|
Altitude Valve
A level control valve or altitude control valve is a type of valve that automatically responds to changes in the height of a liquid in some storage system. A common example is the set of ballcocks in a flush toilet, where each stage of the flush cycle is actuated by the emptying or filling of the tank. Another example is in reservoirs and other tank storage systems, where the tank is refilled from another source when the tank runs low and overfilling is prevented as it refills. In all cases, the valve itself is attached to a sensor, such as a float switch or similar system where float attached to the desired length of cable, or a spring whose strength is calibrated for the desired head pressure.{{cite web , url= https://www.cla-val.com/waterworks-altitude-level-control-valves , title= Altitude and Level Control Valves , accessdate= October 26, 2018 They can be modulating, where the flow is proportional Proportionality, proportion or proportional may refer to: Mathematics * Prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, but are usually discussed as a separate category. In an open valve, fluid flows in a direction from higher pressure to lower pressure. The word is derived from the Latin ''valva'', the moving part of a door, in turn from ''volvere'', to turn, roll. The simplest, and very ancient, valve is simply a freely hinged flap which swings down to obstruct fluid (gas or liquid) flow in one direction, but is pushed up by the flow itself when the flow is moving in the opposite direction. This is called a check valve, as it prevents or "checks" the flow in one direction. Modern control valves may regulate pressure or flow downstream and operate on sophisticated automation systems. Valves have many uses, including controlling water for irrigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballcock
A ballcock (also balltap or float valve) is a mechanism or machine for filling water tanks, such as those found in flush toilets, while avoiding overflow and (in the event of low water pressure) backflow. The modern ballcock was invented by José Antonio de Alzate y Ramírez, a Mexican priest and scientist, who described the device in 1790 in the ''Gaceta de Literatura Méxicana''. The ballcock device was patented in 1797 for use in steam engines by Edmund Cartwright. It consists of a valve connected to a hollow, sealed float by means of a lever mounted near the top of the tank. The float is often ball-shaped, hence the name ''ballcock''. The valve is connected to the incoming water supply Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. T ..., and is opened and closed by the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flush Toilet
A flush toilet (also known as a flushing toilet, water closet (WC) – see also toilet names) is a toilet that disposes of human waste (principally urine and feces) by using the force of water to ''flush'' it through a drainpipe to another location for treatment, either nearby or at a communal facility, thus maintaining a separation between humans and their waste. Flush toilets can be designed for sitting (in which case they are also called "Western" toilets) or for squatting, in the case of squat toilets. Most modern sewage treatment systems are also designed to process specially designed ''toilet paper''. The opposite of a flush toilet is a dry toilet, which uses no water for flushing. Flush toilets are a type of plumbing fixture and usually incorporate an "S", "U", "J", or "P" shaped bend called a trap that causes water to collect in the toilet bowl to hold the waste and act as a seal against noxious sewer gases. Most flush toilets are connected to a sewerage system tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Float Switch
A float switch is a type of level sensor, a device used to detect the level of liquid within a tank. The switch may be used to control a pump, as an indicator, an alarm, or to control other devices. One type of float switch uses a mercury switch inside a hinged float. Another common type is a float that raises a rod to actuate a microswitch. One pattern uses a reed switch mounted in a tube; a float, containing a magnet, surrounds the tube and is guided by it. When the float raises the magnet to the reed switch, it closes. Several reeds can be mounted in the tube for different level indications by one assembly. Bela G. Liptak (ed.), ''Instrument Engineers' Handbook, Fourth Edition, Volume One: Process Measurement and Analysis'', CRC Press, 2003, page 477 File:Float_switch_on.jpg, float switch on File:Float_switch_off.jpg, float switch off A very common application is in sump pumps and condensate pumps where the switch detects the rising level of liquid in the sump or tank and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Float (liquid Level)
Liquid level floats, also known as float balls, are spherical, cylindrical, oblong or similarly shaped objects, made from either rigid or flexible material, that are buoyant in water and other liquids. They are non-electrical hardware frequently used as visual sight-indicators for surface demarcation and level measurement. They may also be incorporated into switch mechanisms or translucent fluid-tubes as a component in monitoring or controlling liquid level. Liquid level floats, or float switches, use the principle of material buoyancy (differential densities) to follow fluid levels. Solid floats are often made of plastics with a density less than water or other application liquid, and so they float. Hollow floats filled with air are much less dense than water or other liquids, and are appropriate for some applications. Stainless Steel Magnetic floats are tubed magnetic floats, used for reed switch activation; they have a hollow tubed connection running through them. These magnet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Pressure
Hydraulic head or piezometric head is a specific measurement of liquid pressure above a vertical datum., 410 pages. See pp. 43–44., 650 pages. See p. 22. It is usually measured as a liquid surface elevation, expressed in units of length, at the entrance (or bottom) of a piezometer. In an aquifer, it can be calculated from the depth to water in a piezometric well (a specialized water well), and given information of the piezometer's elevation and screen depth. Hydraulic head can similarly be measured in a column of water using a standpipe piezometer by measuring the height of the water surface in the tube relative to a common datum. The hydraulic head can be used to determine a ''hydraulic gradient'' between two or more points. "Head" in fluid dynamics In fluid dynamics, ''head'' is a concept that relates the energy in an incompressible fluid to the height of an equivalent static column of that fluid. From Bernoulli's principle, the total energy at a given point in a fluid i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proportionality (mathematics)
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. Two sequences are inversely proportional if corresponding elements have a constant product, also called the coefficient of proportionality. This definition is commonly extended to related varying quantities, which are often called ''variables''. This meaning of ''variable'' is not the common meaning of the term in mathematics (see variable (mathematics)); these two different concepts share the same name for historical reasons. Two functions f(x) and g(x) are ''proportional'' if their ratio \frac is a constant function. If several pairs of variables share the same direct proportionality constant, the equation expressing the equality of these ratios is called a proportion, e.g., (for details see Ratio). Proportionality is closely r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
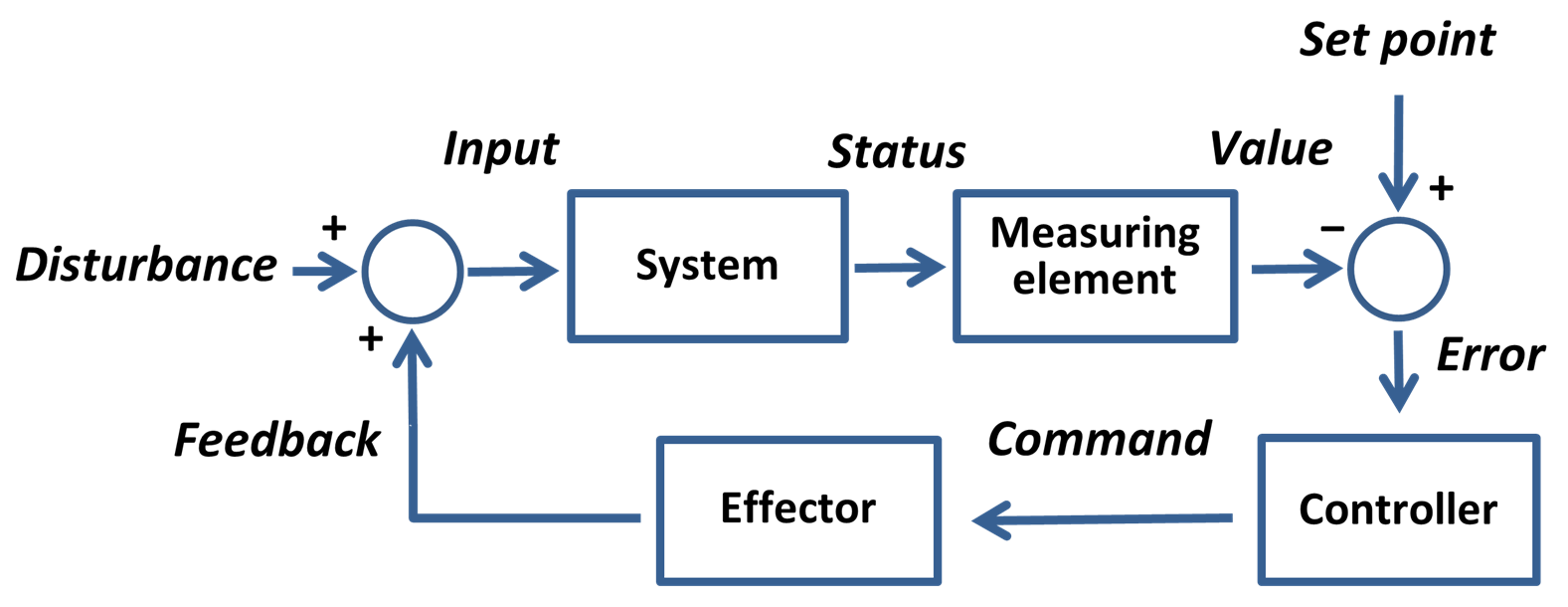
Setpoint (control System)
In cybernetics and control theory, a setpoint (SP; also set point) is the desired or target value for an essential variable, or process value (PV) of a control system. Departure of such a variable from its setpoint is one basis for error-controlled regulation using negative feedback for automatic control. Examples Cruise control The SP-PV error can be used to return a system to its norm. An everyday example is the cruise control on a road vehicle; where external influences such as gradients cause speed changes (PV), and the driver also alters the desired set speed (SP). The automatic control algorithm restores the actual speed to the desired speed in the optimum way, without delay or overshoot, by altering the power output of the vehicle's engine. In this way the SP-PV error is used to control the PV so that it equals the SP. A widespread use of SP-PV error control is the PID controller. Industrial applications Special consideration must be given for engineering applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |