|
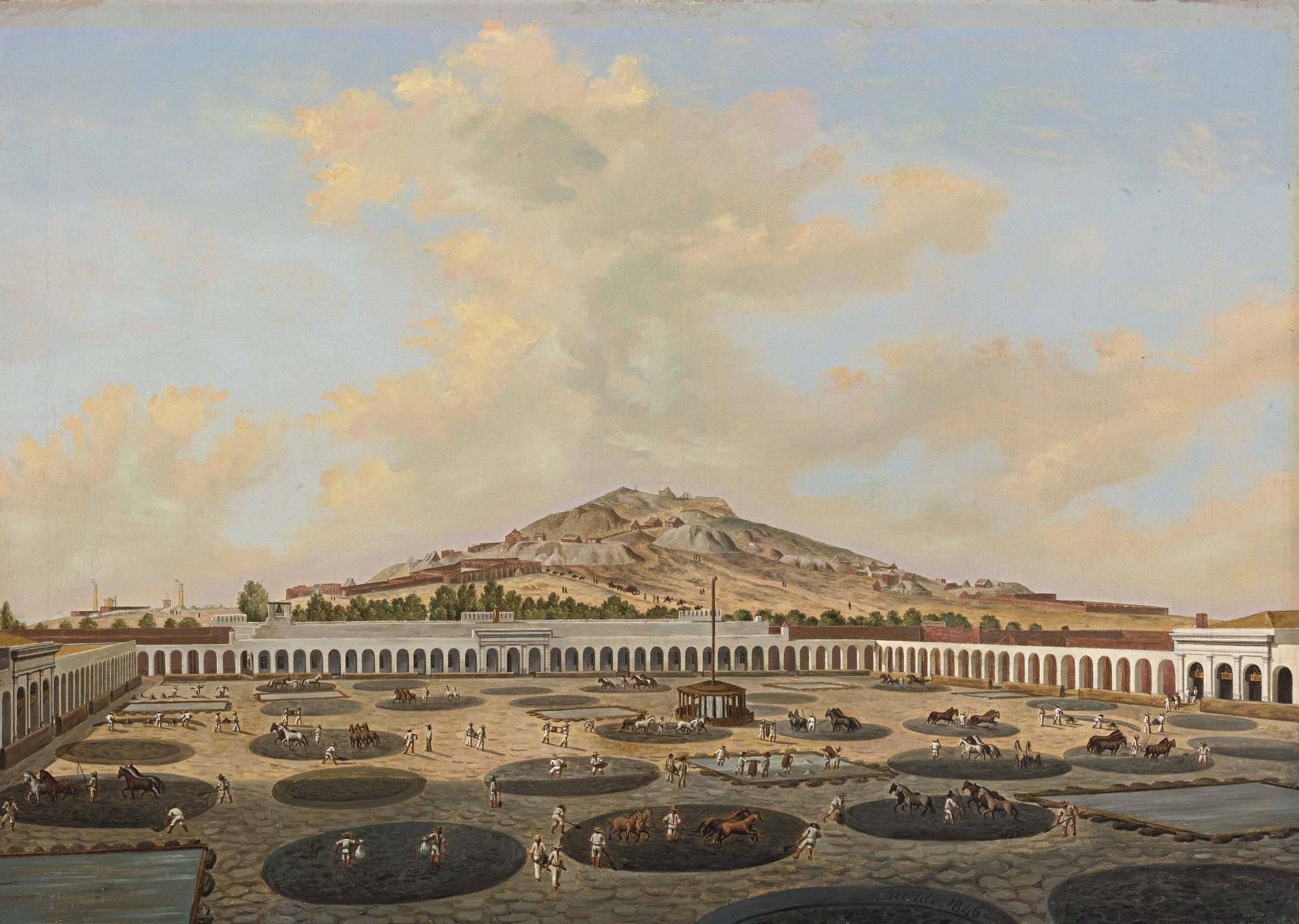
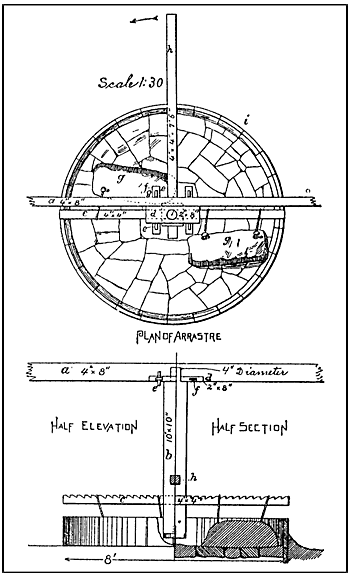
Arrastra
An arrastra (or arastra) is a primitive Mill (grinding), mill for grinding and pulverizing (typically) gold or silver ore. Its simplest form is two or more flat-bottomed drag stones placed in a circular pit paved with flat stones, and connected to a center post by a long arm. With a horse, mule or human providing power at the other end of the arm, the stones were dragged slowly around in a circle, crushing the ore. Some arrastras were powered by a water wheel; a few were powered by steam or gasoline engines, and even electricity. Arrastras were widely used throughout the Mediterranean region since Phoenician times. The Spain, Spanish introduced the arrastra to the New World in the 16th century. The word "arrastra" comes from the Spanish language ''arrastrar,'' meaning to drag along the ground. Arrastras were suitable for use in small or remote mines, since they could be built from local materials and required little investment capital. For gold ore, the gold was typically recov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mill (grinding)
A mill is a device, often a structure, machine or kitchen appliance, that breaks solid materials into smaller pieces by grinding, crushing, or cutting. Such comminution is an important unit operation in many processes. There are many different types of mills and many types of materials processed in them. Historically, mills were powered by hand or by animals (e.g., via a hand crank), working animal (e.g., horse mill), wind ( windmill) or water (watermill). In the modern era, they are usually powered by electricity. The grinding of solid materials occurs through mechanical forces that break up the structure by overcoming the interior bonding forces. After the grinding the state of the solid is changed: the grain size, the grain size disposition and the grain shape. Milling also refers to the process of breaking down, separating, sizing, or classifying aggregate material (e.g. mining ore). For instance rock crushing or grinding to produce uniform aggregate size for construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
History Of Metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys. Metallurgy encompasses both the science and the technology of metals, including the production of metals and the engineering of metal components used in products for both consumers and manufacturers. Metallurgy is distinct from the craft of metalworking. Metalworking relies on metallurgy in a similar manner to how medicine relies on medical science for technical advancement. A specialist practitioner of metallurgy is known as a metallurgist. The science of metallurgy is further subdivided into two broad categories: chemical metallurgy and physical metallurgy. Chemical metallurgy is chiefly concerned with the reduction and oxidation of metals, and the chemical performance of metals. Subjects of study in chemical metallurgy include mineral processing, the extraction of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
History Of Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water. Modern mining processes involve prospecting for ore bodies, analysis of the profit potential of a proposed mine, extraction of the desired materials, and final mine reclamation, reclamation or restoration of the land after the mine is closed. Mining materials are often obtained from ore bodies, lodes, vein (geology), veins, coal mining, seams, qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopedia, online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest-running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, in three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size; the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810), it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent contributors, and the 9th (1875–1889) and Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 11th editions (1911) are landmark encyclopaedias for scholarship and literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Patio Process
The patio process is a process for extracting silver from ore. Smelting, or refining, is most often necessary because silver is only infrequently found as a native element like some metals nobler than the redox couple 2 + 2 ⇌ (gold, mercury, ...). Instead, it is made up of a larger ore body. Thus, smelting, or refining, is necessary to reduce the compound containing the cation into metallic Ag and to remove other byproducts to get at pure silver. The process, which uses mercury amalgamation to recover silver from ore, was first used at scale by Bartolomé de Medina in Pachuca, Mexico, in 1554. It replaced smelting as the primary method of extracting silver from ore at Spanish colonies in the Americas. Although some knowledge of amalgamation techniques were likely known since the classical era, it was in the New World that it was first used on a large industrial scale. Other amalgamation processes were later developed, importantly the pan amalgamation process, and its v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is commonly known as quicksilver. A Heavy metal element, heavy, silvery d-block element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Exposure to mercury and mercury-containing organic compounds is toxic to the nervous system, immune system and kidneys of humans and other animals; mercury poisoning can result from exposure to water-soluble forms of mercury (such as mercuric chloride or methylmercury) either directly or through mechanisms of biomagnification. Mercu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Amalgam (chemistry)
An amalgam is an alloy of mercury (element), mercury with another metal. It may be a liquid, a soft paste or a solid, depending upon the proportion of mercury. These alloys are formed through metallic bonding, with the electrostatic attractive force of the conduction electrons working to bind all the positively charged metal ions together into a Crystal structure, crystal lattice structure. Almost all metals can form amalgams with mercury, the notable exceptions being iron, platinum, tungsten, and tantalum. Gold-mercury amalgam is used in the Gold extraction, extraction of gold from ore, and Amalgam (dentistry), dental amalgams are made with metals such as silver, copper, indium, tin and zinc. Important amalgams Zinc amalgam Zinc amalgam finds use in organic synthesis (e.g., for the Clemmensen reduction). It is the reducing agent in the Jones reductor, used in analytical chemistry. Formerly the zinc plates of dry battery (electric), batteries were amalgamated with a small amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Investment Capital
In economics, capital goods or capital are "those durable produced goods that are in turn used as productive inputs for further production" of goods and services. A typical example is the machinery used in a factory. At the macroeconomic level, "the nation's capital stock includes buildings, equipment, software, and inventories during a given year." The means of production is as a "... series of heterogeneous commodities, each having specific technical characteristics ..." "capital goods", are one of the three types of intermediate goods used in the production process, the other two being land and labour. The three are also known collectively as "primary factors of production". This classification originated during the classical economics period and has remained the dominant method for classification. Capital can be increased by the use of a production process (see production function and factors of production). Outputs of the production process are normally cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New World
The term "New World" is used to describe the majority of lands of Earth's Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas, and sometimes Oceania."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: "[16c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1454–1512). The name ''America'' first appeared on a map in 1507 by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, referring to the area now called Brazil]. Since the 16th century, the term "New World" has been used to describe the Western Hemisphere, often referred to as the Americas. Since the 18th century, it has come to represent the United States, which was initially colonial British America until it established independence following the American Revolutionary War. The second sense is now primary in English: ... However, the term is open to uncertainties: ..." The term arose in the early 16th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |