|
Allokotosaur
Allokotosauria is a clade of early archosauromorph reptiles from the Middle to Late Triassic known from Asia, Africa, North America and Europe. Allokotosauria was first described and named when a new monophyletic grouping of specialized herbivorous archosauromorphs was recovered by Sterling J. Nesbitt, John J. Flynn, Adam C. Pritchard, J. Michael Parrish, Lovasoa Ranivoharimanana and André R. Wyss in 2015. The name Allokotosauria is derived from Greek meaning "strange reptiles" in reference to unexpected grouping of early archosauromorph with a high disparity of features typically associated with herbivory. History Nesbitt ''et al.'' (2015) defined the group as a stem-based taxon containing ''Azendohsaurus madagaskarensis'' and ''Trilophosaurus buettneri'' and all taxa more closely related to them than to ''Tanystropheus longobardicus'', ''Proterosuchus fergusi'', ''Protorosaurus speneri'' or '' Rhynchosaurus articeps''. Therefore, Allokotosauria includes the families Azendohs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
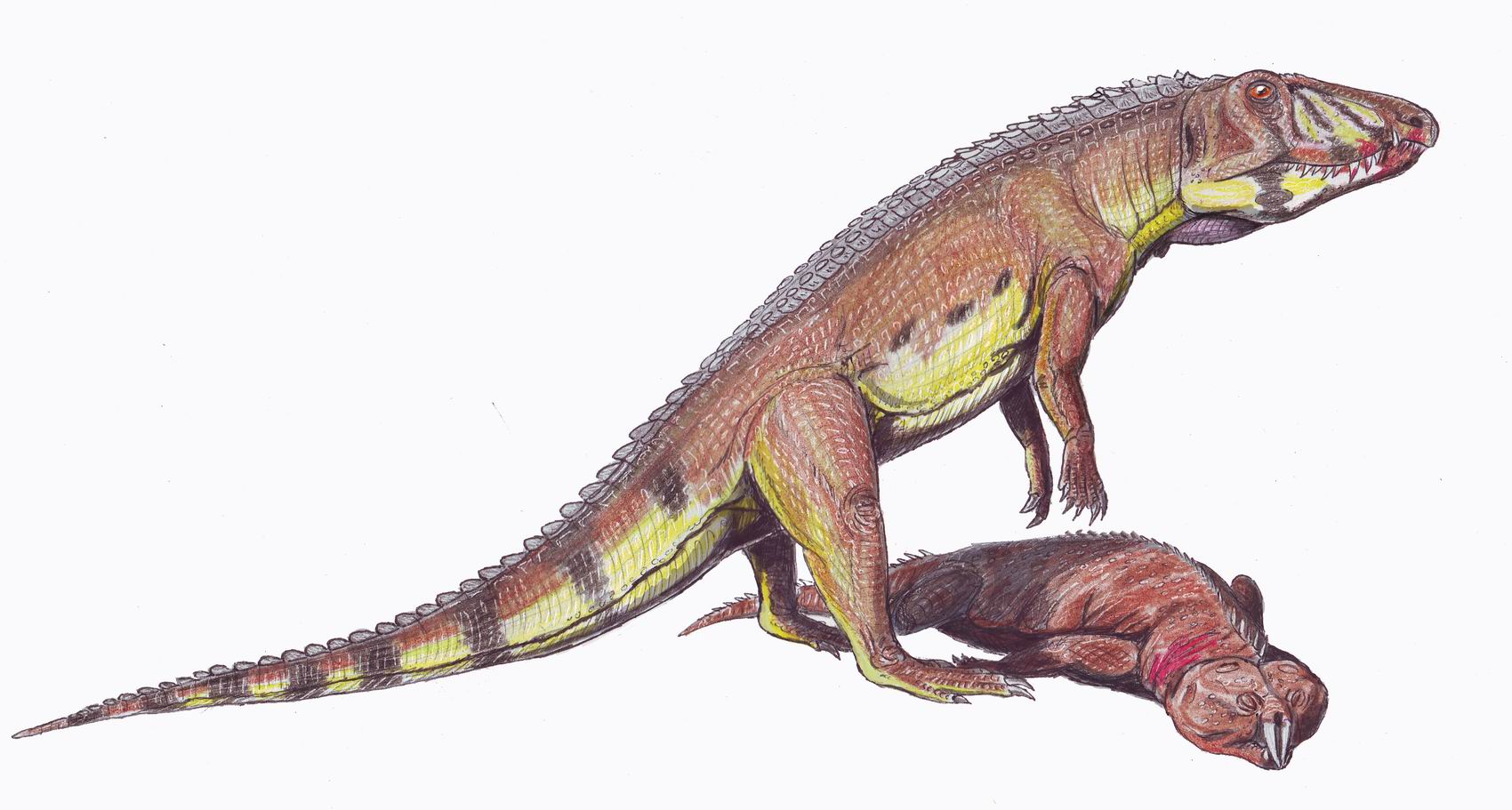
Azendohsaurus Madagaskarensis
''Azendohsaurus'' is an extinct genus of herbivorous archosauromorph reptile from roughly the late Middle to early Late Triassic Period of Morocco and Madagascar. The type species, ''Azendohsaurus laaroussii'', was described and named by Jean-Michel Dutuit in 1972 based on partial jaw fragments and some teeth from Morocco. A second species from Madagascar, ''A. madagaskarensis'', was first described in 2010 by John J. Flynn and colleagues from a multitude of specimens representing almost the entire skeleton. The generic name "Azendoh lizard" is for the village of Azendoh, a local village near where it was first discovered in the Atlas Mountains. It was a bulky quadruped that unlike other early archosauromorphs had a relatively short tail and robust limbs that were held in an odd mix of sprawled hind limbs and raised forelimbs. It had a long neck and a proportionately small head with remarkably sauropod-like jaws and teeth. ''Azendohsaurus'' used to be classified as a herbivorous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azendohsaurus
''Azendohsaurus'' is an extinct genus of Herbivore, herbivorous archosauromorph reptile from roughly the late Middle Triassic, Middle to early Late Triassic, Late Triassic Period of Morocco and Madagascar. The type species, ''Azendohsaurus laaroussii'', was described and named by Jean-Michel Dutuit in 1972 in paleontology, 1972 based on partial jaw fragments and some teeth from Morocco. A second species from Madagascar, ''A. madagaskarensis'', was first described in 2010 in paleontology, 2010 by John J. Flynn and colleagues from a multitude of specimens representing almost the entire skeleton. The Generic name (biology), generic name "Azendoh lizard" is for the village of Azendoh, a local village near where it was first discovered in the Atlas Mountains. It was a bulky quadruped that unlike other early archosauromorphs had a relatively short tail and robust limbs that were held in an odd mix of sprawled hind limbs and raised forelimbs. It had a long neck and a proportionately small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorph
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) than to lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including '' Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and '' Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azendohsauridae
Azendohsauridae is a family of allokotosaurian archosauromorphs that lived during the Middle to Late Triassic period, around 242-216 million years ago. The family was originally named solely for the eponymous ''Azendohsaurus'', marking out its distinctiveness from other allokotosaurs, but the family now includes four other genera: the basal genus '' Pamelaria'', the large horned herbivore '' Shringasaurus'', and two carnivorous genera grouped into the subfamily-level subclade Malerisaurinae, ''Malerisaurus'' and ''Puercosuchus'', and potentially also the dubious genus ''Otischalkia''. Most fossils of azendohsaurids have a Gondwanan distribution, with multiple species known across Morocco and Madagascar in Africa as well as India, although fossils of malerisaurine azendohsaurids have also been found in the southwestern United States of North America. Azendohsaurids are notable for the various dinosaur-like traits found in some species, including the sauropodomorph-like neck, jaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanystropheus Longobardicus
''Tanystropheus'' (~ 'long' + 'hinged') is an extinct genus of archosauromorph reptile which lived during the Triassic period, Triassic Period in Europe, Asia, and North America. It is recognisable by its extremely elongated neck, longer than the torso and tail combined. The neck was composed of 13 vertebrae strengthened by extensive cervical ribs. ''Tanystropheus'' is one of the most well-described non-Archosauriformes, archosauriform archosauromorphs, known from numerous fossils, including nearly complete skeletons. Some species within the genus may have reached a total length of , making ''Tanystropheus'' the longest non-archosauriform archosauromorph as well. ''Tanystropheus'' is the namesake of the family Tanystropheidae, a clade collecting many long-necked Triassic archosauromorphs previously described as "Protorosauria, protorosaurs" or "Prolacertiformes, prolacertiforms". ''Tanystropheus'' contains at least two valid species as well as fossils which cannot be referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamelaria
''Pamelaria'' is an extinct genus of allokotosaurian archosauromorph reptile known from a single species, ''Pamelaria dolichotrachela'', from the Middle Triassic of India. ''Pamelaria'' has sprawling legs, a long neck, and a pointed skull with nostrils positioned at the very tip of the snout. Among early archosauromorphs, ''Pamelaria'' is most similar to '' Prolacerta'' from the Early Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. Both have been placed in the family Prolacertidae. ''Pamelaria'', ''Prolacerta'', and various other Permo-Triassic reptiles such as ''Protorosaurus'' and ''Tanystropheus'' have often been placed in a group of archosauromorphs called Protorosauria (alternatively called Prolacertiformes), which was regarded as one of the most basal group of archosauromorphs. However, more recent phylogenetic analyses indicate that ''Pamelaria'' and ''Prolacerta'' are more closely related to Archosauriformes than are ''Protorosaurus'', ''Tanystropheus'', and other protorosaurs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilophosauridae
Trilophosaurs are lizard-like Triassic allokotosaur reptiles related to the archosaurs. The best known genus is '' Trilophosaurus'', a herbivore up to long. It had a short, unusually heavily built skull, equipped with massive, broad flattened cheek teeth with sharp shearing surfaces for cutting up tough plant material. Teeth are absent from the premaxilla and front of the lower jaw, which in life were probably equipped with a horny beak. The skull is also unusual in that the lower temporal opening is missing, giving the appearance of a euryapsid skull, and originally the Trilophosaurs were classified with placodonts and sauropterygia. Carroll (1988) suggests that the lower opening may have been lost to strengthen the skull. Trilophosaurs are so far known only from the Late Triassic of North America and Europe. Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek language, Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drepanosauromorpha
Drepanosaurs (members of the clade Drepanosauromorpha) are a group of extinct reptiles that lived between the Carnian and Rhaetian stages of the late Triassic Period, approximately between 230 and 210 million years ago. The various species of drepanosaurs were characterized by a bird-like skull, a barrell shaped body, and a horizontally narrow tail. A number of drepanosaurs had specialized grasping limbs and often prehensile tails similar to those of chameleons. Drepanosaurs are generally thought to have been arboreal (tree-dwelling), and probably insectivores. Some studies have alternately suggested fossorial (digging) and aquatic lifestyles for some members. Fossils of drepanosaurs have been found in North America (Arizona, New Mexico, New Jersey, Utah) and Europe (England and northern Italy). The name is taken from the family's namesake genus '' Drepanosaurus'', which means "sickle lizard," a reference to their strongly curved claws. Some studies have included Drepanosaurs with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctosaurus
''Arctosaurus'' is an extinct genus of archosauromorph, possibly an allokotosaurian, but was often classified as a sauropodomorph dinosaur between 1900 and 1976. Although it has also been classified as a theropod, recent review finds that the similarities it shares with theropods are spread throughout several groups of Late Triassic reptiles, and so it cannot be assigned any more specifically than to Archosauriformes. Other authors have suggested trilophosaurian affinities. Based on the size of the vertebra, a size of about in length is extrapolated. Discovery and naming It is based on holotype NMING: F14878, a neck vertebra that was found in 1859 by Captain Sherard Osborn on Cameron Island, Nunavut, Canada, in Late Triassic The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ...-ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trilophosaurus Buettneri
''Trilophosaurus'' (Greek for "lizard with three ridges") is a lizard-like trilophosaurid allokotosaur known from the Late Triassic of North America. It was a herbivore up to 2.5 m long. Description ''Trilophosaurus'' had a short, unusually heavily built skull, equipped with massive, broad flattened cheek teeth with sharp shearing surfaces for cutting up tough plant material. Teeth are absent from the premaxilla and front of the lower jaw, which in life were probably equipped with a horny beak. Based on evidence derived from tooth wear patterns, ''Trilophosaurus'' was able to masticate labiolingually. The skull is also unusual in that the lower temporal opening is missing, giving the appearance of a euryapsid skull. Because of this, the trilophosaurs were once classified with placodonts within Sauropterygia. Carroll (1988) suggested that the lower opening may have been lost to strengthen the skull. Taxonomy ''Trilophosaurus'' is traditionally thought to include two val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage (stratigraphy), stage or earliest geologic age, age of the Middle Triassic series (stratigraphy), series or geologic epoch, epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ago. The Anisian Age succeeds the Olenekian Age (part of the Lower Triassic Epoch) and precedes the Ladinian Age. Stratigraphic definitions The stage and its name were established by Austrian geologists Wilhelm Heinrich Waagen and Carl Diener in 1895. The name comes from ''Anisus'', the Latin name of the river Enns (river), Enns. The original type locality (geology), type locality is at Großreifling in the states of Austria, Austrian state of Styria. The base of the Anisian Stage (also the base of the Middle Triassic series) is sometimes laid at the first appearance of conodont species ''Chiosella, Chiosella timorensis'' in the stratigraphic record. Other stratigraphers prefer to use the base of magnetic chronozone MT1n. There is no accept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem-based Taxon
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxon, taxa in biology that uses phylogenetics, phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explained below. This contrasts with Biological classification, the traditional method, by which taxon names are defined by a ''Type (biology), type'', which can be a specimen or a taxon of lower Taxonomic rank, rank, and a description in words. Phylogenetic nomenclature is regulated currently by the ''PhyloCode, International Code of Phylogenetic Nomenclature'' (''PhyloCode''). Definitions Phylogenetic nomenclature associates names with clades, groups consisting of an ancestor and all its descendants. Such groups are said to be Monophyly, monophyletic. There are slightly different methods of specifying the ancestor, which are discussed below. Once the ancestor is specified, the meaning of the name is fixed: the ancestor and all organisms which are its descendants are included in the taxon named. Listing all these organisms (i.e. prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |