|
Anterior Cranial Fossa
The anterior cranial fossa is a depression in the floor of the cranial base which houses the projecting frontal lobes of the brain. It is formed by the orbital plates of the frontal, the cribriform plate of the ethmoid, and the small wings and front part of the body of the sphenoid; it is limited behind by the posterior borders of the small wings of the sphenoid and by the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove. The lesser wings of the sphenoid separate the anterior and middle fossae. Structure It is traversed by the frontoethmoidal, sphenoethmoidal, and sphenofrontal sutures. Its lateral portions roof in the orbital cavities and support the frontal lobes of the cerebrum; they are convex and marked by depressions for the brain convolutions, and grooves for branches of the meningeal vessels. The central portion corresponds with the roof of the nasal cavity The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Of Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, inferior area of the human skull, skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the Calvaria (skull), calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone *Sphenoid bone *Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus *Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull *Foramen cecum (frontal bone), Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum *Foramen magnum *Foramen ovale (skull), Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture *Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasal Cavity
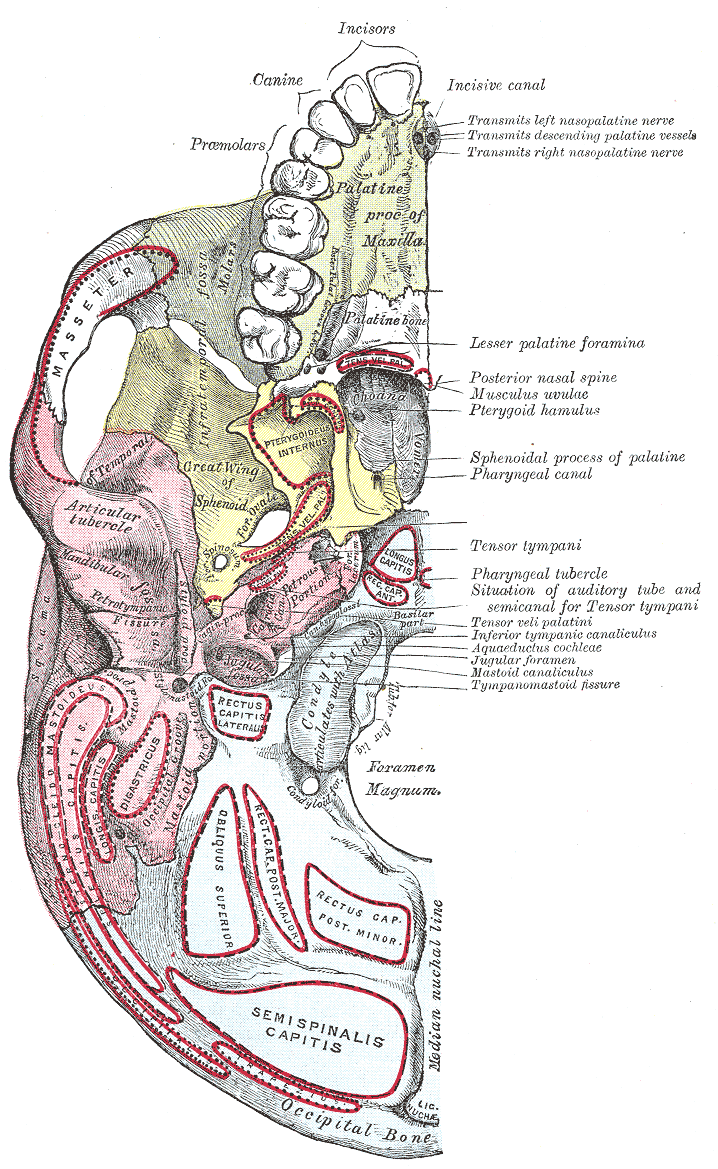
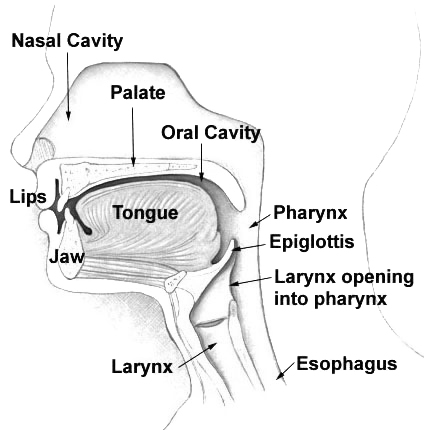
The nasal cavity is a large, air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face. The nasal septum divides the cavity into two cavities, also known as fossae. Each cavity is the continuation of one of the two nostrils. The nasal cavity is the uppermost part of the respiratory system and provides the nasal passage for inhaled air from the nostrils to the nasopharynx and rest of the respiratory tract. The paranasal sinuses surround and drain into the nasal cavity. Structure The term "nasal cavity" can refer to each of the two cavities of the nose, or to the two sides combined. The lateral wall of each nasal cavity mainly consists of the maxilla. However, there is a deficiency that is compensated for by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone, the medial pterygoid plate, the labyrinth of ethmoid and the inferior concha. The paranasal sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity through small orifices called ostia. Most of these ostia communicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Cranial Fossa
The middle cranial fossa is formed by the sphenoid bones, and the temporal bones. It lodges the temporal lobes, and the pituitary gland. It is deeper than the anterior cranial fossa, is narrow medially and widens laterally to the sides of the skull. It is separated from the posterior cranial fossa by the clivus and the petrous crest. It is bounded in front by the posterior margins of the lesser wings of the sphenoid bone, the anterior clinoid processes, and the ridge forming the anterior margin of the chiasmatic groove; behind, by the superior angles of the petrous portions of the temporal bones and the dorsum sellae; laterally by the temporal squamae, sphenoidal angles of the parietals, and greater wings of the sphenoid. It is traversed by the squamosal, sphenoparietal, sphenosquamosal, and sphenopetrosal sutures. Anatomy Features Middle part The middle part of the fossa presents, in front, the chiasmatic groove and tuberculum sellae; the chiasmatic groove ends o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Wings Of The Sphenoid
