|
Adult Development
Adult development encompasses the changes that occur in biological and psychological domains of human life from the end of adolescence until the end of one's life. Changes occur at the cellular level and are partially explained by biological theories of adult development and aging. Biological changes influence psychological and interpersonal/social developmental changes, which are often described by stage theories of human development. Stage theories typically focus on "age-appropriate" developmental tasks to be achieved at each stage. Erik Erikson and Carl Jung proposed stage theories of human development that encompass the entire life span, and emphasized the potential for positive change very late in life. The concept of adulthood has legal and socio-cultural definitions. The legal definition of an adult is a person who is fully grown or developed. This is referred to as the age of majority, which is age 18 in most cultures, although there is a variation from 15 to 21. The ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolescence
Adolescence () is a transitional stage of human Developmental biology, physical and psychological Human development (biology), development that generally occurs during the period from puberty to adulthood (typically corresponding to the age of majority). Adolescence is usually associated with the Teenager (word), teenage years, but its physical, psychological or cultural expressions may begin earlier or end later. Puberty typically begins during preadolescence, particularly in females. Physical growth (particularly in males) and cognitive development can extend past the teens. Age provides only a rough marker of adolescence, and scholars have not agreed upon a precise definition. Some definitions start as early as 10 and end as late as 30. The World Health Organization definition officially designates adolescence as the phase of life from ages 10 to 19. Biological development Puberty in general Puberty is a period of several years in which rapid physical growth and psycholog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In certain types of arthritis, other organs such as the skin are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are several types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (most commonly seen in weightbearing joints) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs as an individual ages and often affects the hips, knees, shoulders, and fingers. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types of arthritis include gout, lupus, and septic arthritis. These are inflammatory based types of rheumatic disease. Early treatment for arthritis commonly includes resting the affected joint and conservative measures such as heating or icing. Weight Weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
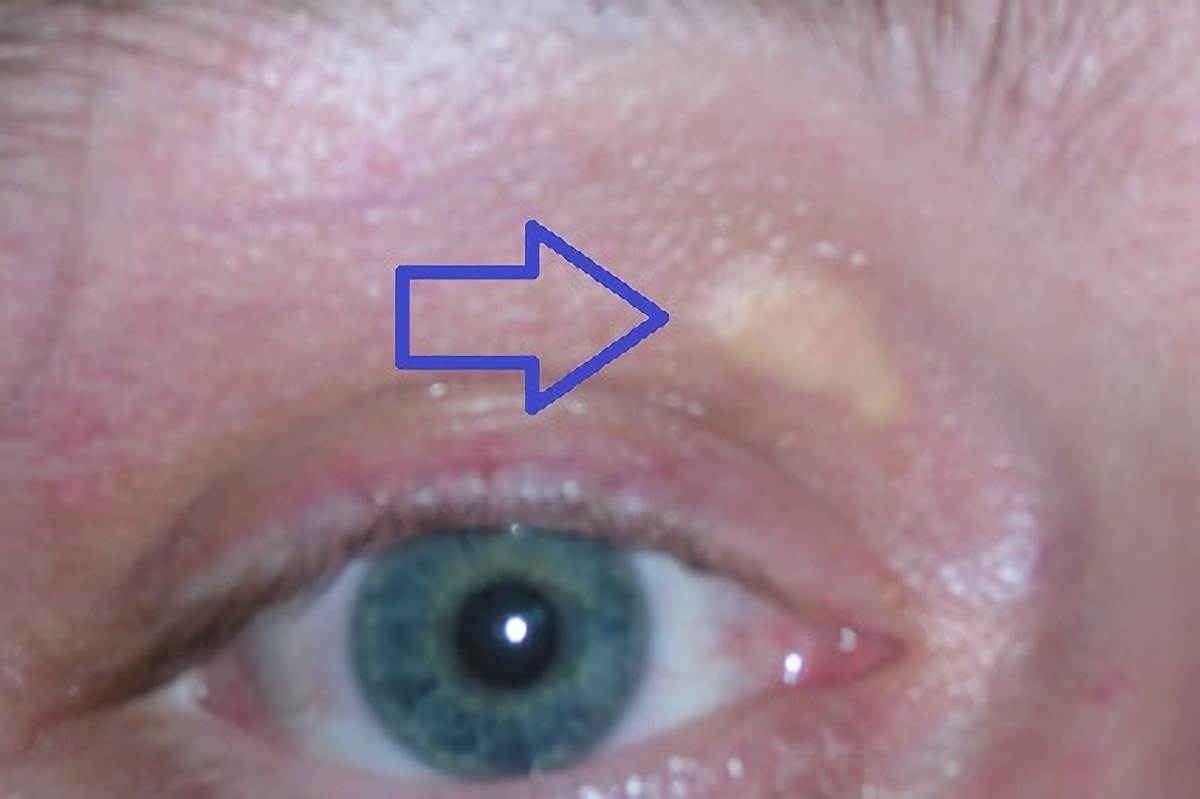
High Cholesterol
Hypercholesterolemia, also called high cholesterol, is the presence of high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is a form of hyperlipidemia (high levels of lipids in the blood), hyperlipoproteinemia (high levels of lipoproteins in the blood), and dyslipidemia (any abnormalities of lipid and lipoprotein levels in the blood). Elevated levels of non-HDL cholesterol and LDL in the blood may be a consequence of diet, obesity, inherited (genetic) diseases (such as LDL receptor mutations in familial hypercholesterolemia), or the presence of other diseases such as type 2 diabetes and an underactive thyroid. Cholesterol is one of three major classes of lipids produced and used by all animal cells to form membranes. Plant cells manufacture phytosterols (similar to cholesterol) but in small quantities. Cholesterol is the precursor of the steroid hormones and bile acids. Since cholesterol is insoluble in water, it is transported in the blood plasma within protein particles ( lipop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms itself. It is, however, a major risk factor for stroke, coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, peripheral arterial disease, vision loss, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Hypertension is a major cause of premature death worldwide. High blood pressure is classified as essential hypertension, primary (essential) hypertension or secondary hypertension. About 90–95% of cases are primary, defined as high blood pressure due to non-specific lifestyle and Genetics, genetic factors. Lifestyle factors that increase the risk include excess salt in the diet, overweight, excess body weight, smoking, physical inactivity and Alcohol (drug), alcohol use. The remaining 5–10% of cases are categorized as secondary hypertension, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximately 13% of CVD deaths, while tobacco accounts for 9%, di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In certain types of arthritis, other organs such as the skin are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are several types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (most commonly seen in weightbearing joints) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs as an individual ages and often affects the hips, knees, shoulders, and fingers. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types of arthritis include gout, lupus, and septic arthritis. These are inflammatory based types of rheumatic disease. Early treatment for arthritis commonly includes resting the affected joint and conservative measures such as heating or icing. Weight Weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the exact timing can vary. Menopause is usually a natural change related to a decrease in circulating blood estrogen levels. It can occur earlier in those who smoke tobacco. Other causes include surgery that removes both ovaries, some types of chemotherapy, or anything that leads to a decrease in hormone levels. At the physiological level, menopause happens because of a decrease in the ovaries' production of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. While typically not needed, measuring hormone levels in the blood or urine can confirm a diagnosis. Menopause is the opposite of menarche, the time when periods start. In the years before menopause, a woman's periods typically become irregular, which means that periods may be longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from ) is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms and in some eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms such as yeast. Biochemistry, Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (Morphology (biology), morphology) and death. These changes include Bleb (cell biology), blebbing, Plasmolysis, cell shrinkage, Karyorrhexis, nuclear fragmentation, Pyknosis, chromatin condensation, Apoptotic DNA fragmentation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses 50 to 70 1,000,000,000, billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For the average human child between 8 and 14 years old, each day the approximate loss is 20 to 30 billion cells. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopenia
Sarcopenia ( ICD-10-CM code M62.84) is a type of muscle loss that occurs with aging and/or immobility. It is characterized by the degenerative loss of skeletal muscle mass, quality, and strength. The rate of muscle loss is dependent on exercise level, co-morbidities, nutrition and other factors. The muscle loss is related to changes in muscle synthesis signalling pathways. It is distinct from cachexia, in which muscle is degraded through cytokine-mediated degradation, although the two conditions may co-exist. Sarcopenia is considered a component of frailty syndrome. Sarcopenia can lead to reduced quality of life, falls, fracture, and disability. Sarcopenia is a factor in changing body composition. When associated with aging populations, certain muscle regions are expected to be affected first, specifically the anterior thigh and abdominal muscles. In population studies, body mass index (BMI) is seen to decrease in aging populations while bioelectrical impedance analysis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different things which can interfere with a normal sense of smell, including damage to the nose or smell receptors, anosmia, upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of Eleanor Gamble, published in 1898, which compared olfactory to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macular Degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred vision, blurred or vision loss, no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Some people experience a gradual worsening of vision that may affect one or both eyes. While it does not result in complete blindness, loss of central vision can make it hard to recognize faces, drive, read, or perform other activities of daily life. Visual release hallucinations, Visual hallucinations may also occur. Macular degeneration typically occurs in older people, and is caused by damage to the macula of retina, macula of the retina. Genetic factors and smoking may play a role. The condition is diagnosed through a complete eye exam. Severity is divided into early, intermediate, and late types. The late type is additionally divided into "dry" and "wet" forms, with the dry form making up 90% of cases. The difference between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |