|
Zirconium Diboride
Zirconium diboride (ZrB2) is a highly covalent refractory ceramic material with a hexagonal crystal structure. ZrB2 is an ultra-high temperature ceramic (UHTC) with a melting point of 3246 °C. This along with its relatively low density of ~6.09 g/cm3 (measured density may be higher due to hafnium impurities) and good high temperature strength makes it a candidate for high temperature aerospace applications such as hypersonic flight or rocket propulsion systems. It is an unusual ceramic, having relatively high thermal and electrical conductivities, properties it shares with isostructural titanium diboride and hafnium diboride. ZrB2 parts are usually hot pressed (pressure applied to the heated powder) and then machined to shape. Sintering of ZrB2 is hindered by the material's covalent nature and presence of surface oxides which increase grain coarsening before densification during sintering. Pressureless sintering of ZrB2 is possible with sintering additives suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scanning Tunneling Microscope
A scanning tunneling microscope (STM) is a type of scanning probe microscope used for imaging surfaces at the atomic level. Its development in 1981 earned its inventors, Gerd Binnig and Heinrich Rohrer, then at IBM Zürich, the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1986. STM senses the surface by using an extremely sharp conducting tip that can distinguish features smaller than 0.1 nm with a 0.01 nm (10 pm) depth resolution. This means that individual atoms can routinely be imaged and manipulated. Most scanning tunneling microscopes are built for use in ultra-high vacuum at temperatures approaching absolute zero, but variants exist for studies in air, water and other environments, and for temperatures over 1000 °C. STM is based on the concept of quantum tunneling. When the tip is brought very near to the surface to be examined, a bias voltage applied between the two allows electrons to tunnel through the vacuum separating them. The resulting ''tunneling current'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
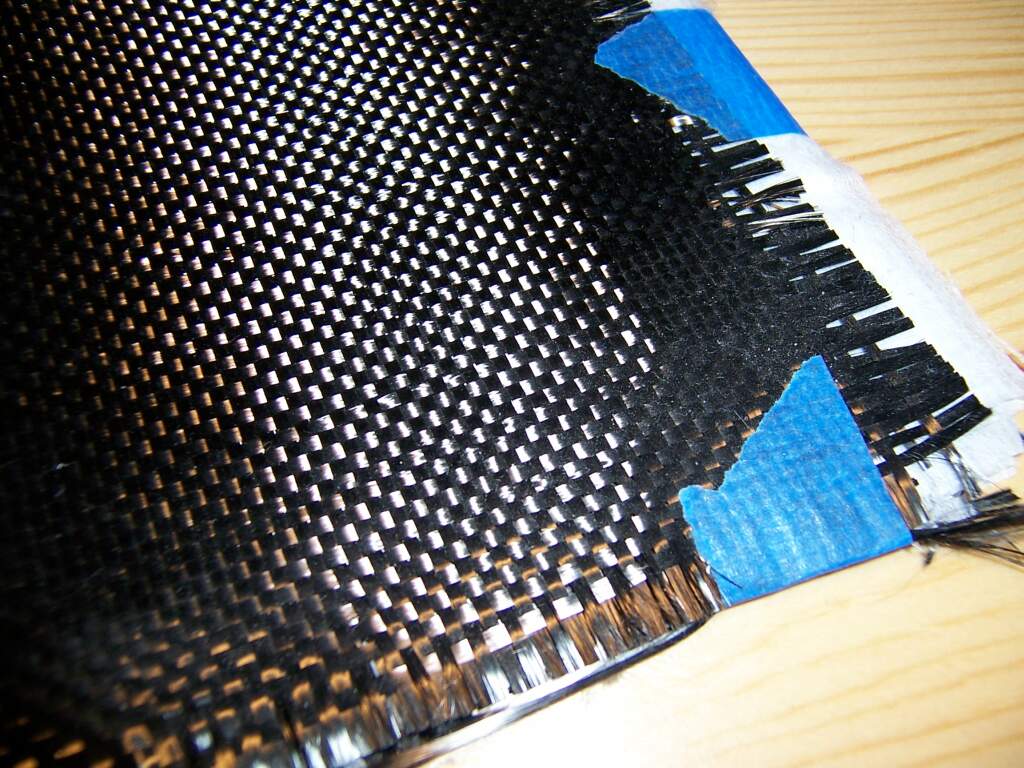
Carbon Fibers
Carbon fibers American and British English spelling differences, or carbon fibres (alternatively CF, graphite fiber or graphite fibre) are fibers about in diameter and composed mostly of carbon atoms. Carbon fibers have several advantages: high stiffness, high tensile strength, high strength to weight ratio, high chemical resistance, high-temperature tolerance, and low thermal expansion. These properties have made carbon fiber very popular in aerospace, civil engineering, military, motorsports, and other competition sports. However, they are relatively expensive compared to similar fibers, such as glass fiber, basalt fibers, or plastic fibers. To produce a carbon fiber, the carbon atoms are bonded together in crystals that are more or less aligned parallel to the fiber's long axis as the crystal alignment gives the fiber a high strength-to-volume ratio (in other words, it is strong for its size). Several thousand carbon fibers are bundled together to form a tow (fibre), tow, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boric Acid
Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula . It may also be called hydrogen orthoborate, trihydroxidoboron or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves in water, and occurs in nature as the mineral sassolite. It is a weak acid that yields various borate anions and salt (chemistry), salts, and can react with Alcohol (chemistry), alcohols to form borate esters. Boric acid is often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, neutron absorber, or precursor to other boron compounds. The term "boric acid" is also used generically for any oxyacid of boron, such as metaboric acid and tetraboric acid . History Orthoboric acid was first prepared by Wilhelm Homberg (1652–1715) from borax, by the action of mineral acids, and was given the name ("sedative salt of Homberg"). However, boric acid and borates have been used since the time of the ancient Greece, anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conference Series
OMICS Publishing Group is a predatory publisher of open access academic journals. It started publishing its first journal in 2008. By 2015, it claimed over 700 journals, although about half of them were defunct. Its subsidiaries and brands include Allied Academies, Conference Series LLC LTD, EuroSciCon LTD, Hilaris Publishing, iMedPub LTD, International Online Medical Council (IOMC), Longdom Publishing SL, Meetings International, Prime Scholars, Pulsus Group, Research & Reviews, SciTechnol, Trade Science Inc, Life Science Events, Walsh Medical Media, and IT Medical Team. OMICS has come under attack by numerous academics and the United States government over the validity of the peer review by OMICS journals, the appropriateness of its fees and marketing, and the apparent advertising of the names of scientists as journal editors or conference speakers without their knowledge or permission. The U.S. National Institutes of Health sent a cease-and-desist letter to OMICS in 2013, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zirconium Dioxide
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zirconium silicate or zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant stabilized cubic structured zirconia, cubic zirconia, is synthesized in various colours for use as a gemstone and a diamond simulant. Production, chemical properties, occurrence Zirconia is produced by calcining zirconium compounds, exploiting its high thermostability.Ralph Nielsen "Zirconium and Zirconium Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Structure Three phases are known: monoclinic below 1170 °C, tetragonal between 1170 °C and 2370 °C, and cubic above 2370 °C. The trend is for higher symmetry at higher temperatures, as is usually the case. A small percentage of the oxides of calcium or yttrium stabilize in the cubic phase. The very r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exothermic
In thermodynamics, an exothermic process () is a thermodynamic process or reaction that releases energy from the system to its surroundings, usually in the form of heat, but also in a form of light (e.g. a spark, flame, or flash), electricity (e.g. a battery), or sound (e.g. explosion heard when burning hydrogen). The term ''exothermic'' was first coined by 19th-century French chemist Marcellin Berthelot. The opposite of an exothermic process is an endothermic process, one that absorbs energy, usually in the form of heat. The concept is frequently applied in the physical sciences to chemical reactions where chemical bond energy is converted to thermal energy (heat). Two types of chemical reactions Exothermic and endothermic describe two types of chemical reactions or systems found in nature, as follows: Exothermic An exothermic reaction occurs when heat is released to the surroundings. According to the IUPAC, an exothermic reaction is "a reaction for which the overall stand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallite
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains. Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel Wikt:longulite , longulites. Structure The orientation of crystallites can be random with no preferred direction, called random Texture (chemistry), texture, or directed, possibly due to growth and processing conditions. While the structure of a single crystal is highly ordered and its crystal lattice, lattice is continuous and unbroken, amorphous solid, amorphous materials, such as glass and many polymers, are non-crystalline and do not display any structures, as their constituents are not arranged in an ordered manner. Polycrystalline structures and paracrystalline phases are in between these two extremes. Polycrystalline materials, or polycrystals, are solids that are composed of many crystallites of varying size and orientation. Most materials are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precursor (chemistry)
In chemistry, a precursor is a compound that participates in a chemical reaction that produces another compound. In biochemistry Biochemistry, or biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. A sub-discipline of both chemistry and biology, biochemistry may be divided into three fields: structural biology, enzymology, a ..., the term "precursor" often refers more specifically to a chemical compound preceding another in a metabolic pathway, such as a protein precursor. Illicit drug precursors In 1988, the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances introduced detailed provisions and requirements relating the control of precursors used to produce drugs of abuse. In Europe the Regulation (EC) No. 273/2004 of the European Parliament and of the Council on drug precursors was adopted on 11 February 2004. ( European law on drug precursors) Illicit explosives precursors On Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void (i.e. "empty") spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0 and 1, or as a percentage between 0% and 100%. Strictly speaking, some tests measure the "accessible void", the total amount of void space accessible from the surface (cf. closed-cell foam). There are many ways to test porosity in a substance or part, such as industrial CT scanning. The term porosity is used in multiple fields including pharmaceutics, ceramics, metallurgy, materials, manufacturing, petrophysics, hydrology, earth sciences, soil mechanics, rock mechanics, and engineering. Void fraction in two-phase flow In gas-liquid two-phase flow, the void fraction is defined as the fraction of the flow-channel volume that is occupied by the gas phase or, alternatively, as the fraction of the cross-sectional area of the channel that is occupied by the gas phase. Void fraction usually varies from location to l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-propagating High-temperature Synthesis
Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis (SHS) is a method for producing both inorganic and organic compounds by exothermic combustion reactions in solids of different nature. Reactions can occur between a solid reactant coupled with either a gas, liquid, or other solid. If the reactants, intermediates, and products are all solids, it is known as a solid flame. If the reaction occurs between a solid reactant and a gas phase reactant, it is called infiltration combustion. Since the process occurs at high temperatures, the method is ideally suited for the production of refractory materials including powders, metallic alloys, or ceramics. The modern SHS process was reported and patented in 1971,"''Self-propagated high-temperature synthesis of refractory inorganic compounds''", A.G. Merzhanov, I.P. Borovinskaya. Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR, Vol. 204, N 2, pp. 366-369, May, 1972 although some SHS-like processes were known previously. Advantages and Disadvantages Self-propagating high- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of The European Ceramic Society
The ''Journal of the European Ceramic Society'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Elsevier on behalf of the European Ceramic Society. It covers research related to conventional categories of ceramic: structural, functional, traditional or composite. It was established in 1985 as the ''International Journal of High Technology Ceramics'', obtaining its current name in 1989. Abstracting and indexing This journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2022 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 5.7. References External links *{{Official website, https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/journal-of-the-european-ceramic-societyJournal page at society website Materials science jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element; it has symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovas and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental boron is found in smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |