|
Anti-scratch Coating
Anti-scratch coating is a type of protective coating or film applied to an object's surface for mitigation against scratches. Scratches are small surface-level cuts left on a surface following interaction with a sharper object. Anti-scratch coatings provide scratch resistances by containing tiny microscopic materials with scratch-resistant properties. Scratch resistance materials come in the form of additives, filters, and binders. Besides materials, scratch resistances is impacted by coating formation techniques. Scratch resistance is measured using the Scratch-hardness test. Commercially, anti-scratch coatings are used in the automotive, optical, photographic, and electronics industries, where resale and/or functionality is impaired by scratches. Anti-scratch coatings are of growing importance as traditional scratch resistance materials like metals and glass are replaced with low-scratch resistant plastics. Applications Automotive, Optical, and Electronics are major sectors of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, or substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. powder coatings. Paints and lacquers are coatings that mostly have dual uses, which are protecting the substrate and being decorative, although some artists paints are only for decoration, and the paint on large industrial pipes is for identification (e.g. blue for process water, red for fire-fighting control) in addition to preventing corrosion. Along with corrosion resistance, functional coatings may also be applied to change the surface properties of the substrate, such as adhesion, wettability, or wear resistance.Howarth G.A "Synthesis of a legislation compliant corrosion protection coating system based on urethane, oxazolidine and waterborne epoxy technology" Master of Science Thesis April 1997 Imperial College London In other cases the coating adds a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials describe, in principle, chemical substances or materials of which a single unit is sized (in at least one dimension) between 1 and 100 nm (the usual definition of nanoscale). Nanomaterials research takes a materials science-based approach to nanotechnology, leveraging advances in materials metrology and synthesis which have been developed in support of microfabrication research. Materials with structure at the nanoscale often have unique optical, electronic, thermo-physical or mechanical properties. Nanomaterials are slowly becoming commercialized and beginning to emerge as commodities. Definition In ISO/TS 80004, ''nanomaterial'' is defined as the "material with any external dimension in the nanoscale or having internal structure or surface structure in the nanoscale", with ''nanoscale'' defined as the "length range approximately from 1 nm to 100 nm". This includes both ''nano-objects'', which are discrete pieces of material, and ''nanostructu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Discs
An optical disc is a flat, usuallyNon-circular optical discs exist for fashion purposes; see shaped compact disc. disc-shaped object that stores information in the form of physical variations on its surface that can be read with the aid of a beam of light. Optical discs can be reflective, where the light source and detector are on the same side of the disc, or transmissive, where light shines through the disc to be detected on the other side. Optical discs can store analog information (e.g. LaserDisc), digital information (e.g. DVD), or store on the same disc (e.g. CD Video). Their main uses are the distribution of media and data, and long-term archival. Design and technology The encoding material sits atop a thicker substrate (usually polycarbonate) that makes up the bulk of the disc and forms a dust defocusing layer. The encoding pattern follows a continuous, spiral path covering the entire disc surface and extending from the innermost track to the outermost track. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerprint
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers. Human fingerprints are detailed, unique, difficult to alter, and durable over the life of an individual, making them suitable as long-term markers of human identity. They may be employed by police or other authorities to identify individuals who wish to conceal their identity, or to identify people who are incapacitated or dead and thus unab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oleophobic
Lipophobicity, also sometimes called lipophobia (from the Greek λιποφοβία from λίπος ''lipos'' "fat" and φόβος ''phobos'' "fear"), is a chemical property of chemical compounds which means "fat rejection", literally "fear of fat". Lipophobic compounds are those not soluble in lipids or other non-polar solvents. From the other point of view, they do not absorb fats. "Oleophobic" (from the Latin ''oleum'' "oil", Greek ελαιοφοβικό ''eleophobico'' from έλαιο ''eleo'' "oil" and φόβος ''phobos'' "fear") refers to the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from oil. (Strictly speaking, there is no repulsive force involved; it is an absence of attraction.) The most common lipophobic substance is water. Fluorocarbons are also lipophobic/oleophobic in addition to being hydrophobic. Uses A lipophobic coating has been used on the touchscreens of Apple's iPhones since the 3GS, their iPads, Nokia's N9 and Lumia devices, the HTC HD2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorocarbons
Fluorocarbons are chemical compounds with carbon-fluorine bonds. Compounds that contain many C-F bonds often have distinctive properties, e.g., enhanced stability, volatility, and hydrophobicity. Several fluorocarbons and their derivatives are commercial polymers, refrigerants, drugs, and anesthetics. Nomenclature Perfluorocarbons or PFCs, are organofluorine compounds with the formula CxFy, meaning they contain only carbon and fluorine. The terminology is not strictly followed and many fluorine-containing organic compounds are also called fluorocarbons. Compounds with the prefix perfluoro- are hydrocarbons, including those with heteroatoms, wherein all C-H bonds have been replaced by C-F bonds. Fluorocarbons includes perfluoroalkanes, fluoroalkenes, fluoroalkynes, and perfluoroaromatic compounds. Perfluoroalkanes Chemical properties Perfluoroalkanes are very stable because of the strength of the carbon–fluorine bond, one of the strongest in organic chemistry. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
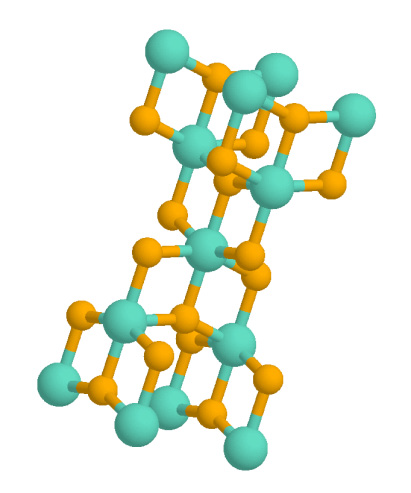
Silicon Dioxide
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant families of materials, existing as a compound of several minerals and as a synthetic product. Examples include fused quartz, fumed silica, opal, and aerogels. It is used in structural materials, microelectronics, and as components in the food and pharmaceutical industries. All forms are white or colorless, although impure samples can be colored. Silicon dioxide is a common fundamental constituent of glass. Structure In the majority of silicon dioxides, the silicon atom shows tetrahedral coordination, with four oxygen atoms surrounding a central Si atomsee 3-D Unit Cell. Thus, SiO2 forms 3-dimensional network solids in which each silicon atom is covalently bonded in a tetrahedral manner to 4 oxygen atoms. In contrast, CO2 is a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index International, CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structures of rutile and anatase are tetragonal in symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics Industry
The electronics industry is the industry (economics), industry that produces electronic devices. It emerged in the 20th century and is today one of the largest global industries. Contemporary society uses a vast array of electronic devices that are built in factories operated by the industry, which are almost always partially automated. Electronic products are primarily assembled from metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) transistors and integrated circuits, the latter principally by photolithography and often on printed circuit boards. Circuit boards are assembled largely using surface-mount technology, which typically involves the automated placement of electronic parts on circuit boards using pick-and-place machines. Surface-mount technology and pick-and-place machines make it possible to assemble large numbers of circuit boards at high speed. The industry's size, the use of toxic materials, and the difficulty of recycling have led to a series of problems with electronic waste. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-reflective Coating
An antireflective, antiglare or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lens (optics), lenses, other optical elements, and photovoltaic cells to reduce reflection (physics), reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost due to reflection. In complex systems such as cameras, binoculars, telescopes, and optical microscope, microscopes the reduction in reflections also improves the Contrast (vision), contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on glasses, eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight. Many coatings consist of transparent thin-film optics, thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond-like Carbon
Diamond-like carbon (DLC) is a class of amorphous carbon material that displays some of the typical properties of diamond. DLC is usually applied as coatings to other materials that could benefit from such properties. DLC exists in seven different forms. All seven contain significant amounts of sp3 hybridized carbon atoms. The reason that there are different types is that even diamond can be found in two crystalline polytypes. The more common one uses a cubic lattice, while the less common one, lonsdaleite, has a hexagonal lattice. By mixing these polytypes at the nanoscale, DLC coatings can be made that at the same time are amorphous, flexible, and yet purely sp3 bonded "diamond". The hardest, strongest, and slickest is tetrahedral amorphous carbon (ta-C). Ta-C can be considered to be the "pure" form of DLC, since it consists almost entirely of sp3 bonded carbon atoms. Fillers such as hydrogen, graphitic sp2 carbon, and metals are used in the other 6 forms to reduce produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |