|
Agrobiodiversity
Agricultural biodiversity or agrobiodiversity is a subset of general biodiversity pertaining to agriculture. It can be defined as "the variety and variability of animals, plants and micro-organisms at the genetic, species and ecosystem levels that sustain the ecosystem structures, functions and processes in and around production systems, and that provide food and non-food agricultural products.” It is managed by farmers, pastoralists, fishers and forest dwellers, agrobiodiversity provides stability, adaptability and resilience and constitutes a key element of the livelihood strategies of rural communities throughout the world. Agrobiodiversity is central to sustainable food systems and sustainable diets. The use of agricultural biodiversity can contribute to food security, nutrition security, and livelihood security, and it is critical for climate adaptation and climate mitigation. Etymology It is not clear when exactly the term agrobiodiversity was coined nor by whom. The 199 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioversity International
Bioversity International is a global research-for-development organization that delivers scientific evidence, management practices and policy options to use and safeguard agricultural biodiversity to attain global food security, food- and nutrition security, working with partners in low-income countries in different regions where agricultural biodiversity can contribute to improved nutrition, resilience, productivity and climate change adaptation. In 2019, Bioversity International joined with the International Center for Tropical Agriculture (as the Alliance of Bioversity International and CIAT) to "deliver research-based solutions that harness agricultural biodiversity and sustainably transform food systems to improve people's lives". Both institutions are members of the CGIAR, a global research partnership for a food-secure future. The organization is highly decentralized, with about 300 staff working around the world with regional offices located in Central and South America, We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEM Corn
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. Certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, and obsidian) and occasionally organic materials that are not minerals (such as amber, jet, and pearl) may also be used for jewelry and are therefore often considered to be gemstones as well. Most gemstones are hard, but some softer minerals such as brazilianite may be used in jewelry because of their color or luster or other physical properties that have aesthetic value. However, generally speaking, soft minerals are not typically used as gemstones by virtue of their brittleness and lack of durability. Found all over the world, the industry of coloured gemstones (i.e. anything other than diamonds) is currently estimated at US$1.55billion and is projected to steadily increase to a value of $4.46billion by 2033. A gem expert is a gemologis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
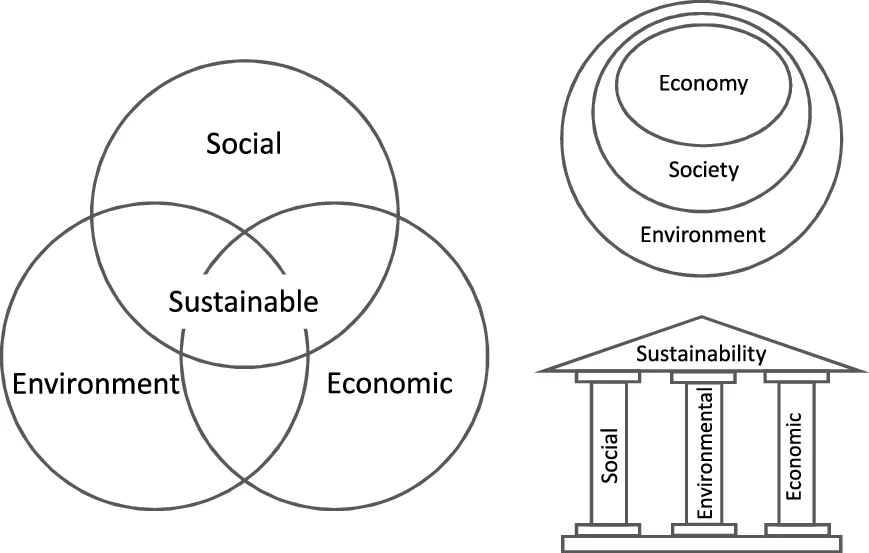
Sustainable
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female carpel, stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains. Insects are the major pollinators of most plants, and insect pollinators include all families of bees and most families of Aculeata, aculeate wasps; ants; many families of flies; many lepidopterans (both butterflies and moths); and many families of beetles. Vertebrates, mainly bats and birds, but also some non-bat mammals (monkeys, lemurs, Phalangeriformes, possums, rodents) and some lizards pollinate certain plants. Among the pollinating birds are hummingbirds, honeyeaters and sunbirds with long beaks; they pollinate a number of deep-throated flowers. Humans may also carry out artificial pollination. A pollinator is different from a pollenizer, a plant that is a source of pollen for the pollination process. Background Plants fall into pollination s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Wild Relative
A crop wild relative (CWR) is a wild plant closely related to a domesticated plant. It may be a wild ancestor of the domesticated (cultivated) plant or another closely related taxon. Overview The wild relatives of crop plants constitute an increasingly important resource for improving agricultural production and for maintaining sustainable agro-ecosystems. Their natural selection in the wild accumulates a rich set of useful traits that can be introduced into crop plants by crossing. With the advent of anthropogenic climate change and greater ecosystem instability CWRs are likely to prove a critical resource in ensuring food security for the new millennium. It was Nikolai Vavilov, the Russian botanist who first realized the importance of crop wild relatives in the early 20th century. Genetic material from CWRs has been utilized by humans for thousands of years to improve the quality and yield of crops. Farmers have used traditional breeding methods for millennia, wild maize ('' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Onion Blossoms (Allium)
Wild, wild, wilds or wild may refer to: Common meanings * Wilderness, a wild natural environment * Wildlife, an undomesticated organism * Wildness, the quality of being wild or untamed Art, media and entertainment Film and television * ''Wild'' (2014 film), a 2014 American film from the 2012 book * ''Wild'' (2016 film), a 2016 German film * ''The Wild'', a 2006 Disney 3D animation film * ''Wild'' (TV series), a 2006 American documentary television series * ''The Wilds'' (TV series), a 2020 television series Literature * '' Wild: From Lost to Found on the Pacific Crest Trail'' a 2012 non-fiction book by Cheryl Strayed * ''Wild, An elemental Journey'', a 2006 autobiographical book by Jay Griffiths * ''The Wild'' (novel), a 1991 novel by Whitley Strieber * ''The Wild'', a science fiction novel by David Zindell * ''The Wilds'', a 1998 limited-edition horror novel by Richard Laymon Music * ''Wild'' (band), a five-piece classical female group Albums and EPs * ''Wild'' (EP), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglected And Underutilized Crop
Neglected and underutilised crops are domesticated plant species used for food, medicine, trading, or cultural practices within local communities but not widely commodified or studied as part of mainstream agriculture. Such crops may be in declining production. They are considered underutilised in scientific inquiry for their perceived potential to contribute to knowledge regarding nutrition, food security, genetic resistance, or sustainability. Other terms to describe such crops include minor, orphan, underused, local, traditional, alternative, minor, niche, or underdeveloped. Overview Three crops: maize, wheat, and rice, account for approximately 50% of the world's consumption of calories and protein, and about 95% of the world's food needs are provided by just 30 species of plants. Despite this, the list of crop species compiled as edible extends to around 12,650. Among these are plants that have been used for food and other uses on a larger scale historically, but whose us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dietary Diversity
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. The word diet often implies the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management reasons (with the two often being related). Although humans are omnivores, each culture and each person holds some food preferences or some food taboos. This may be due to personal tastes or ethical reasons. Individual dietary choices may be more or less healthy. Complete nutrition requires ingestion and absorption of vitamins, minerals, essential amino acids from protein and essential fatty acids from fat-containing food, also food energy in the form of carbohydrate, protein, and fat. Dietary habits and choices play a significant role in the quality of life, health and longevity. Health A healthy diet can improve and maintain health, which can include aspects of mental and physical health. Specific diets, such as the DASH diet, can be used in treatment and management of chronic conditions. Dieta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Resources
Genetic resources are genetic material of actual or potential value, where genetic material means any material of plant, animal, microbial genetics, microbial or other origin containing functional units of heredity. Genetic resources is one of the three levels of biodiversity defined by the Convention on Biological Diversity in Rio, 1992. __NOTOC__ Examples *Animal genetic resources for food and agriculture *Forest genetic resources *Germplasm, genetic resources that are preserved for various purposes such as breeding, preservation, and research *Plant genetic resources *Genetic resources conservation and sustainable use See also *Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources, a strategy to preserve genetic resources cryogenically *Commission on Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, the only permanent intergovernmental body that addresses biological diversity for food and agriculture *International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture, an internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Biodiversity
Food biodiversity is defined as "the diversity of plants, animals and other organisms used for food, covering the genetic resources within species, between species and provided by ecosystems." Food biodiversity can be considered from two main perspectives: production and consumption. From a consumption perspective, food biodiversity describes the diversity of foods in human diets and their contribution to dietary diversity, cultural identity and good nutrition. Production of food biodiversity looks at the thousands of food products, such as fruits, nuts, vegetables, meat and condiments sourced from agriculture and from the wild (e.g. forests, uncultivated fields, water bodies). Food biodiversity covers the diversity ''between species,'' for example different animal and crop species, including those considered neglected and underutilized species. Food biodiversity also comprises the diversity ''within species,'' for example different varieties of fruit and vegetables, or different br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem Services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean air and water, decomposition of wastes, and flood control. Ecosystem services are grouped into four broad categories of services. There are ''provisioning services'', such as the production of food and water; ''regulating services'', such as the control of climate and disease; ''supporting services'', such as nutrient cycles and oxygen production; and ''cultural services'', such as recreation, tourism, and spiritual gratification. Evaluations of ecosystem services may include assigning an economic value to them. For example, Estuary, estuarine and coastal ecosystems are marine ecosystems that perform the four categories of ecosystem services in several ways. Firstly, their provisioning services include marine resources and genetic resource ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agroecosystem
Agroecosystems are the ecosystems supporting the food production systems in farms and gardens. As the name implies, at the core of an agroecosystem lies the human activity of agriculture. As such they are the basic unit of study in Agroecology, and Regenerative Agriculture using ecological approaches. Like other ecosystems, agroecosystems form partially closed systems in which animals, plants, microbes, and other living organisms and their environment are interdependent and regularly interact. They are somewhat arbitrarily defined as a spatially and functionally coherent unit of agricultural activity.Agro-ecosystem Health Project. 1996. Agroecosystem health. University of Guelph, Guelph, Canada. An agroecosystem can be seen as not restricted to the immediate site of agricultural activity (e.g. the farm). That is, it includes the region that is impacted by this activity, usually by changes to the complexity of species assemblages and energy flows, as well as to the net nutrient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |