|
Anatase
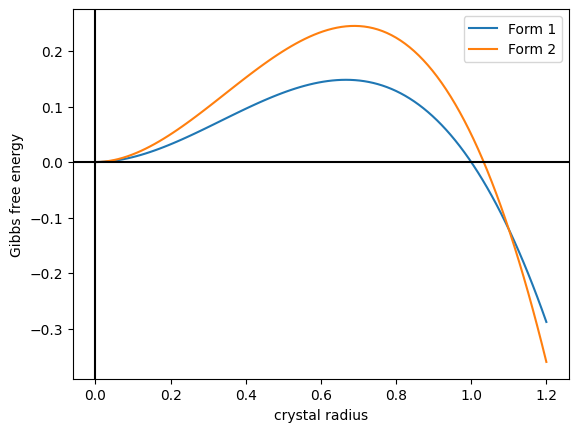
Anatase is a metastable mineral form of titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal crystal structure. Although colorless or white when pure, anatase in nature is usually a black solid due to impurities. Three other Polymorphism (materials science), polymorphs (or mineral forms) of titanium dioxide are known to occur naturally: brookite, akaogiite, and rutile, with rutile being the most common and most Chemical stability, stable of the bunch. Anatase is formed at relatively low temperatures and found in minor concentrations in Igneous rock, igneous and Metamorphic rock, metamorphic rocks. Glass coated with a thin film of TiO2 shows Anti-fog, antifogging and Self-cleaning surfaces, self-cleaning properties under ultraviolet radiation. Anatase is always found as small, isolated, and sharply developed crystals, and like rutile, it crystallizes in a Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal system. Anatase is metastable at all temperatures and pressures, with ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
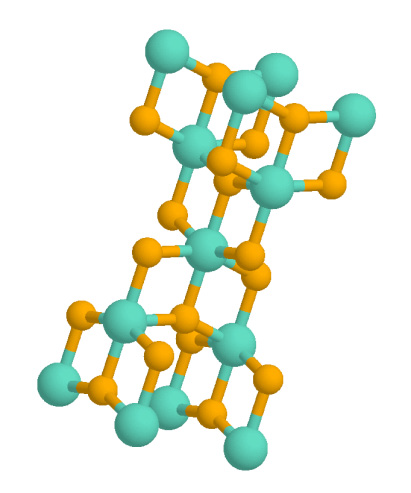
Anatase Crystal Structure
Anatase is a metastable mineral form of titanium dioxide (TiO2) with a tetragonal crystal structure. Although colorless or white when pure, anatase in nature is usually a black solid due to impurities. Three other polymorphs (or mineral forms) of titanium dioxide are known to occur naturally: brookite, akaogiite, and rutile, with rutile being the most common and most stable of the bunch. Anatase is formed at relatively low temperatures and found in minor concentrations in igneous and metamorphic rocks. Glass coated with a thin film of TiO2 shows antifogging and self-cleaning properties under ultraviolet radiation. Anatase is always found as small, isolated, and sharply developed crystals, and like rutile, it crystallizes in a tetragonal system. Anatase is metastable at all temperatures and pressures, with rutile being the equilibrium polymorph. Nevertheless, anatase is often the first titanium dioxide phase to form in many processes due to its lower surface energy, with a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound derived from titanium with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or Colour Index International, CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble in water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits Octahedral molecular geometry, octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structures of rutile and anatase are tetragonal in symmetry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Brookite
Brookite is the Orthorhombic crystal system, orthorhombic variant of titanium dioxide (TiO2), which occurs in four known natural Polymorphism (materials science), polymorphic forms (minerals with the same composition but different structure). The other three of these forms are akaogiite (Monoclinic crystal system, monoclinic), anatase (Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal) and rutile (Tetragonal crystal system, tetragonal). Brookite is rare compared to anatase and rutile and, like these forms, it exhibits Photocatalysis, photocatalytic activity. Brookite also has a larger Crystal structure, cell volume than either anatase or rutile, with 8 TiO2 groups per unit cell, compared with 4 for anatase and 2 for rutile.Anatase and Brookite . Wikis.lib.ncsu.edu (2007-05-08). Retrieved on 2011-10-14. Iron (Fe), tantalum (Ta) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Polymorphism (materials Science)
In crystallography, polymorphism is the phenomenon where a compound or element can crystallize into more than one crystal structure. The preceding definition has evolved over many years and is still under discussion today. Discussion of the defining characteristics of polymorphism involves distinguishing among types of transitions and structural changes occurring in polymorphism versus those in other phenomena. Overview Phase transitions (phase changes) that help describe polymorphism include polymorphic transitions as well as melting and vaporization transitions. According to IUPAC, a polymorphic transition is "A reversible transition of a solid crystalline phase at a certain temperature and pressure (the inversion point) to another phase of the same chemical composition with a different crystal structure." Additionally, Walter McCrone described the phases in polymorphic matter as "different in crystal structure but identical in the liquid or vapor states." McCrone also def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mohs Scale Of Mineral Hardness
The Mohs scale ( ) of mineral hardness is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material. The scale was introduced in 1812 by the German geologist and mineralogist Friedrich Mohs, in his book (English: Attempt at an elementary method for the natural-historical determination and recognition of fossils); it is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science, some of which are more quantitative. The method of comparing hardness by observing which minerals can scratch others is of great antiquity, having been mentioned by Theophrastus in his treatise ''On Stones'', , followed by Pliny the Elder in his ''Naturalis Historia'', . The Mohs scale is useful for identification of minerals in the field, but is not an accurate predictor of how well materials endure in an industrial setting. Reference minerals The Mohs scale of mineral hardness is based on the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rutile
Rutile is an oxide mineral composed of titanium dioxide (TiO2), the most common natural form of TiO2. Rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known, including anatase, akaogiite, and brookite. Rutile has one of the highest refractive indices at visible wavelengths of any known crystal and also exhibits a particularly large birefringence and high dispersion. Owing to these properties, it is useful for the manufacture of certain optical elements, especially polarization optics, for longer visible and infrared wavelengths up to about 4.5 micrometres. Natural rutile may contain up to 10% iron and significant amounts of niobium and tantalum. Rutile derives its name from the Latin ('red'), in reference to the deep red color observed in some specimens when viewed by transmitted light. Rutile was first described in 1803 by Abraham Gottlob Werner using specimens obtained in Horcajuelo de la Sierra, Madrid (Spain), which is consequently the type locality. Occurrence Rutile is a comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oxide Minerals
The oxide mineral class includes those minerals in which the oxide anion (O2−) is bonded to one or more metal alloys. The hydroxide-bearing minerals are typically included in the oxide class. Minerals with complex anion groups such as the Silicate mineral, silicates, Sulfate mineral, sulfates, carbonate mineral, carbonates and Phosphate mineral, phosphates are classed separately. Simple oxides *XO form **Periclase group ***Periclase ***Manganosite **Zincite group ***Zincite ***Bromellite ***Tenorite ***Litharge * form **Cuprite **Ice * form **Hematite group ***Corundum ***Hematite ***Ilmenite * form **Rutile group ***Rutile ***Pyrolusite ***Cassiterite **Baddeleyite **Uraninite **Thorianite * form **Spinel group ***Spinel ***Gahnite ***Magnetite ***Franklinite ***Chromite **Chrysoberyl **Columbite *Hydroxide subgroup: **Brucite **Manganite **Romanèchite **Goethite group: ***Diaspore ***Goethite Nickel–Strunz class 4: oxides Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Minerals'; p. 1. In the series ''Geology: Landforms, Minerals, and Rocks''. Rosen Publishing Group. The Geology, geological definition of mineral normally excludes compounds that occur only in living organisms. However, some minerals are often biogenic (such as calcite) or organic compounds in the sense of chemistry (such as mellite). Moreover, living organisms often synthesize inorganic minerals (such as hydroxylapatite) that also occur in rocks. The concept of mineral is distinct from rock (geology), rock, which is any bulk solid geologic material that is relatively homogeneous at a large enough scale. A rock may consist of one type of mineral or may be an aggregate (geology), aggregate of two or more different types of minerals, spaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cleavage (crystal)
Cleavage, in mineralogy and materials science, is the tendency of crystalline materials to split along definite crystallographic structural planes. These planes of relative weakness are a result of the regular locations of atoms and ions in the crystal, which create smooth repeating surfaces that are visible both in the microscope and to the naked eye. If bonds in certain directions are weaker than others, the crystal will tend to split along the weakly bonded planes. These flat breaks are termed "cleavage".Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, '' Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed., Wiley, The classic example of cleavage is mica, which cleaves in a single direction along the basal pinacoid, making the layers seem like pages in a book. In fact, mineralogists often refer to "books of mica". Diamond and graphite provide examples of cleavage. Each is composed solely of a single element, carbon. In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four others in a tetrahedral patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dauphiné
The Dauphiné ( , , ; or ; or ), formerly known in English as Dauphiny, is a former province in southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was originally the Dauphiné of Viennois. In the 12th century, the local ruler Count Guigues IV of Albon (–1142) bore a dolphin on his coat of arms and was nicknamed (French for 'dolphin'). His descendants changed their title from Count of Albon to Dauphin of Viennois. The state took the name of Dauphiné. It became a state of the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century. In 1349, the Dauphiné was transferred from the last non-royal Dauphin (who had great debts and no direct heir) to the future king of France, Charles V, through the purchase of lands. The terms of the transfer stipulated that the heir apparent of France would henceforth be called and included significant autonomy and tax exemption for the Dauphiné region, most of which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Le Bourg-d'Oisans
Le Bourg-d'Oisans () is a commune in the Isère department in southeastern France. It is located in the Oisans region of the French Alps. Le Bourg-d'Oisans is located in the valley of the Romanche River, on the road from Grenoble to Briançon and on the south side of the Col de la Croix de Fer. It is often on the route of the Tour de France, as the town sits at the base of the road climbing to Alpe d'Huez with 21 hairpin bends. It is surrounded by several well-known mountain resorts, such as the Alpe d'Huez and Les Deux Alpes. The Écrins National Park lies to the southeast of Le Bourg-d'Oisans. Population See also *Communes of the Isère department *Livet-et-Gavet *Alpe d'Huez L'Alpe d'Huez () is a ski resort in Southeastern France at . It is a mountain pasture in the central French Western Alps, in the Communes of France, commune of Huez, which is part of the Isère Departments of France, department in the Auvergne-R ... References Communes of Isère ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jean-Claude Delamétherie
Jean-Claude Delamétherie (also ''de La Métherie'', ''de Lamétherie'', 4 September 1743 – 1 July 1817) was a French mineralogist, geologist and paleontologist. Career Delamétherie was born in La Clayette. He edited ''Journal de physique, de chimie, d'histoire naturelle et des arts'' from 1785. He was elected member of Leopoldina in 1792. He was a supporter of the French Revolution, but opposed to the Jacobins, and was forced to leave Paris during the Reign of Terror, interrupting publication of the ''Journal de physique'' until 1797. Numerous minerals were first systematically described by Delamétherie. In 1795, Delamétherie first described the Lherzolite (which he named after the site of its discovery, Étang de Lers in the Pyrenees). Delamétherie was an advocate of transmutation of species.Corbey, Raymond. (2005). ''The Metaphysics of Apes: Negotiating the Animal-Human Boundary''. Cambridge University Press. p. 62. He was an atheist and materialist.Corsi, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |