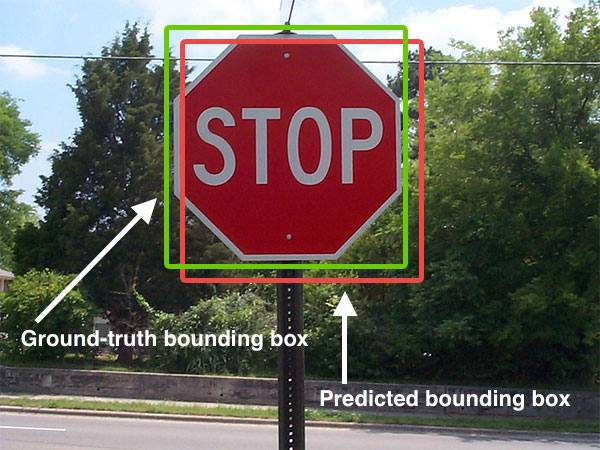
|
Affine Shape Adaptation
Affine shape adaptation is a methodology for iteratively adapting the shape of the smoothing kernels in an affine group of smoothing kernels to the local image structure in neighbourhood region of a specific image point. Equivalently, affine shape adaptation can be accomplished by iteratively warping a local image patch with affine transformations while applying a rotationally symmetric filter to the warped image patches. Provided that this iterative process converges, the resulting fixed point will be ''affine invariant''. In the area of computer vision, this idea has been used for defining affine invariant interest point operators as well as affine invariant texture analysis methods. Affine-adapted interest point operators The interest points obtained from the scale-adapted Laplacian blob detector or the multi-scale Harris corner detector with automatic scale selection are invariant to translations, rotations and uniform rescalings in the spatial domain. The images that cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Affine Group
In mathematics, the affine group or general affine group of any affine space is the group of all invertible affine transformations from the space into itself. In the case of a Euclidean space (where the associated field of scalars is the real numbers), the affine group consists of those functions from the space to itself such that the image of every line is a line. Over any field, the affine group may be viewed as a matrix group in a natural way. If the associated field of scalars is the real or complex field, then the affine group is a Lie group. Relation to general linear group Construction from general linear group Concretely, given a vector space , it has an underlying affine space obtained by "forgetting" the origin, with acting by translations, and the affine group of can be described concretely as the semidirect product of by , the general linear group of : :\operatorname(V) = V \rtimes \operatorname(V) The action of on is the natural one (linear transformations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computer Vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the form of decisions. "Understanding" in this context signifies the transformation of visual images (the input to the retina) into descriptions of the world that make sense to thought processes and can elicit appropriate action. This image understanding can be seen as the disentangling of symbolic information from image data using models constructed with the aid of geometry, physics, statistics, and learning theory. The scientific discipline of computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. Image data can take many forms, such as video sequences, views from multiple cameras, multi-dimensional data from a 3D scanning, 3D scanner, 3D point clouds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blob Detection
In computer vision and image processing, blob detection methods are aimed at detecting regions in a digital image that differ in properties, such as brightness or color, compared to surrounding regions. Informally, a ''blob'' is a region of an image in which some properties are constant or approximately constant; all the points in a blob can be considered in some sense to be similar to each other. The most common method for blob detection is by using convolution. Given some property of interest expressed as a function of position on the image, there are two main classes of blob detectors: (i) '' differential methods'', which are based on derivatives of the function with respect to position, and (ii) ''methods based on local extrema'', which are based on finding the local maxima and minima of the function. With the more recent terminology used in the field, these detectors can also be referred to as ''interest point operators'', or alternatively interest region operato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corner Detection
Corner detection is an approach used within computer vision systems to extract certain kinds of Feature detection (computer vision), features and infer the contents of an image. Corner detection is frequently used in motion detection, image registration, video tracking, photographic mosaic, image mosaicing, panorama stitching, 3D reconstruction and object recognition. Corner detection overlaps with the topic of interest point detection. Formalization A corner can be defined as the intersection of two edges. A corner can also be defined as a point for which there are two dominant and different edge directions in a local neighbourhood of the point. An interest point is a point in an image which has a well-defined position and can be robustly detected. This means that an interest point can be a corner but it can also be, for example, an isolated point of local intensity maximum or minimum, line endings, or a point on a curve where the curvature is locally maximal. In practice, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scale Space
Scale-space theory is a framework for multi-scale signal representation developed by the computer vision, image processing and signal processing communities with complementary motivations from physics and biological vision. It is a formal theory for handling image structures at different scales, by representing an image as a one-parameter family of smoothed images, the scale-space representation, parametrized by the size of the smoothing kernel used for suppressing fine-scale structures. The parameter t in this family is referred to as the ''scale parameter'', with the interpretation that image structures of spatial size smaller than about \sqrt have largely been smoothed away in the scale-space level at scale t. The main type of scale space is the ''linear (Gaussian) scale space'', which has wide applicability as well as the attractive property of being possible to derive from a small set of '' scale-space axioms''. The corresponding scale-space framework encompasses a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the resulting function and to the process of computing it. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). Graphically, it expresses how the 'shape' of one function is modified by the other. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution f*g differs from cross-correlation f \star g only in that either f(x) or g(x) is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Blob Detection
In computer vision and image processing, blob detection methods are aimed at detecting regions in a digital image that differ in properties, such as brightness or color, compared to surrounding regions. Informally, a ''blob'' is a region of an image in which some properties are constant or approximately constant; all the points in a blob can be considered in some sense to be similar to each other. The most common method for blob detection is by using convolution. Given some property of interest expressed as a function of position on the image, there are two main classes of blob detectors: (i) '' differential methods'', which are based on derivatives of the function with respect to position, and (ii) ''methods based on local extrema'', which are based on finding the local maxima and minima of the function. With the more recent terminology used in the field, these detectors can also be referred to as ''interest point operators'', or alternatively interest region operato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corner Detection
Corner detection is an approach used within computer vision systems to extract certain kinds of Feature detection (computer vision), features and infer the contents of an image. Corner detection is frequently used in motion detection, image registration, video tracking, photographic mosaic, image mosaicing, panorama stitching, 3D reconstruction and object recognition. Corner detection overlaps with the topic of interest point detection. Formalization A corner can be defined as the intersection of two edges. A corner can also be defined as a point for which there are two dominant and different edge directions in a local neighbourhood of the point. An interest point is a point in an image which has a well-defined position and can be robustly detected. This means that an interest point can be a corner but it can also be, for example, an isolated point of local intensity maximum or minimum, line endings, or a point on a curve where the curvature is locally maximal. In practice, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
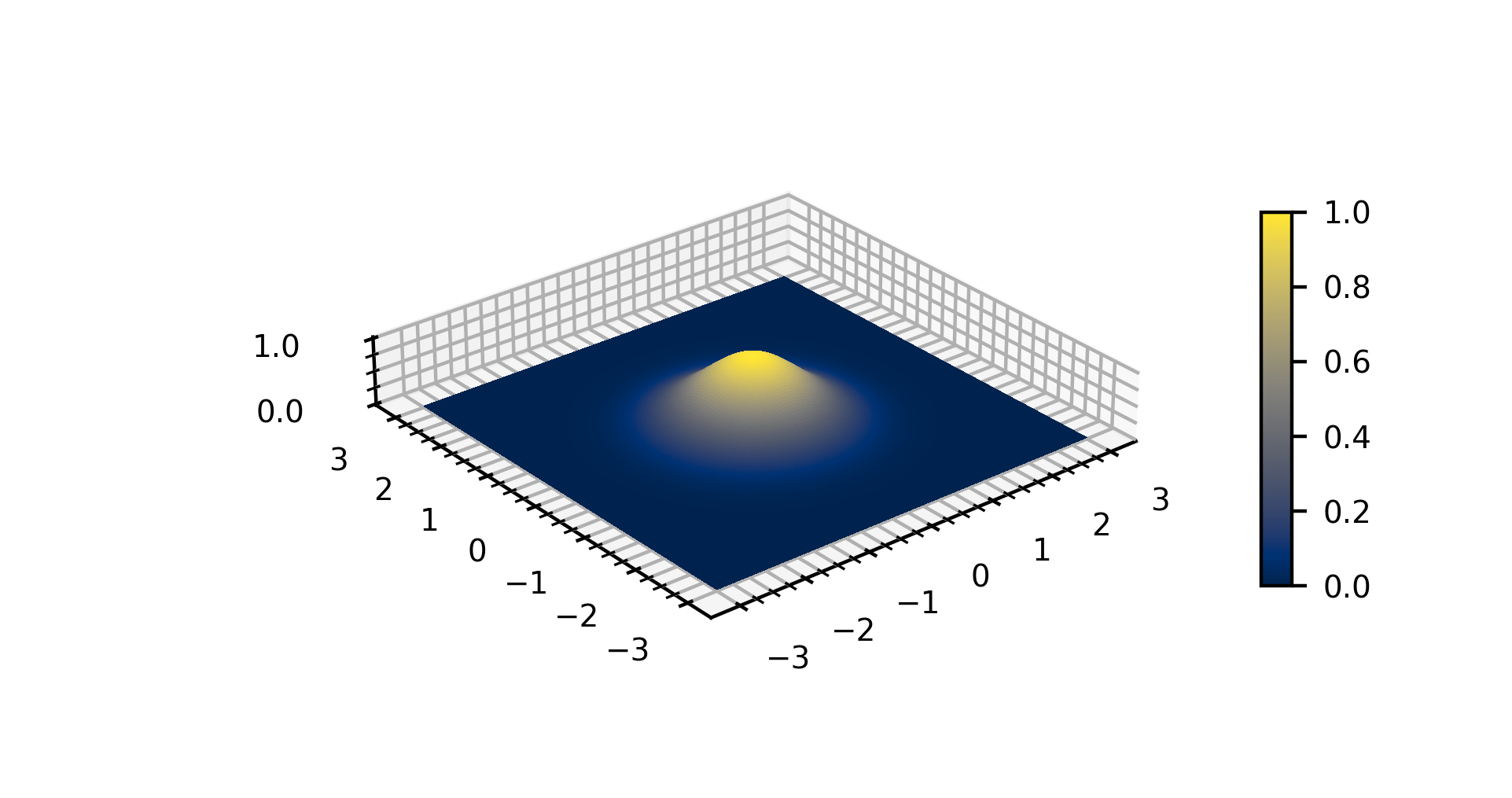
Gaussian Function
In mathematics, a Gaussian function, often simply referred to as a Gaussian, is a function (mathematics), function of the base form f(x) = \exp (-x^2) and with parametric extension f(x) = a \exp\left( -\frac \right) for arbitrary real number, real constants , and non-zero . It is named after the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss. The graph of a function, graph of a Gaussian is a characteristic symmetric "Normal distribution, bell curve" shape. The parameter is the height of the curve's peak, is the position of the center of the peak, and (the standard deviation, sometimes called the Gaussian Root mean square, RMS width) controls the width of the "bell". Gaussian functions are often used to represent the probability density function of a normal distribution, normally distributed random variable with expected value and variance . In this case, the Gaussian is of the form g(x) = \frac \exp\left( -\frac \frac \right). Gaussian functions are widely used in statistics to describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Harris-Affine
In the fields of computer vision and image analysis, the Harris affine region detector belongs to the category of feature detection. Feature detection is a preprocessing step of several algorithms that rely on identifying characteristic points or interest points so to make correspondences between images, recognize textures, categorize objects or build panoramas. Overview The Harris affine detector can identify similar regions between images that are related through affine transformations and have different illuminations. These ''affine-invariant'' detectors should be capable of identifying similar regions in images taken from different viewpoints that are related by a simple geometric transformation: scaling, rotation and shearing. These detected regions have been called both ''invariant'' and ''covariant''. On one hand, the regions are detected ''invariant'' of the image transformation but the regions ''covariantly'' change with image transformation. Do not dwell too much on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hessian Affine Region Detector
The Hessian affine region detector is a feature detector used in the fields of computer vision and image analysis. Like other feature detectors, the Hessian affine detector is typically used as a preprocessing step to algorithms that rely on identifiable, characteristic interest points. The Hessian affine detector is part of the subclass of feature detectors known as ''affine-invariant'' detectors: Harris affine region detector, Hessian affine regions, maximally stable extremal regions, Kadir–Brady saliency detector, edge-based regions (EBR) and intensity-extrema-based (IBR) regions. Algorithm description The Hessian affine detector algorithm is almost identical to the Harris affine region detector. In fact, both algorithms were derived bKrystian MikolajczykanCordelia Schmidin 2002, based on earlier work in, see also for a more general overview. How does the Hessian affine differ? The Harris affine detector relies on interest points detected at multiple scales using the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Scale Space
Scale-space theory is a framework for multi-scale signal representation developed by the computer vision, image processing and signal processing communities with complementary motivations from physics and biological vision. It is a formal theory for handling image structures at different scales, by representing an image as a one-parameter family of smoothed images, the scale-space representation, parametrized by the size of the smoothing kernel used for suppressing fine-scale structures. The parameter t in this family is referred to as the ''scale parameter'', with the interpretation that image structures of spatial size smaller than about \sqrt have largely been smoothed away in the scale-space level at scale t. The main type of scale space is the ''linear (Gaussian) scale space'', which has wide applicability as well as the attractive property of being possible to derive from a small set of '' scale-space axioms''. The corresponding scale-space framework encompasses a th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |