|
Zambezian Cryptosepalum Dry Forests
The Zambezian dry evergreen forest, also known as the Zambezian ''Cryptosepalum'' dry forest, is a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion of Southern Africa. It consists of several areas of thick forest in western Zambia and adjacent Angola. It is one of the largest areas of tropical evergreen forest outside the equatorial zone. Location The forest are found on rolling hills of sandy soil drained by the Kabompo River of northern Barotseland in Western Zambia, with one area across the border in Angola. The Western Zambezian grasslands separate the forest enclaves from one another. The Barotse Floodplain, part of the Zambezian flooded grasslands ecoregion, lies to the southwest. The Central Zambezian miombo woodlands and the Angolan miombo woodlands lie on the better soils to the east and west, respectively. The ecoregion is at 1100 to 1200 meters elevation. The climate is tropical savanna, with average annual temperature around 21°C. Flora The characteristic trees are tall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afrotropical Realm
The Afrotropical realm is one of Earth's eight biogeographic realms. It includes Africa south of the Sahara Desert, the majority of the Arabian Peninsula, the island of Madagascar, southern Iran and extreme southwestern Pakistan, and the islands of the western Indian Ocean. It was formerly known as the Ethiopian Zone or Ethiopian Region. Major ecological regions Most of the Afrotropic, with the exception of Africa's southern tip, has a tropical climate. A broad belt of deserts, including the Atlantic and Sahara deserts of northern Africa and the Arabian Desert of the Arabian Peninsula, separate the Afrotropic from the Palearctic realm, which includes northern Africa and temperate Eurasia. Sahel and Sudan South of the Sahara, two belts of tropical grassland and savanna run east and west across the continent, from the Atlantic Ocean to the Ethiopian Highlands. Immediately south of the Sahara lies the Sahel belt, a transitional zone of semi-arid short grassland and vachellia s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syzygium Guineense
''Syzygium guineense'' ( bm, Kokisa) is a leafy forest tree of the family Myrtaceae, found in many parts of Africa both wild and domesticated. Both its fruits and leaves are edible; the pulp and the fruit skin are sucked and the seed discarded. It is sometimes called "waterberry", but this may also refer to other species of ''Syzygium''. ''Syzygium guineense'' is a highly variable species, leading to debate concerning its taxonomy, including its subspecies. Frank White lists four subspecies: ''afromontanum'', ''barotsense'', ''guineense'', and ''huillense'', the last of which is a suffrutex. However, many other subspecies and varieties have been proposed. Its height is usually between 10 and 15 meters, but some specimens have been found as tall as 25 meters. The trunk is broad and fluted and the crown rounded and heavy, with a bark that is smooth when young, but becomes rough and black with age. The branches are dropping, the stems are thick and angular. The young leaves are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive Long-tailed Cuckoo
The olive long-tailed cuckoo (''Cercococcyx olivinus'') is a species of cuckoo in the family Cuculidae Cuckoos are birds in the Cuculidae family, the sole taxon in the order Cuculiformes . The cuckoo family includes the common or European cuckoo, roadrunners, koels, malkohas, couas, coucals and anis. The coucals and anis are sometimes separa .... It is found throughout the African tropical rainforest. References olive long-tailed cuckoo Birds of the African tropical rainforest olive long-tailed cuckoo Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Cuculiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crested Guineafowl
The crested guineafowl (''Guttera pucherani'') is a member of the Numididae, the guineafowl bird family. It is found in open forest, woodland and forest-savanna mosaics in sub-Saharan Africa. Description It has a total length around 50 cm (20 in) and weighs .''CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses'' by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), . The plumage is overall blackish with dense white spots. It has a distinctive black crest on the top of its head, the form of which varies from small curly feathers to down depending upon subspecies, and which easily separates it from all other species of guineafowl, except the plumed guineafowl. The names "crested" and "plumed" are often misapplied across the species. Breeding The species is monogamous with probable strong and long-lasting pair bonds. Courtship feeding is common, the author having seen a captive male run 5–10 m to the hen to present some particular morsel. The nest is a well-hidden scrape in long grass o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow-rumped Tinkerbird
The yellow-rumped tinkerbird (''Pogoniulus bilineatus'') is a bird species in the family Lybiidae (African barbets), which is native to the moist tropical and subtropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa. Relationships It used to be placed in the family Bucconidae (puffbirds), which has been split up; alternatively, it may be included in a vastly expanded Ramphastidae (toucans). Subspecies ''Pogoniulus bilineatus'' includes the following subspecies:Gill F, D Donsker & P Rasmussen (Eds). 2020. IOC World Bird List (v10.2). doi : 10.14344/IOC.ML.10.2. * ''P. b. leucolaimus'' - (Verreaux, J & Verreaux, E, 1851) * ''P. b. poensis'' - (Alexander, 1908) * ''P. b. mfumbiri'' - (Ogilvie-Grant, 1907) * ''P. b. jacksoni'' - (Sharp, 1897) * ''P. b. fischeri'' - (Reichenow, 1880) * ''P. b. bilineatus'' - (Sundevall, 1850) Range It is found in Angola, Benin, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Republic of the Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ivory Coast, Equatorial Guinea, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-chested Tinkerbird
The white-chested tinkerbird (''Pogoniulus makawai'') is a species of bird in the Lybiidae family (African barbets). It is endemic to the Zambezian Cryptosepalum dry forests of Zambia. It is only known from the single type specimen, collected in 1964 by Jali Makawa, the field assistant and collector for Constantine Benson. Genetic evidence suggests that it may not be a separate species, but instead be a population embedded within the yellow-rumped tinkerbird The yellow-rumped tinkerbird (''Pogoniulus bilineatus'') is a bird species in the family Lybiidae (African barbets), which is native to the moist tropical and subtropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa. Relationships It used to be placed in the ... if it is not an aberrant individual. References External links White-chested Tinkerbird (Pogoniulus makawai) BirdLife species factsheet white-chested tinkerbird Endemic birds of Zambia white-chested tinkerbird Taxonomy articles created by Polbot {{Piciformes-st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosevear's Striped Grass Mouse
Rosevear's lemniscomys or Rosevear's striped grass mouse (''Lemniscomys roseveari'') is a species of rodent in the family Muridae. It is found in Zambia and possibly Angola, where its natural habitat is cryptosephalum dry forest. The species is threatened by habitat loss Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby .... References Rodents of Africa Fauna of Central Africa Fauna of Southern Africa Lemniscomys Taxonomy articles created by Polbot Mammals described in 1980 {{Murinae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
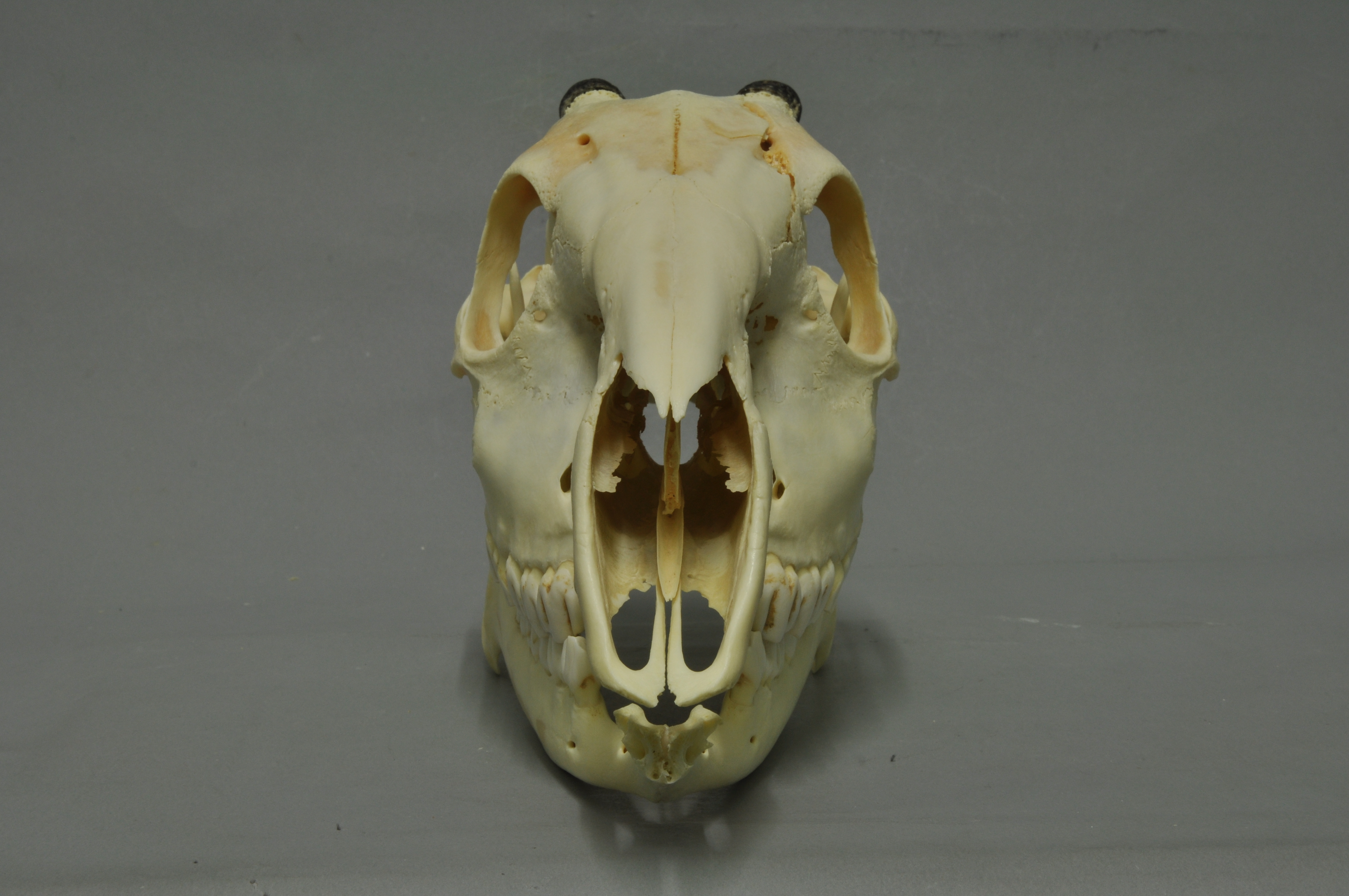
Bushpigs
:''"Bush pig" may also refer to the red river hog. The bushpig (''Potamochoerus larvatus'') is a member of the pig family that inhabits forests, woodland, riverine vegetation and cultivated areas in East and Southern Africa. Probably introduced populations are also present in Madagascar. There have also been unverified reports of their presence on the Comoro island of Mayotte. Bushpigs are mainly nocturnal. There are several subspecies. The vernacular name 'bushpig' may be used for either '' Potamochoerus'' species. Description Adult bushpigs stand from at the shoulder,Kingdon, J. (1997). ''The Kingdon Guide to African Mammals.'' Academic Press Limited, London. and mature boars can reach a weight of , although is more common. Sows are . They resemble the domestic pig, and can be identified by their pointed, tufted ears and face mask. Bushpigs vary in hair colour and skin colour over their range, southern ''koiropotamus'' and ''nyasae'' populations are dark reddish, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predator
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with herbivory, as seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predators may actively search for or pursue prey or wait for it, often concealed. When prey is detected, the predator assesses whether to attack it. This may involve ambush or pursuit predation, sometimes after stalking the prey. If the attack is successful, the predator kills the prey, removes any inedible parts like the shell or spines, and eats it. Predators are adapted and often highly specialized for hunting, with acute senses such as vision, hearing, or smell. Many predatory animals, both vertebrate an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Duiker
The blue duiker (''Philantomba monticola'') is a small antelope found in central, southern and eastern Africa. It is the smallest duiker. The species was first described by Swedish naturalist Carl Peter Thunberg in 1789. 12 subspecies are identified. The blue duiker reaches at the shoulder and weighs . Sexually dimorphic, the females are slightly larger than the males. The dark tail measures slightly above . It has short, spiky horns, around long and hidden in hair tufts. The subspecies show a great degree of variation in their colouration. The blue duiker bears a significant resemblance to Maxwell's duiker. Activity is diurnal (limited to daytime). Secretive and cautious, the blue duiker confines itself to the forest fringes. Territorial, individuals of opposite sexes form pairs and occupy territories, nearly large and marked by preorbital gland secretions. The blue duiker feeds on fallen fruits, foliage, flowers and pieces of bark, provided mainly by the forest cano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow-backed Duiker
The yellow-backed duiker (''Cephalophus silvicultor'') is a forest dwelling antelope in the order Artiodactyla from the family Bovidae. Yellow-backed duikers are the most widely distributed of all duikers. They are found mainly in Central and Western Africa, ranging from Senegal to Western Uganda with possibly a few in Gambia. Their range also extends southward into Rwanda, Burundi, Zaire, and most of Zambia. Taxonomy and etymology The scientific name of the yellow-backed duiker is ''Cephalophus silvicultor''. It is the type species of ''Cephalophus'', and placed in the subfamily Cephalophinae and family Bovidae. The species was first described by English botanist Adam Afzelius in the journal ''Nova Acta Regiæ Societatis Scientiarum Upsaliensis'' in 1815. The generic name has possibly originated from the combination of the New Latin word ''cephal'', meaning head, and the Greek word ''lophos'', meaning crest. The specific name ''silvicultor'' is composed by two Latin words: '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ungulates
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized gut bacteria to allow them to digest cellulose. Some modern species, such as pigs, are omnivorous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_with_its_prey.jpg)