The lesser wings of the sphenoid or orbito-sphenoids are two thin triangular plates, which arise from the upper and anterior parts of the body, and, projecting lateralward, end in sharp points ig. 1 In some animals, they remain as separate bones called orbitosphenoids. Structure The main features of the lesser wing are the optic canal, the anterior clinoid process, and the superior orbital fissure. Surfaces The superior surface of each is flat, and supports part of the frontal lobe of the brain. The inferior surface forms the back part of the roof of the orbit, and the upper boundary of the superior orbital fissure. This fissure is of a triangular form, and leads from the cavity of the cranium into that of the orbit: it is bounded medially by the body; above, by the small wing; below, by the medial margin of the orbital surface of the great wing; and is completed laterally by the frontal bone. It transmits the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve, and the abducent nerve, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Lobes
The olfactory bulb (Latin: ''bulbus olfactorius'') is a neural structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the sense of smell. It sends olfactory information to be further processed in the amygdala, the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and the hippocampus where it plays a role in emotion, memory and learning. The bulb is divided into two distinct structures: the main olfactory bulb and the accessory olfactory bulb. The main olfactory bulb connects to the amygdala via the piriform cortex of the primary olfactory cortex and directly projects from the main olfactory bulb to specific amygdala areas. The accessory olfactory bulb resides on the dorsal-posterior region of the main olfactory bulb and forms a parallel pathway. Destruction of the olfactory bulb results in ipsilateral anosmia, while irritative lesions of the uncus can result in olfactory and gustatory hallucinations. Structure In most vertebrates, the olfactory bulb is the most rostral (forward) part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoidal Spine
The superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone (Fig. 145) presents in front a prominent spine, the ethmoidal spine, for articulation with the cribriform plate of the ethmoid; behind this is a smooth surface slightly raised in the middle line, and grooved on either side for the olfactory lobes of the brain The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for .... Additional images File:Gray193.png, Base of the skull. Upper surface. References Bones of the head and neck {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Ethmoidal Foramen
Lateral to either olfactory groove are the internal openings of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina (or canals). The posterior ethmoidal foramen opens at the back part of this margin under cover of the projecting lamina of the sphenoid, and transmits the posterior ethmoidal vessels and nerve A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the Electrochemistry, electrochemical nerv .... External links * Bones of the head and neck {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethmoidal Foramina (other)
{{disambig ...
Ethmoidal foramen may refer to: * Anterior ethmoidal foramen * Posterior ethmoidal foramen Lateral to either olfactory groove are the internal openings of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal foramina (or canals). The posterior ethmoidal foramen opens at the back part of this margin under cover of the projecting lamina of the sphenoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasociliary Nerve
The nasociliary nerve is a branch of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1) (which is in turn a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). It is intermediate in size between the other two branches of the ophthalmic nerve, the frontal nerve and lacrimal nerve. Structure Course The nasociliary nerve enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure, through the common tendinous ring, and between the two heads of the lateral rectus muscle and between the superior and inferior rami of the oculomotor nerve. It passes across the optic nerve (CN II) along with the ophthalmic artery. It then runs obliquely beneath (inferior to) the superior rectus muscle and superior oblique muscle to the medial wall of the orbital cavity whereupon it emits the posterior ethmoidal nerve, and the anterior ethmoidal nerve. Branches Branches of the nasociliary nerve include: * posterior ethmoidal nerve * anterior ethmoidal nerve * long ciliary nerves * infratrochlear nerve * communicating branch to cil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Nerves
The olfactory nerve, also known as the first cranial nerve, cranial nerve I, or simply CN I, is a cranial nerve that contains sensory nerve fibers relating to the sense of smell. The afferent nerve fibers of the olfactory receptor neurons transmit nerve impulses about odors to the central nervous system (olfaction). Derived from the embryonic nasal placode, the olfactory nerve is somewhat unusual among cranial nerves because it is capable of some regeneration if damaged. The olfactory nerve is sensory in nature and originates on the olfactory mucosa in the upper part of the nasal cavity. From the olfactory mucosa, the nerve (actually many small nerve fascicles) travels up through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone to reach the surface of the brain. Here the fascicles enter the olfactory bulb and synapse there; from the bulbs (one on each side) the olfactory information is transmitted into the brain via the olfactory tract. The fascicles of the olfactory nerve are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Sagittal Sinus
The superior sagittal sinus (also known as the superior longitudinal sinus), within the human head, is an unpaired dural venous sinus lying along the attached margin of the falx cerebri. It allows blood to drain from the lateral aspects of the anterior cerebral hemispheres to the confluence of sinuses. Cerebrospinal fluid drains through arachnoid granulations into the superior sagittal sinus and is returned to the venous circulation. Structure It is triangular in section. It is narrower anteriorly, and gradually increases in size as it passes posterior-ward. It commences at the foramen cecum, through which it receives emissary veins from the nasal cavity. It passes posterior-ward along its entire course. It is accommodated within a groove which runs across the inner surface of the frontal bone, the adjacent margins of the two parietal lobes, and the superior division of the cruciate eminence of the occipital lobe. Near the internal occipital protuberance, it deviates to e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Bone
In the human skull, the frontal bone or sincipital bone is an unpaired bone which consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, part of the bony orbital cavity holding the eye, and part of the bony part of the nose respectively. The name comes from the Latin word ''frons'' (meaning "forehead"). Structure The frontal bone is made up of two main parts. These are the squamous part, and the orbital part. The squamous part marks the vertical, flat, and also the biggest part, and the main region of the forehead. The orbital part is the horizontal and second biggest region of the frontal bone. It enters into the formation of the roofs of the orbital and nasal cavities. Sometimes a third part is included as the nasal part of the frontal bone, and sometimes this is included with the squamous part. The nasal part is between the brow ridges, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |