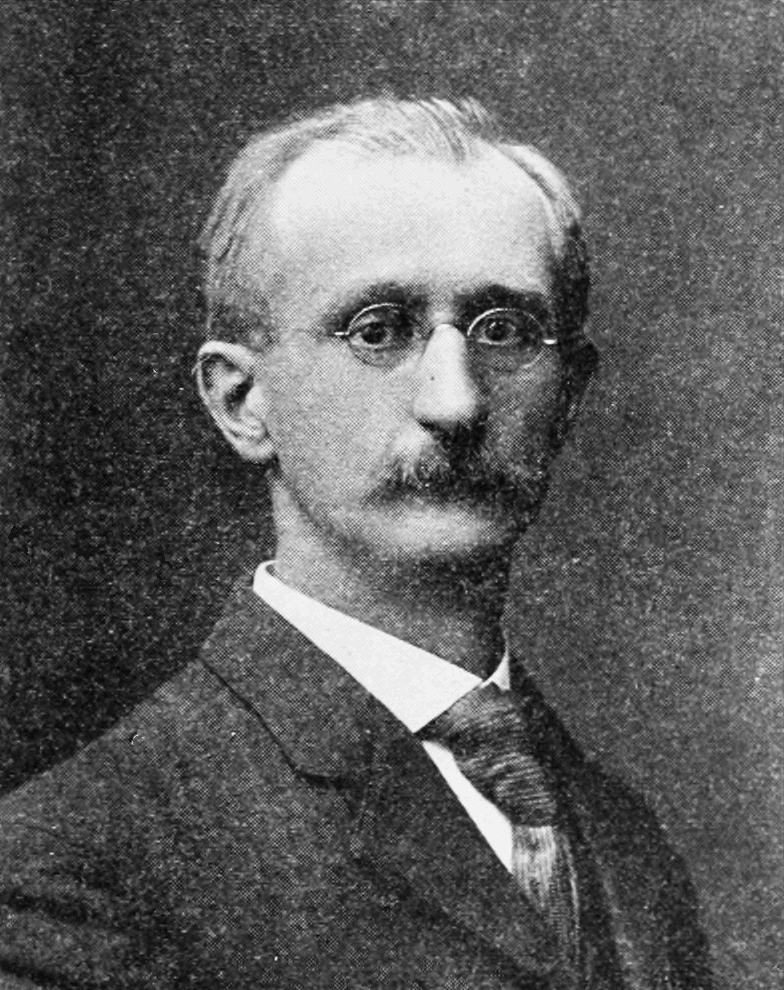|
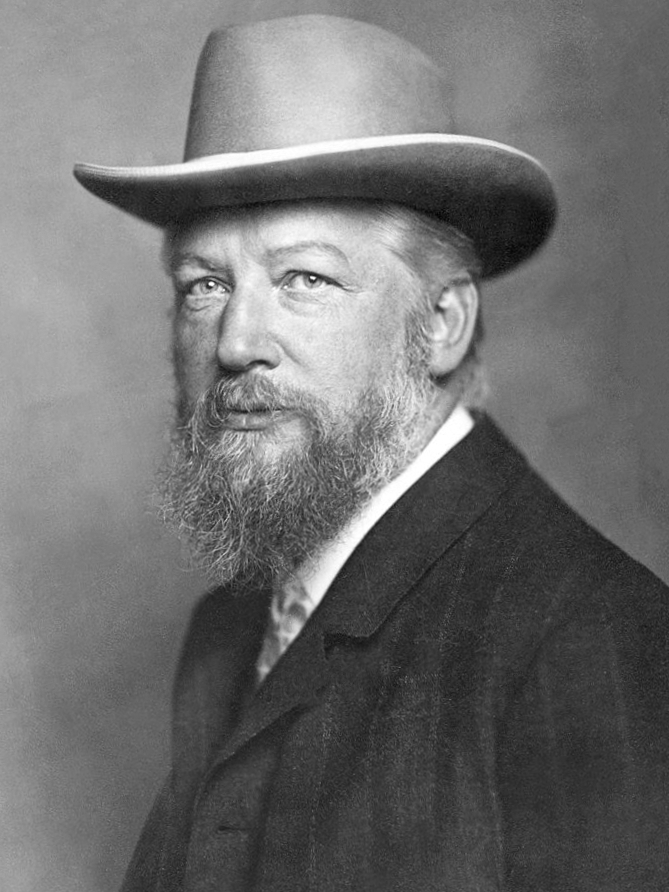
Wilhelm Ostwald
Wilhelm Friedrich Ostwald (; – 4 April 1932) was a Latvian chemist and philosopher. Ostwald is credited with being one of the founders of the field of physical chemistry, with Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff, Walther Nernst and Svante Arrhenius. He received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1909 for his scientific contributions to the fields of catalysis, chemical equilibria and reaction velocities. Following his 1906 retirement from academic life, Ostwald became much involved in philosophy, art, and politics. He made significant contributions to each of these fields. He has been described as a polymath. Early life and education Ostwald was born ethnically Baltic German in Riga, Russian Empire (now Latvia) to master-cooper Gottfried Wilhelm Ostwald and Elisabeth Leuckel. He was the middle child of three, born after Eugen and before Gottfried. Ostwald developed an interest in science as a child and conducted experiments at his home, particularly related to fireworks and photogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostwald Ripening
Ostwald ripening is a phenomenon observed in solid solutions and liquid sols that involves the change of an inhomogeneous structure over time, in that small crystals or sol particles first dissolve and then redeposit onto larger crystals or sol particles. Dissolution of small crystals or sol particles and the redeposition of the dissolved species on the surfaces of larger crystals or sol particles was first described by Wilhelm Ostwald in 1896. For colloidal systems, Ostwald ripening is also found in water-in-oil emulsions, while flocculation is found in oil-in-water emulsions. Mechanism This thermodynamically-driven spontaneous process occurs because larger particles are more energetically favored than smaller particles. This stems from the fact that molecules on the surface of a particle are energetically less stable than the ones in the interior. Consider a cubic crystal of atoms: all the atoms inside are bonded to 6 neighbours and are quite stable, but atoms on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riga
Riga ( ) is the capital, Primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city of Latvia. Home to 591,882 inhabitants (as of 2025), the city accounts for a third of Latvia's total population. The population of Riga Planning Region, Riga metropolitan area, which stretches beyond the city limits, is estimated at 847,162 (as of 2025). The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava (river), Daugava river where it meets the Baltic Sea. Riga's territory covers and lies above sea level on a flat and sandy plain. Riga was founded in 1201, and is a former Hanseatic League member. Riga's historical centre is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, noted for its Art Nouveau/Jugendstil architecture and 19th century wooden architecture. Riga was the European Capital of Culture in 2014, along with Umeå in Sweden. Riga hosted the 2006 Riga summit, 2006 NATO Summit, the Eurovision Song Contest 2003, the 2013 World Women's Curling Championship, and the 2006 IIHF Wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energeticism
Energeticism, also called energism or energetics (), is a superseded theory in science that posits that energy is the ultimate element of physical reality. Energeticism was developed during the end of the 19th century by Wilhelm Ostwald, Georg Helm and Pierre Duhem. It was also promoted by physicist Ernst Mach who opposed atomic theory, though his full commitment to it was sometimes ambiguous. Energetiscism attempted to substitute the hypothesis of atoms and molecules by energy relations. Ludwig Boltzmann and Max Planck constantly rebutted the idea of energeticism in favor of atomic theory. The program of energeticism faded away in the 20th century with the experimental confirmation of the existence of atoms. Origin While teaching chemistry in Riga Polytechnic Institute, Wilhelm Ostwald became convinced that certain reactions could only be explained in terms of energy, without the need of invoking the hypothesis of the existence of atoms. He was inspired by Josiah Willard Gibbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Albrecht Kahlenberg
Louis Albrecht Kahlenberg (20 January 1870 – 18 March 1941) was an American chemist who contributed to electrochemistry, the study of ionic compounds, electrolytic disassociation of salts and studies in pharmaceutical chemistry. He served as a professor at the University of Wisconsin. Kahlenberg was born in Two Rivers, Wisconsin Two Rivers is a city in Manitowoc County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 11,271 at the 2020 census. It claims to be the birthplace of the ice cream sundae (though other cities, such as Ithaca, New York, make the same claim). The c ... where his father Albert and Bertha had immigrated from Germany. He studied at the local Lutheran school, the Two Rivers High School and then trained at the Oshkosh Normal School so as to become a teacher. He then went to the Milwaukee Normal School and then received a BS from the University of Wisconsin in 1892. He fellowship allowed him to continue studies and he received an MS in 1893. He then went to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick G
Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Given name Nobility = Anhalt-Harzgerode = *Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) = Austria = * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederick II, Duke of Austria (1219–1246), last Duke of Austria from the Babenberg dynasty * Frederick the Fair (Frederick I of Austria (Habsburg), 1286–1330), Duke of Austria and King of the Romans = Baden = * Frederick I, Grand Duke of Baden (1826–1907), Grand Duke of Baden * Frederick II, Grand Duke of Baden (1857–1928), Grand Duke of Baden = Bohemia = * Frederick, Duke of Bohemia (died 1189), Duke of Olomouc and Bohemia = Britain = * Frederick, Prince of Wales (1707–1751), eldest son of King George II of Great Britain = Brandenburg/Prussia = * Frederick I, Elector of Brandenburg (1371–1440), also known as Frederick VI, Burgrave of Nuremberg * Frederick II, Elector of Brandenburg (1413–1470), Margrave of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Walden
Paul Walden (; ; ; 26 July 1863 – 22 January 1957) was a Russian, Latvian and German chemist known for his work in stereochemistry and history of chemistry. In particular, he discovered the Walden rule, he invented the stereochemical reaction known as Walden inversion and synthesized the first room-temperature ionic liquid, ethylammonium nitrate. Early life and education Walden was born in Rozulas in the Russian Empire (now Stalbe parish, Pārgauja municipality, Latvia) in a large Latvian peasant family. At the age of four, he lost his father and later his mother. Thanks to financial support from his two older brothers who lived in Riga (one was a merchant and another served as a lieutenant in the military) Walden managed to complete his education – first graduated with honors from the district school in the town of Cēsis (1876), and then from the Riga Technical High School (1882). In December 1882, he enrolled into the Riga Technical University and became seriously ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Bredig
Georg Bredig (October 1, 1868 – April 24, 1944) was a German physical chemist. Bredig was a faculty member at the University of Leipzig (1895-1901) and professor of chemistry at Heidelberg (1901–1910); Technische Hochschule, Zurich (1910); and Technische Hochschule, Karlsruhe (1911–1933). Bredig did fundamental research in catalysis, preparing aqueous colloidal dispersions of metals and comparing the catalytic properties of metal colloids to the action of enzymes (or "ferments"). He made significant contributions in reaction kinetics and electrochemistry. Despite being a respected scientist in his field, Bredig was forced to leave the university by the National Socialists in 1933, ending his teaching and research career. Princeton University offered Bredig a pro forma position, enabling him to emigrate to the United States in 1940. Life Georg Bredig was the father of Max Bredig and his wife Ernestine (Troplowitz) Bredig. He was born on October 1, 1868, in Glogau, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Amos Noyes
Arthur Amos Noyes (September 13, 1866 – June 3, 1936) was an American chemist, inventor and educator, born in Newburyport, Massachusetts, son of Amos and Anna Page Noyes, née Andrews. He received a PhD in 1890 from Leipzig University under the guidance of Wilhelm Ostwald. He served as the acting president of MIT between 1907 and 1909 and as professor of chemistry at the California Institute of Technology from 1919 to 1936. "Although he Noyeslaboratory at MIT was like an institute in its intramural funding (from Carnegie Institute of Washington and Noyes's patent royalties), Noyes recruited many of his disciples as undergraduates and took a deep interest in undergraduate engineering education, both at MIT and later at Caltech. Roscoe Gilkey Dickinson was one of his famous students. Noyes was a major influence both on the educational philosophy of the core curriculum of Caltech as well as in the negotiations leading to the creation of the National Research Council alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig University
Leipzig University (), in Leipzig in Saxony, Germany, is one of the world's oldest universities and the second-oldest university (by consecutive years of existence) in Germany. The university was founded on 2 December 1409 by Frederick I, Elector of Saxony and his brother William II, Margrave of Meissen, and originally comprised the four scholastic faculties. Since its inception, the university has engaged in teaching and research for over 600 years without interruption. Famous alumni include Angela Merkel, Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz, Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, Leopold von Ranke, Friedrich Nietzsche, Robert Schumann, Richard Wagner, Tycho Brahe, Georgius Agricola. The university is associated with ten Nobel laureates, most recently with Svante Pääbo who won the Nobel Prize for Medicine in 2022. History Founding and development until 1900 The university was modelled on the University of Prague, from which the German-speaking faculty members withdrew to Leipzig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riga Polytechnicum
Riga Technical University (RTU) () is the oldest technical university in the Baltic countries established on October 14, 1862. It is located in Riga, Latvia and was previously known as Riga Polytechnical Institute and Riga Polytechnicum. In 1958, the Riga Polytechnic Institute was established as a separate institution, separating the departments of engineering from the Latvian State University. Over the years, the Riga Polytechnic Institute evolved and expanded its academic offerings, becoming one of the leading technical universities in the region. In 1990, it was renamed Riga Technical University (RTU), and today, it has nine faculties and is the largest STEM-oriented university in Latvia. In the 2022 QS EECA university rankings, RTU was ranked 57th among the universities in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. History Riga Polytechnical Institute (1862–1918) Riga Polytechnicum was first established in 1862 and was the first polytechnical institute in Imperial Russia. It offe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Exner Medal
The Wilhelm Exner Medal has been awarded by the Austrian Industry Association, (ÖGV), for excellence in research and science since 1921. The medal is dedicated to Wilhelm Exner (1840–1931), former president of the Association, who initialized the chamber of commerce in Austria, the Vienna Technical Museum and the World Exhibition in Vienna. According to Wilhelm Exner the combination of science and economy formed the groundwork for economical growth and wealth. Wilhelm Exner considered the radical changes in the economic and social framework of the 20th century to be an opportunity and aimed to tackle the issues arising offensively and constructively. He represented the cosmopolitan Austrian liberalism with a commitment to modernization and transformation of the economy, science and society. Throughout his career, he has taken a variety of key initiatives and has been involved by helping economy and business. The Wilhelm Exner Medal is awarded to scientists and researchers tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |