|
XBase
xBase is the generic term for all programming languages that derive from the original dBASE (Ashton-Tate) programming language and database formats. These are sometimes informally known as dBASE "clones". While there was a non-commercial predecessor to the Ashton-Tate product (Vulcan written by Wayne Ratliff), most clones are based on Ashton-Tate's 1986 dBASE III+ release — scripts written in the dBASE III+ dialect are most likely to run on all the clones. History of the X Ashton-Tate always maintained that everything relating to dBASE was proprietary, and as a result, filed lawsuits against several of the "clone" software vendors. One effect of this action was to cause the clone vendors to avoid using the term "dBASE": a trademark term held by Ashton-Tate. This gave rise to the creation of the generic term "xBase" meaning "dBASE or dBASE-like." A suggested name that narrowly failed was "*base" (pronounced "star base" and an Homage (arts), homage to Vulcan and ''Star Trek'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
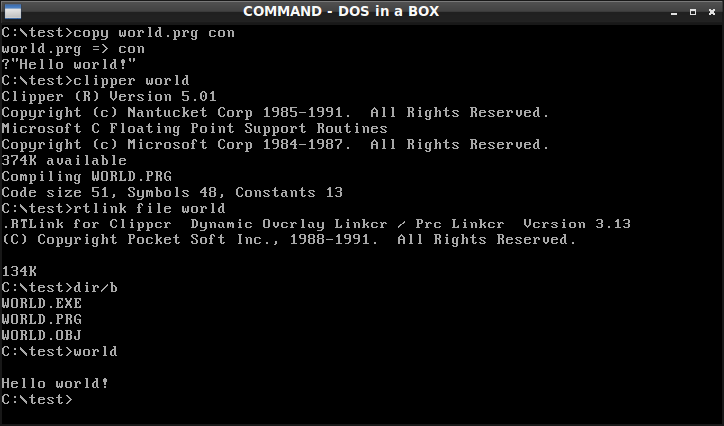
Clipper (programming Language)
Clipper is an xBase compiler that implements a variant of the ''xBase'' computer programming language. It is used to create or extend software programs that originally ran usually on DOS. Although it is a powerful general-purpose programming language, it was used mainly to create database business programs. One major dBase feature not implemented in Clipper is the dBase#Interactivity, dot-prompt (. prompt) interactive command set, which was an important part of the original dBase implementation. Clipper, from Nantucket Corp and later Computer Associates, started out as a native code compiler for dBase III databases, and later evolved. History Clipper was created by Nantucket Corporation, a company that was started in 1984 by Barry ReBell (management) and Brian Russell (technical). Larry Heimendinger was Nantucket's president. In 1992, the company was sold to Computer Associates for 190 million dollars and the product was renamed to CA-Clipper. Clipper was created as a replaceme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual FoxPro
Visual FoxPro is a programming language that was developed by Microsoft. It is a data-centric and procedural programming language with object-oriented programming (OOP) features. It was derived from FoxPro (which was itself descended from FoxBASE) which was developed by Fox Software beginning in 1984. Fox Technologies merged with Microsoft in 1992, after which the software acquired further features and the prefix "Visual". FoxPro 2.6 worked on Mac OS, DOS, Windows, and Unix. Visual FoxPro 3.0, the first "Visual" version, reduced platform support to only Mac and Windows, and later versions 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 were Windows-only. The current version of Visual FoxPro is COM-based and Microsoft has stated that they do not intend to create a Microsoft .NET version. Version 9.0, released in December 2004 and updated in October 2007 with the SP2 patch, was the final version of the product. Support ended in January 2010 and extended support in January 2015. History Visual FoxPro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
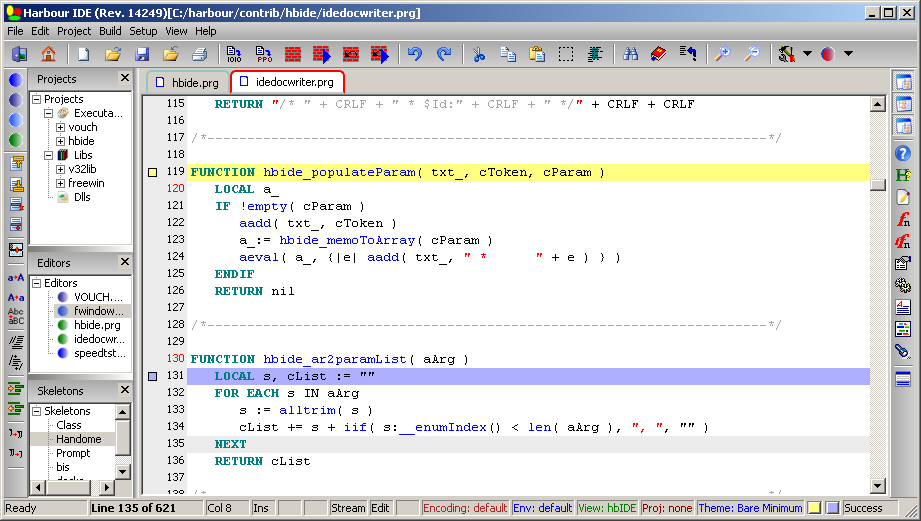
Harbour (software)
Harbour is a computer programming language, used mainly to create database/business programs. It is a modernised cross-platform version of the older Clipper system, which in turn developed from the dBase database market of the 1980s and 1990s. It is free and open-source software which license is GNU General Public License (GPL) compatible. Harbour code uses the same databases and can be compiled under a wide variety of platforms, including Windows, Linux, Unix variants, several Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD) descendants, macOS, Minix 3, Windows CE, Pocket PC, Symbian, iOS, Android, QNX, VxWorks, OS/2 (including eComStation and ArcaOS), BeOS–Haiku (operating system), Haiku, IBM AIX, AIX, and DOS. History The idea of a free software Clipper compiler had been arising for a long time and the subject occurred often in discussion on comp.lang.clipper. Antonio Linares founded the Harbour project and the implementation was started in March 1999. The name "Harbour" was propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DBase
dBase (also stylized dBASE) was one of the first database management systems for microcomputers and the most successful in its day. The dBase system included the core database engine, a query system, a Form (programming), forms engine, and a programming language that tied all of these components together. Originally released as Vulcan for PTDOS in 1978, the CP/M port caught the attention of Ashton-Tate in 1980. They licensed it, re-released it as dBASE II, and later ported it to IBM PC computers running DOS. On the PC platform in particular, dBase became one of the best-selling software titles for a number of years. A major upgrade was released as dBase III and ported to a wider variety of platforms, including UNIX and OpenVMS, VMS. By the mid-1980s, Ashton-Tate was one of the "big three" software publishers in the early business-software market, along with Lotus Development and WordPerfect. Starting in the mid-1980s, several companies produced their own variations on the dBase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XBase Programming Language Family
xBase is the generic term for all programming languages that derive from the original dBASE (Ashton-Tate) programming language and database formats. These are sometimes informally known as dBASE "clones". While there was a non-commercial predecessor to the Ashton-Tate product (Vulcan written by Wayne Ratliff), most clones are based on Ashton-Tate's 1986 dBASE III+ release — scripts written in the dBASE III+ dialect are most likely to run on all the clones. History of the X Ashton-Tate always maintained that everything relating to dBASE was proprietary, and as a result, filed lawsuits against several of the "clone" software vendors. One effect of this action was to cause the clone vendors to avoid using the term "dBASE": a trademark term held by Ashton-Tate. This gave rise to the creation of the generic term "xBase" meaning "dBASE or dBASE-like." A suggested name that narrowly failed was "*base" (pronounced "star base" and an homage to Vulcan and ''Star Trek''), and some wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AdvPL
AdvPL (''Advanced Protheus Language'') is a proprietary programming language based on xBase xBase is the generic term for all programming languages that derive from the original dBASE (Ashton-Tate) programming language and database formats. These are sometimes informally known as dBASE "clones". While there was a non-commercial predec .... It was released in 1999 and is used for development of applications in the ERP Protheus made by TOTVS. References XBase programming language family Table-oriented programming {{prog-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FoxPro
FoxPro is a text-based (computing), text-based Procedural programming, procedurally oriented programming language and database management system (DBMS), and it is also an object-oriented programming language, originally published by Fox Software and later by Microsoft, for MS-DOS, Windows, Macintosh, and UNIX. The final published release of FoxPro was 2.6. Development continued under the Visual FoxPro label, which in turn was discontinued in 2007. Description FoxPro was derived from FoxBase (Fox Software, Perrysburg, Ohio), which was in turn derived from dBase III (Ashton-Tate) and dBase II. FoxPro is both a DBMS and a relational database management system (RDBMS), since it extensively supports multiple relationships between multiple .dbf files (tables). However, it lacks support for Transaction processing, transactional processing. FoxPro was sold and supported by Microsoft after they acquired Fox Software in its entirety in 1992. At that time there was an active worldwid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programming Language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually defined by a formal language. Languages usually provide features such as a type system, Variable (computer science), variables, and mechanisms for Exception handling (programming), error handling. An Programming language implementation, implementation of a programming language is required in order to Execution (computing), execute programs, namely an Interpreter (computing), interpreter or a compiler. An interpreter directly executes the source code, while a compiler produces an executable program. Computer architecture has strongly influenced the design of programming languages, with the most common type (imperative languages—which implement operations in a specified order) developed to perform well on the popular von Neumann architecture. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Query Languages
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve information. A well known example is the Structured Query Language (SQL). Types Broadly, query languages can be classified according to whether they are ''database'' query languages or ''information retrieval'' query languages. The difference is that a database query language attempts to give factual answers to factual questions, while an information retrieval query language attempts to find documents containing information that is relevant to an area of inquiry. Other types of query languages include: * Full-text. The simplest query language is treating all terms as bag of words that are to be matched with the postings in the inverted index and where subsequently ranking models are applied to retrieve the most relevant documents. Only tokens ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
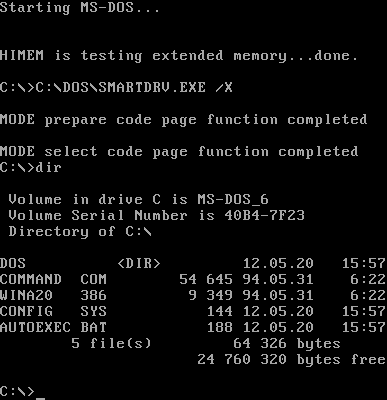
DOS Software
DOS (, ) is a family of disk-based operating systems for IBM PC compatible computers. The DOS family primarily consists of IBM PC DOS and a rebranded version, Microsoft's MS-DOS, both of which were introduced in 1981. Later compatible systems from other manufacturers include DR-DOS (1988), ROM-DOS (1989), PTS-DOS (1993), and FreeDOS (1994). MS-DOS dominated the IBM PC compatible market between 1981 and 1995. Although the name has come to be identified specifically with MS-DOS and compatible operating systems, ''DOS'' is a platform-independent acronym for ''disk operating system'', whose use predates the IBM PC. Dozens of other operating systems also use the acronym, beginning with the mainframe DOS/360 from 1966. Others include Apple DOS, Apple ProDOS, Atari DOS, Commodore DOS, TRSDOS, and AmigaDOS. History Origins IBM PC DOS (and the separately sold MS-DOS) and its predecessor, 86-DOS, ran on Intel 8086 16-bit processors. It was developed to be sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VP-Info
VP-Info is a database language and compiler for the personal computer. VP-Info was a competitor to the Clipper and dBase applications in the late 1980s and 1990s. VP-Info was originally intended to run on MS-DOS, DR-DOS and the PC-MOS/386 operating system, but now is run on the vDOS,vDOS: https://www.vdos.info/ or DOSbox-X, emulators. The last release of VP-Info, a multi-tasking, multi-user version released in 1992 with a built-in compiler, and was named SharkBase, or simply "Shark". Origin In the early 1980s, David Clark met George Gratzer, a mathematics professor at the University of Manitoba, at ComputerLand in Winnipeg where Gratzer was looking for someone who could program in dBase. Clark had been using dBase II, but was frustrated by its limitations for reporting on more than 2 tables at a time. While working for Standard Knitting (a client of Gratzer's and Clark's), David wrote a report generator called ''dComp'' that would allow up to six related data files to be in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |