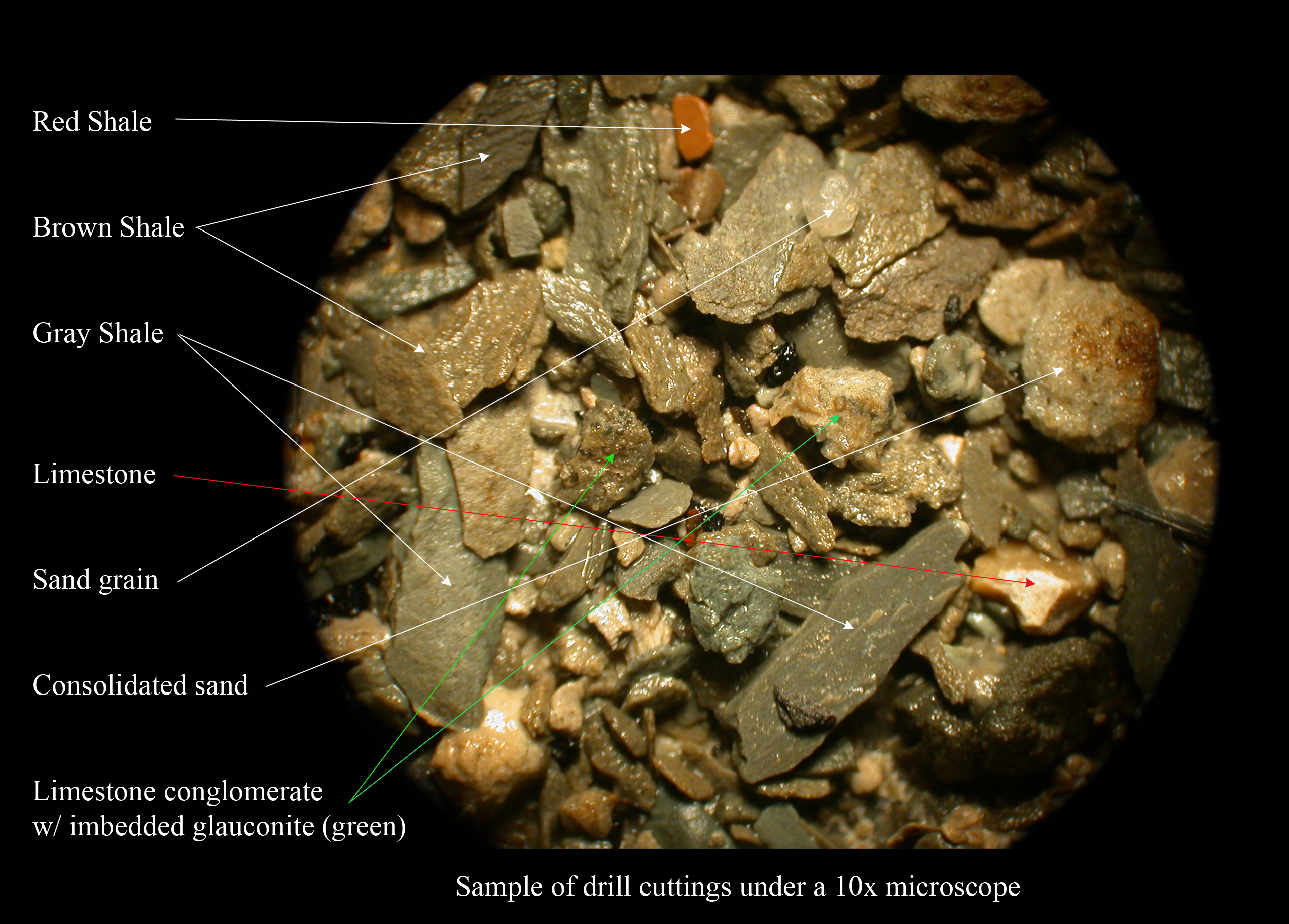
|
Winnipegosis Komatiite Belt
The Winnipegosis komatiite belt is a long and wide greenstone belt located in the Lake Winnipegosis area of central Manitoba, Canada. It has no surface exposure and was identified based on geophysical signatures and drilling during mineral exploration by Cominco during the 1990s.McGregor, C. R. 2011. Open File OF2011-1: GIS compilation of relogged sub-Phanerozoic Precambrian exploration drillcore from the Thompson Nickel Belt, eastern Flin Flon Belt and Winnipegosis Komatiite Belt (parts of NTS 63B, C, F, G, J, K). Manitoba Geological Survey. The belt has an age of 1870 ± 7 million years and is predominantly composed of basaltic and komatiitic volcanic rocks with minor intrusive and sedimentary rocks.Hulbert, L., Stern, R., Kyser, T. K., Pearson, J., Lesher, M., & Grinenko, L. 1994. The Winnipegosis Komatiite Belt, central Manitoba. Page 21 of: Manitoba Mining and Minerals Convention 1994, Program and Abstracts. Manitoba Energy and Mines.Waterton, P., Pearson, D. G., Kjars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of The Circum-Superior Belt Highlighting Location Of The Winnipegosis Komatiite Belt
A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes. Many maps are static, fixed to paper or some other durable medium, while others are dynamic or interactive. Although most commonly used to depict geography, maps may represent any space, real or fictional, without regard to context or scale, such as in brain mapping, DNA mapping, or computer network topology mapping. The space being mapped may be two dimensional, such as the surface of the earth, three dimensional, such as the interior of the earth, or even more abstract spaces of any dimension, such as arise in modeling phenomena having many independent variables. Although the earliest maps known are of the heavens, geographic maps of territory have a very long tradition and exist from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
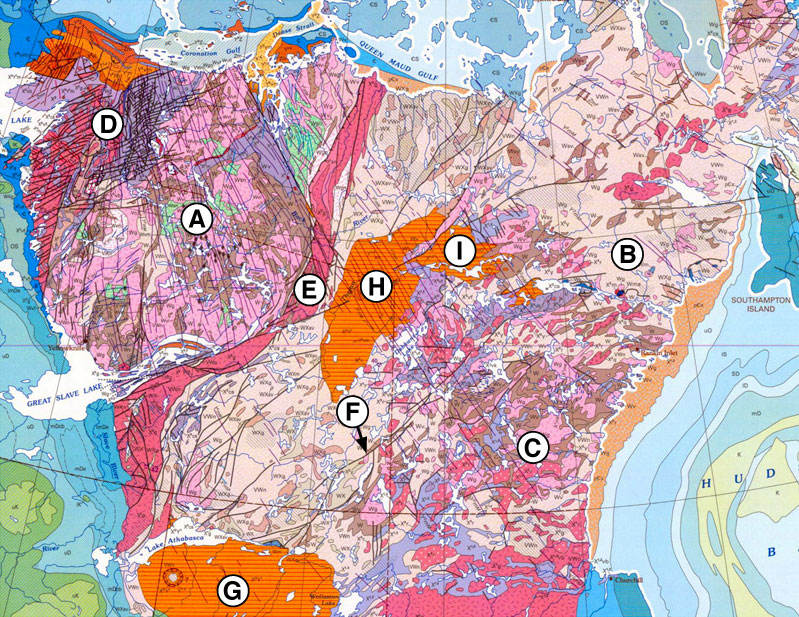
Thompson Nickel Belt
The Thompson Belt, also referred to as the Thompson Nickel Belt, is an Archean and early Proterozoic geologic feature in Manitoba, Canada. It contains gneiss related to deformation of the Trans-Hudson orogeny The Trans-Hudson orogeny or Trans-Hudsonian orogeny was the major mountain building event (orogeny) that formed the Precambrian Canadian Shield and the North American Craton (also called Laurentia), forging the initial North American contine .... References Geology of Manitoba Archean geology Proterozoic geology Precambrian North America Proterozoic North America {{Canada-geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include basalt, diabase and gabbro. Mafic rocks often also contain calcium-rich varieties of plagioclase feldspar. Mafic materials can also be described as ferromagnesian. History The term ''mafic'' is a portmanteau of "magnesium" and "ferric" and was coined by Charles Whitman Cross, Joseph P. Iddings, Louis Valentine Pirsson, and Henry Stephens Washington in 1912. Cross' group had previously divided the major rock-forming minerals found in igneous rocks into ''salic'' minerals, such as quartz, feldspars, or feldspathoids, and ''femic'' minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene. However, micas and aluminium-rich amphiboles were excluded, while some calcium minerals containing little iron or magnesium, such as wollastonite or apatite, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (rock)
Dolomite (also known as dolomite rock, dolostone or dolomitic rock) is a sedimentary carbonate rock that contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2. It occurs widely, often in association with limestone and evaporites, though it is less abundant than limestone and rare in Cenozoic rock beds (beds less than about 66 million years in age). The first geologist to distinguish dolomite rock from limestone was Belsazar Hacquet in 1778. Most dolomite was formed as a magnesium replacement of limestone or of lime mud before lithification. The geological process of conversion of calcite to dolomite is known as dolomitization and any intermediate product is known as dolomitic limestone. The "dolomite problem" refers to the vast worldwide depositions of dolomite in the past geologic record in contrast to the limited amounts of dolomite formed in modern times. Recent research has revealed sulfate-reducing bacteria living in anoxic conditions precipitate dolomite which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especially quartz and calcite.Blatt, Harvey and Robert J. Tracy (1996) ''Petrology: Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic'', 2nd ed., Freeman, pp. 281–292 Shale is characterized by its tendency to split into thin layers ( laminae) less than one centimeter in thickness. This property is called '' fissility''. Shale is the most common sedimentary rock. The term ''shale'' is sometimes applied more broadly, as essentially a synonym for mudrock, rather than in the more narrow sense of clay-rich fissile mudrock. Texture Shale typically exhibits varying degrees of fissility. Because of the parallel orientation of clay mineral flakes in shale, it breaks into thin layers, often splintery and usually parallel to the otherwise indistinguishable bedding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholeiitic Basalt
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma into a more evolved, silica rich end member. Rock types of the tholeiitic magma series include tholeiitic basalt, ferro-basalt, tholeiitic basaltic andesite, tholeiitic andesite, dacite and rhyolite. The variety of basalt in the series was originally called ''tholeiite'' but the International Union of Geological Sciences recommends that ''tholeiitic basalt'' be used in preference to that term.Le Maitre ''et al.'' 2002 Tholeiitic rock types tend to be more enriched in iron and less enriched in aluminium than calc-alkaline rock types. They are thought to form in a less oxidized environment than calc-alkaline rocks. Tholeiitic basalt is formed at mid-ocean ridges and makes up much of the oceanic crust. Almost all the basalt found on the Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surface to the mantle. These convection cells bring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snow Lake Arc
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes. It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout its life cycle, starting when, under suitable conditions, the ice crystals form in the atmosphere, increase to millimeter size, precipitate and accumulate on surfaces, then metamorphose in place, and ultimately melt, slide or sublimate away. Snowstorms organize and develop by feeding on sources of atmospheric moisture and cold air. Snowflakes nucleate around particles in the atmosphere by attracting supercooled water droplets, which freeze in hexagonal-shaped crystals. Snowflakes take on a variety of shapes, basic among these are platelets, needles, columns and rime. As snow accumulates into a snowpack, it may blow into drifts. Over time, accumulated snow metamorphoses, by sintering, sublimation and freeze-thaw. Where the climate is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sask Craton
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dakota. Saskatchewan and Alberta are the only landlocked provinces of Canada. In 2022, Saskatchewan's population was estimated at 1,205,119. Nearly 10% of Saskatchewan’s total area of is fresh water, mostly rivers, reservoirs and lakes. Residents primarily live in the southern prairie half of the province, while the northern half is mostly forested and sparsely populated. Roughly half live in the province's largest city Saskatoon or the provincial capital Regina. Other notable cities include Prince Albert, Moose Jaw, Yorkton, Swift Current, North Battleford, Melfort, and the border city Lloydminster. English is the primary language of the province, with 82.4% of Saskatchewanians speaking English as their first language. Saskatchewan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearne Craton
The Hearne Craton is a craton in northern Canada which, together with the Rae Craton, forms the Western Churchill Province. Hearne is one of the six Archaean cratons of the Canadian Shield (the other being Slave, Rae, Wyoming, Superior, Nain) that are bound together by Palaeoproterozoic orogenic belts. Before being merged these six cratons formed independent microcontinents. Geological setting The Hearne Craton is separated from the Rae Craton by the -long Snowbird Tectonic Zone (STZ). During the Neoarchaean and Palaeoproterozoic the STZ played a major role when the Western Churchill Province was first assembled and then reworked. The STZ is a record of Neoarchaean plate tectonics similar in scale to modern orogenic belts. When Laurentia formed at 2.0–1.7 Ga Hearne and Rae formed a central strip to which the Slave, Superior, Sask, and Wyoming cratons were accreted. This strip is bounded by a series of orogens: the 1.92–1.69 Ga Trans-Hudson to the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rae Craton
250px, North America cratons and basement rock. The Rae Craton is an Archean craton located in northern Canada north of the Superior Craton. Ungava Peninsula The Ungava Peninsula, situated on the northeast portion of the Canadian Shield, is where the Rae Province connects with the Superior Province. See also * Canadian Shield * North American Craton North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is ... References * Madore, L., and Y. Larbi. (2001) "Regional structural character of the northeastern Ungava Peninsula: Connection between the Rae and Superior provinces." St. John's 2001 Technical Programme SS2: Tectonic Integration of Circum-Superior Orogens. Online Abstrac Cratons Historical geology Geology of the Northwest Territories Geology of North America {{palaeo-geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |