|
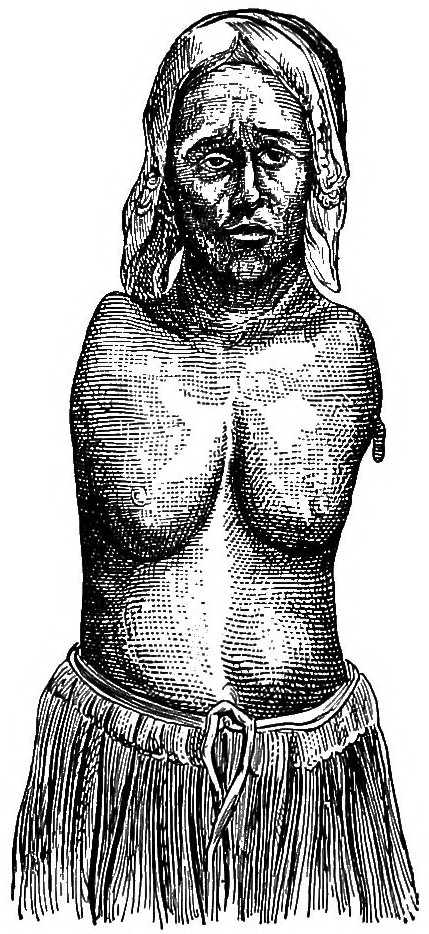
Amelia (birth Defect)
Amelia is the birth defect of lacking one or more limbs. The term may be modified to indicate the number of legs or arms missing at birth, such as tetra-amelia for the absence of all four limbs. The term is . Symptoms The diagnosis of amelia syndrome is established clinically and can be made on routine prenatal ultrasonography. WNT3 is the only gene known to be associated with tetra-amelia syndrome. Molecular genetic testing on a clinical basis can be used to diagnose the incidence of the syndrome. The mutation detection frequency is unknown as only a limited number of families have been studied. Affected infants are often stillborn or die shortly after birth. Description Amelia may be present as an isolated defect, but it is often associated with major malformations in other organ systems. These frequently include cleft lip and/or palate, body wall defects, malformed head, and defects of the neural tube, kidneys, and diaphragm. Facial clefts may be accompanied by other faci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracy Barrell
Tracy Lee Barrell, Order of Australia, OAM (born 1974) is a triple Hemimelia, congenital amputee Paralympic swimmer from Australia. She won two gold medals at the 1992 Summer Paralympics, 1992 Barcelona Games. She is a strong advocate for people with disabilities and an Indigenous Australians, indigenous Australian. Personal life Barrell was born in 1974 in New South Wales. From birth she had no legs and only one arm. Barrell stated that doctors said her disability was a congenital malformation resulting from exposure to an Thalidomide, anti morning sickness pill that her mother Terri had taken. Barrell sat on a skateboard and used her one arm for her mobility as a child. She decided not to use prosthetic legs. She attended St Patrick's College, Sutherland in Sydney. She got married in February 1995 to Steve and got divorced 3 years later. She has two sons with her new partner Brad – Bryce (2001) and Oscar (2004). She separated from her partner and raised the children as a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysmelia
Dysmelia (from the Greek (), "bad" + (), "limb" + English suffix -ia) is a congenital disorder of a limb resulting from a disturbance in embryonic development. Types Dysmelia can refer to * missing ( aplasia) limbs: amelia (including tetraamelia), oligodactyly, congenital amputation e.g. tibial or radial aplasia * malformation of limbs: shortening (micromelia, rhizomelia or mesomelia), ectrodactyly, phocomelia, meromelia, syndactyly, brachydactyly, club foot * extra limbs: polymelia, polydactyly, polysyndactyly * others: hemimelia, symbrachydactyly Occurrence rate Birth defects involving limbs occur in 0.69 per 1000. Causes Dysmelia can be caused by * Inheritance of abnormal genes, e.g. polydactyly, ectrodactyly or brachydactyly, symptoms of deformed limbs then often occur in combination with other symptoms (syndromes) * external causes during pregnancy (thus not inherited), e.g. via amniotic band syndrome * teratogenic drugs (e.g. thalidomide, which cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limb (anatomy)
A limb (from Old English ''lim'', meaning "body part") is a jointed, muscled appendage of a tetrapod vertebrate animal used for weight-bearing, terrestrial locomotion and physical interaction with other objects. The distalmost portion of a limb is known as its extremity. The limbs' bony endoskeleton, known as the appendicular skeleton, is homologous among all tetrapods, who use their limbs for walking, running and jumping, swimming, climbing, grasping, touching and striking. All tetrapods have four limbs that are organized into two bilaterally symmetrical pairs, with one pair at each end of the torso, which phylogenetically correspond to the four paired fins ( pectoral and pelvic fins) of their fish ( sarcopterygian) ancestors. The cranial pair (i.e. closer to the head) of limbs are known as the forelimbs or ''front legs'', and the caudal pair (i.e. closer to the tail or coccyx) are the hindlimbs or ''back legs''. In animals with a more erect bipedal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WNT3
Proto-oncogene protein Wnt-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''WNT3'' gene In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei .... The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes that encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and patterning during embryogenesis. This gene is a member of the WNT gene family. It encodes a protein showing 98% amino acid identity to mouse Wnt3 protein, and 84% to human WNT3A protein, another WNT gene product. The mouse studies show the requirement of Wnt3 in primary axis formation in the mouse. Studies of the gene expression suggest that this gene may play a key role in some cases of human breast, rectal, lung, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or through biochemical analysis to measure specific protein output. In a medical setting, genetic testing can be used to diagnose or rule out suspected genetic disorders, predict risks for specific conditions, or gain information that can be used to customize medical treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. Genetic testing can also be used to determine biological relatives, such as a child's biological parentage (genetic mother and father) through DNA paternity testing, or be used to broadly predict an individual's ancestry. Genetic testing of plants and animals can be used for similar reasons as in humans (e.g. to assess relatedness/ancestry or predict/diagnose genetic disorders), to gain information used for selective breed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gould Pyle 110
Gould may refer to: People * Gould (name), a surname Places United States * Gould, Arkansas, a city * Gould, Colorado, an unincorporated community * Gould, Ohio, an unincorporated community * Gould, Oklahoma, a town * Gould, West Virginia, an unincorporated community * Gould City, Michigan * Gould City, Washington * Gould Township, Minnesota Multiple countries * Gould Lake (other) * Mount Gould (other) Elsewhere * Gould (crater), a lunar crater formation * Gould Coast, Antarctica * Gould Dome, Alberta, Canada Other uses * Gould baronets, two titles, one in the Baronetage of England and one in the Baronetage of Great Britain * Gould Belt, a partial ring of stars in the Milky Way * Gould designation, a type of star identifier * Gould League, an independent Australian organisation promoting environmental education * Gould Electronics, a company involved in the electronics and semiconductor industries * Gould Racing, a British motorsport company * USC Gould ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetra-amelia
Tetra-amelia syndrome (''tetra-'' + '' amelia''), also called autosomal recessive tetraamelia, is an extremely rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by the absence of all four limbs. Other areas of the body are also affected by malformations, such as the face, skull, reproductive organs, anus, lungs and pelvis. The disorder can be caused by recessive mutations in the WNT3 or RSPO2 genes. Presentation Tetra-amelia syndrome is characterized by the complete absence of all four limbs. The syndrome causes severe malformations of various parts of the body, including the face and head, heart, nervous system, skeleton, and genitalia. In many cases, the lungs are underdeveloped, which makes breathing difficult or impossible. Because children with tetra-amelia syndrome have such serious medical problems, most are stillborn or die shortly after birth. Cause RSPO2 and WNT3 genes Researchers have found loss-of-function mutations in the WNT3 or the RSPO2 genes in peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teratology
Teratology is the study of abnormalities of physiological development in organisms during their life span. It is a sub-discipline in medical genetics which focuses on the classification of congenital abnormalities in dysmorphology caused by teratogens and also in pharmacology and toxicology. Teratogens are substances that may cause non-heritable birth defects via a toxic effect on an embryo or fetus. Defects include malformations, disruptions, deformations, and dysplasia that may cause stunted growth, delayed mental development, or other congenital disorders that lack structural malformations. These defects can be recognized prior to or at birth as well as later during early childhood. The related term developmental toxicity includes all manifestations of abnormal development that are caused by environmental insult. The extent to which teratogens will impact an embryo is dependent on several factors, such as how long the embryo has been exposed, the stage of development the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalidomide
Thalidomide, sold under the brand names Contergan and Thalomid among others, is an oral administered medication used to treat a number of cancers (e.g., multiple myeloma), graft-versus-host disease, and many skin disorders (e.g., complications of leprosy such as skin lesions). Updated as required. Thalidomide has been used to treat conditions associated with HIV: aphthous ulcers, HIV-associated wasting syndrome, diarrhea, and Kaposi's sarcoma, but increases in HIV viral load have been reported. Common side effects include sleepiness, rash, and dizziness. Severe side effects include tumor lysis syndrome, blood clots, and peripheral neuropathy. Thalidomide is a known human teratogen and carries an extremely high risk of severe, life-threatening birth defects if administered or taken during pregnancy. It causes skeletal deformities such as Amelia (birth defect), amelia (absence of legs and/or arms), absence of bones, and phocomelia (malformation of the limbs). A single dose of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniotic Band Constriction
Constriction ring syndrome (CRS) is a congenital disorder with unknown cause. Because of the unknown cause there are many different, and sometimes incorrect, names. It is a malformation due to intrauterine bands or rings that produce deep grooves in (most commonly distal) extremities such as fingers and toes. In rare cases the constriction ring can form around other parts of the fetus and cause amputation or even intrauterine death. The anatomy proximal to the site of constriction (or amputation) is developmentally normal. CRS can be associated with other malformations, with club foot being most common. The precise configuration of the bands, lymphedema, and character of the amputations are not predictable and vary with each individual patient. Also, more than one extremity is usually affected, and it is rare for only one ring to present as an isolated malformation with no other manifestation of this syndrome. Signs and symptoms The constriction of appendages by amniotic bands may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysmelia
Dysmelia (from the Greek (), "bad" + (), "limb" + English suffix -ia) is a congenital disorder of a limb resulting from a disturbance in embryonic development. Types Dysmelia can refer to * missing ( aplasia) limbs: amelia (including tetraamelia), oligodactyly, congenital amputation e.g. tibial or radial aplasia * malformation of limbs: shortening (micromelia, rhizomelia or mesomelia), ectrodactyly, phocomelia, meromelia, syndactyly, brachydactyly, club foot * extra limbs: polymelia, polydactyly, polysyndactyly * others: hemimelia, symbrachydactyly Occurrence rate Birth defects involving limbs occur in 0.69 per 1000. Causes Dysmelia can be caused by * Inheritance of abnormal genes, e.g. polydactyly, ectrodactyly or brachydactyly, symptoms of deformed limbs then often occur in combination with other symptoms (syndromes) * external causes during pregnancy (thus not inherited), e.g. via amniotic band syndrome * teratogenic drugs (e.g. thalidomide, which cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |