|
Atmospheric Circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of Atmosphere of Earth, air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the large-scale structure of its circulation remains fairly constant. The smaller-scale weather systems – middle latitudes, mid-latitude low-pressure area, depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur chaotically, and long-range weather predictions of those cannot be made beyond ten days in practice, or a month in theory (see chaos theory and the butterfly effect). The Earth's weather is a consequence of its illumination by the Sun and the laws of thermodynamics. The atmospheric circulation can be viewed as a heat engine driven by the Sun's energy and whose heat sink, energy sink, ultimately, is the blackness of space. The work produced by that engine causes the motion of the masses of air, and in that process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Global Circulation - En
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering Water distribution on Earth, 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most of which is located in the form of continental landmasses within Earth's land hemisphere. Most of Earth's land is at least somewhat humid and covered by vegetation, while large Ice sheet, sheets of ice at Polar regions of Earth, Earth's polar polar desert, deserts retain more water than Earth's groundwater, lakes, rivers, and Water vapor#In Earth's atmosphere, atmospheric water combined. Earth's crust consists of slowly moving tectonic plates, which interact to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's outer core, Earth has a liquid outer core that generates a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be accepted by Earth science, geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid-to-late 1960s. The processes that result in plates and shape Earth's crust are called ''tectonics''. Tectonic plates also occur in other planets and moons. Earth's lithosphere, the rigid outer shell of the planet including the crust (geology), crust and upper mantle, is fractured into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary (or fault (geology), fault): , , or . The relative movement of the plates typically ranges from zero to 10 cm annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
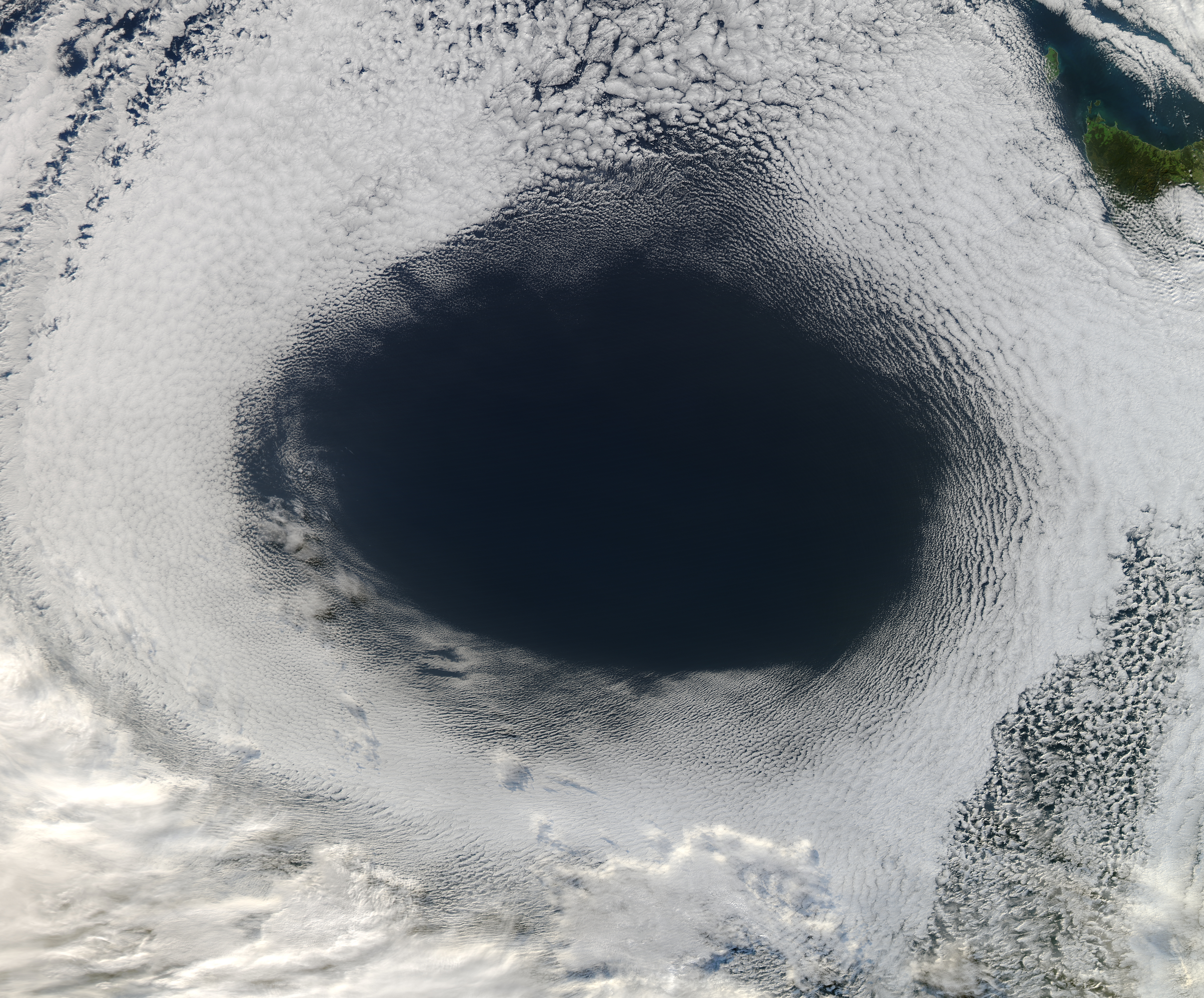
High-pressure Area
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interplays between the relatively larger-scale dynamics of an entire planet's atmospheric circulation. The strongest high-pressure areas result from masses of cold air which spread out from polar regions into cool neighboring regions. These highs weaken once they extend out over warmer bodies of water. Weaker—but more frequently occurring—are high-pressure areas caused by atmospheric subsidence: Air becomes cool enough to precipitate out its water vapor, and large masses of cooler, drier air descend from above. Within high-pressure areas, winds flow from where the pressure is highest, at the center of the area, towards the periphery where the pressure is lower. However, the direction is not straight from the center outwards, but curved du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
30th Parallel (other) , a circle of latitude in the Southern Hemisphere
{{Disambig ...
30th parallel may refer to: *30th parallel north, a circle of latitude in the Northern Hemisphere *30th parallel south Following are circles of latitude between the 25th parallel south and the 30th parallel south: 26th parallel south The 26th parallel south latitude is a circle of latitude that is 26 degrees south of Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Wind
The trade winds or easterlies are permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisphere, strengthening during the winter and when the Arctic oscillation is in its warm phase. Trade winds have been used by captains of sailing ships to cross the world's oceans for centuries. They enabled European colonization of the Americas, and trade routes to become established across the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. In meteorology, they act as the prevailing winds, steering flow for tropical storms that form over the Atlantic, Pacific, and southern Indian Ocean, Indian oceans and cause rainfall in North America, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar and East Africa. Shallow Trade wind cumulus cloud, cumulus clouds are seen within trade wind regimes and are capped from becoming taller by a trade wind Inversion (meteorology), inversion, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Hadley
George Hadley (12 February 1685 – 28 June 1768) was an English lawyer and amateur meteorologist who proposed the atmospheric mechanism by which the trade winds are sustained, which is now named in his honour as Hadley circulation. As a key factor in ensuring that European sailing vessels reached North American shores, understanding the trade winds was becoming a matter of great importance at the time. Hadley was intrigued by the fact that winds which should by all rights have blown straight north had a pronounced westerly flow, and it was this mystery he set out to solve. Life Hadley was born in London, England to George Hadley ( High Sheriff of Hertfordshire) and Katherine FitzJames. He had an unremarkable childhood, and was eclipsed in his early years by his older brother John Hadley (1682–1744), the inventor of the octant (a precursor to the sextant). With John and his other brother Henry, George had constructed effective Newtonian telescopes. George Hadley entered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Latitudes
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges or highs. It is a high-pressure area at the divergence of trade winds and the westerlies. Etymology A likely and documented explanation is that the term is derived from the "dead horse" ritual of seamen (see Beating a dead horse). In this practice, the seaman paraded a straw-stuffed effigy of a horse around the deck before throwing it overboard. Seamen were paid partly in advance before a long voyage, and they frequently spent their pay all at once, resulting in a period of time without income. This period was called the "dead horse" time, and it usually lasted a month or two. The seaman's ceremony was to celebrate having worked off the "dead horse" debt. As west-bound shipping from Europe usually reached the subtropics at about the time the "dead horse" was wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadley Cell
The Hadley cell, also known as the Hadley circulation, is a global-scale tropical atmospheric circulation that features air rising near the equator, flowing poleward near the tropopause at a height of above the Earth's surface, cooling and descending in the subtropics at around 25 degrees latitude, and then returning equatorward near the surface. It is a thermally direct circulation within the troposphere that emerges due to differences in insolation and heating between the tropics and the subtropics. On a yearly average, the circulation is characterized by a circulation cell on each side of the equator. The Southern Hemisphere Hadley cell is slightly stronger on average than its northern counterpart, extending slightly beyond the equator into the Northern Hemisphere. During the summer and winter months, the Hadley circulation is dominated by a single, cross-equatorial cell with air rising in the summer hemisphere and sinking in the winter hemisphere. Analogous circulations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumference, halfway between the North Pole, North and South Pole, South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In three-dimensional space, spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its geographical pole, poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane (geometry), plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |