faugeras Recognition by parts * Generalized cylinders ( Thomas Binford) * Geons ( Irving Biederman) * Dickinson, Forsyth and Ponce Appearance-based methods * Use example images (called templates or exemplars) of the objects to perform recognition * Objects look differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Applications Of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been used in applications throughout industry and academia. In a manner analogous to electricity or computers, AI serves as a general-purpose technology. AI programs are designed to simulate human perception and understanding. These systems are capable of adapting to new information and responding to changing situations. Machine learning has been used for various scientific and commercial purposes including language translation, image recognition, decision-making, credit scoring, and e-commerce. Agriculture In agriculture, AI has been proposed as a way for farmers to identify areas that need irrigation, fertilization, or pesticide treatments to increase yields, thereby improving efficiency. AI has been used to attempt to classify livestock pig call emotions, automate greenhouses, detect diseases and pests, and optimize irrigation. Architecture & Design AI in architecture has created a way for architects to create things beyond human unders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Convolutional Neural Network
A convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of feedforward neural network that learns features via filter (or kernel) optimization. This type of deep learning network has been applied to process and make predictions from many different types of data including text, images and audio. Convolution-based networks are the de-facto standard in deep learning-based approaches to computer vision and image processing, and have only recently been replaced—in some cases—by newer deep learning architectures such as the transformer. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by the regularization that comes from using shared weights over fewer connections. For example, for ''each'' neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded ''convolution'' (or cross-correlation) kernels, only 25 weights for each convolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mixture Model
In statistics, a mixture model is a probabilistic model for representing the presence of subpopulations within an overall population, without requiring that an observed data set should identify the sub-population to which an individual observation belongs. Formally a mixture model corresponds to the mixture distribution that represents the probability distribution of observations in the overall population. However, while problems associated with "mixture distributions" relate to deriving the properties of the overall population from those of the sub-populations, "mixture models" are used to make statistical inferences about the properties of the sub-populations given only observations on the pooled population, without sub-population identity information. Mixture models are used for clustering, under the name model-based clustering, and also for density estimation. Mixture models should not be confused with models for compositional data, i.e., data whose components are constra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ATR Flow
ATR may refer to: Medicine * Acute transfusion reaction * Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3 related, a protein involved in DNA damage repair Science and mathematics * Advanced Test Reactor, nuclear research reactor at the Idaho National Laboratory, US * Attenuated total reflectance in infrared spectroscopy * Advanced tongue root, a phonological feature in linguistics * Atractyloside, a toxin and inhibitor of "ADP/ATP translocase" * ATR0, an axiom system in reverse mathematics Technology * Answer to reset, a message output by a contact Smart Card * Automatic target recognition, recognition ability * Autothermal reforming, a natural gas reforming technology Transport * ATR (aircraft manufacturer) an Italian-French aircraft manufacturer ** ATR 42 airliner ** ATR 72 airliner * IATA code for Atar International Airport * Andaman Trunk Road * Air Transport Rack, standards for plug-in electronic modules in aviation and elsewhere; various suppliers e.g. ARINC * Atmore (Amtrak station), Amtr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Object Detection
Object detection is a computer technology related to computer vision and image processing that deals with detecting instances of semantic objects of a certain class (such as humans, buildings, or cars) in digital images and videos. Well-researched domains of object detection include face detection and pedestrian detection. Object detection has applications in many areas of computer vision, including image retrieval and video surveillance. Uses It is widely used in computer vision tasks such as image annotation, vehicle counting, activity recognition, face detection, face recognition, video object co-segmentation. It is also used in tracking objects, for example tracking a ball during a football match, tracking movement of a cricket bat, or tracking a person in a video. Often, the test images are sampled from a different data distribution, making the object detection task significantly more difficult. To address the challenges caused by the domain gap between training and test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |