|
Web Literacy
Web literacy comprises the skills and competencies needed for reading, writing and participating on the web. It has been described as "both content and activity" – i.e., web users should not just learn about the web but also about how to make their own website.Davidson, C.N. & Surman, M"Why Web Literacy Should Be Part of Every Education" Fast Company. Retrieved 2 February 2015. History of the concept In the latter part of the 1990s, literacy researchers started to explore the differences between printed text and the network-enabled devices with screens. This research was largely focused on two areas: the credibility of information that can be found on the World Wide WebDetweiler, M. C., Hess, S. M., & Peck, A. C. (1996, October). Acquiring User-Centered Design Skills by Designing and Evaluating World Wide Web Pages. In ''Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting'' (Vol. 40, No. 8, pp. 459-462). SAGE Publications and the difference that hypertext mak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet. Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers. Servers and resources on the World Wide Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup language supports plain text, images, embedded video and audio contents, and scripts (short programs) that implement complex user interaction. The HTML language also supports hyperlinks (embedded URLs) which provide immediate access to other web resources. Web navigation, or web surfing, is the common practice of following such hyperlinks across multiple websites. Web applications are web pages that function as applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertext
Hypertext is text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references ( hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typically activated by a mouse click, keypress set, or screen touch. Apart from text, the term "hypertext" is also sometimes used to describe tables, images, and other presentational content formats with integrated hyperlinks. Hypertext is one of the key underlying concepts of the World Wide Web, where Web pages are often written in the Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). As implemented on the Web, hypertext enables the easy-to-use publication of information over the Internet. Etymology The English prefix "hyper-" comes from the Greek prefix "ὑπερ-" and means "over" or "beyond"; it has a common origin with the prefix "super-" which comes from Latin. It signifies the overcoming of the previous linear constraints of written text. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCONUL
SCONUL (Society of College, National and University Libraries) is the membership organisation for all academic and national libraries in the UK and Ireland. History SCONUL was founded in 1950 as the Standing Conference of National and University Libraries. In 1994 when British polytechnics became universities it merged with COPOL, the Council of Polytechnic Librarians, and in 2001 it extended its membership to libraries of Colleges of Higher Education and changed to its current name. Aims SCONUL states its aims as: ''For the benefit of our libraries and their users we aim:'' * ''to promote the sharing and development of good practice'' * ''to influence policy makers and encourage debate'' * ''to raise the profile of higher education and national libraries'' Activities SCONUL's activities include advocacy for the higher education library community, training and sharing best practice, making arrangements for reciprocal access to libraries, and the collection of statistics. Struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
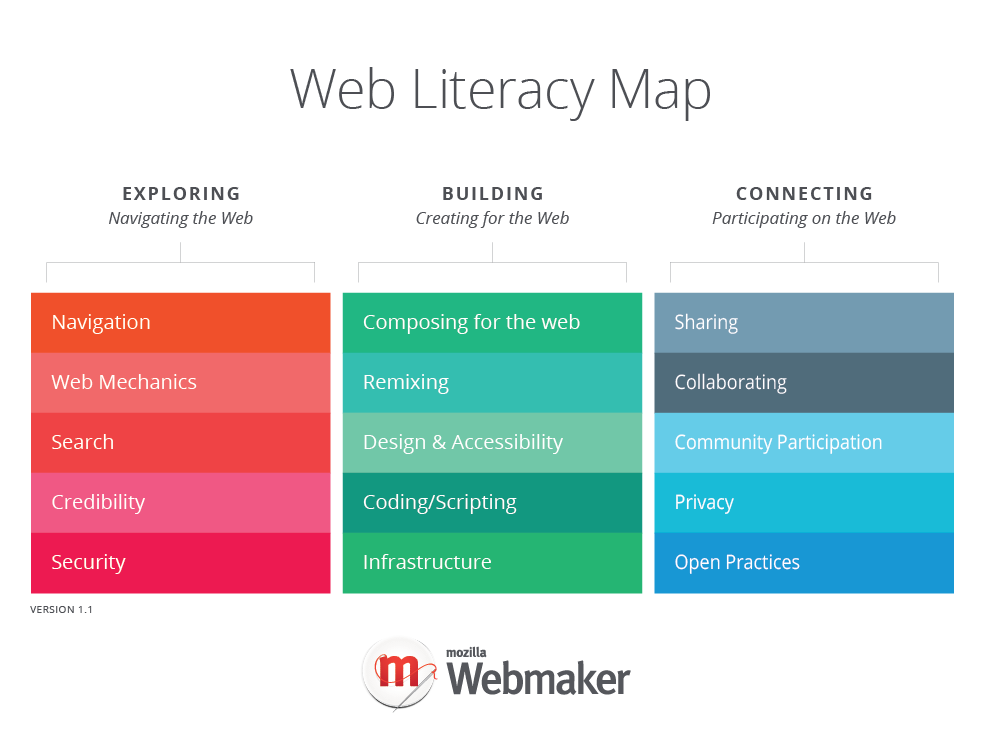
Web Literacy Map V1
Web most often refers to: * Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal * World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to: Computing * WEB, a literate programming system created by Donald Knuth * GNOME Web, a Web browser * Web.com, a web-design company * Webs (web hosting), a Web hosting and website building service Engineering * Web (manufacturing), continuous sheets of material passed over rollers ** Web, a roll of paper in offset printing * Web, the vertical element of an I-beam or a rail profile * Web, the interior beams of a truss Films * ''Web'' (2013 film), a documentary * ''Webs'' (film), a 2003 science-fiction movie * ''The Web'' (film), a 1947 film noir * Charlotte's Web (2006 film) Literature * ''Web'' (comics), a MLJ comicbook character (created 1942) * ''Web'' (novel), by John Wyndham (1979) * The Web (series), a science fiction series (1997–1999) * World English Bible, a public-domain Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozilla Foundation
The Mozilla Foundation (stylized as moz://a) is an American non-profit organization that exists to support and collectively lead the open source Mozilla project. Founded in July 2003, the organization sets the policies that govern development, operates key infrastructure and controls Mozilla trademarks and copyrights. It owns a taxable subsidiary: the Mozilla Corporation, which employs many Mozilla developers and coordinates releases of the Mozilla Firefox web browser and Mozilla Thunderbird email client. The Mozilla Foundation was founded by the Netscape-affiliated Mozilla Organization. The organization is currently based in the Silicon Valley city of Mountain View, California, United States. The Mozilla Foundation describes itself as "a non-profit organization that promotes openness, innovation and participation on the Internet". The Mozilla Foundation is guided by the Mozilla Manifesto, which lists 10 principles which Mozilla believes "are critical for the Internet to cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyber Self-defense
In cybersecurity, cyber self-defense refers to self-defense against cyberattack. While it generally emphasizes active cybersecurity measures by computer users themselves, cyber self-defense is sometimes used to refer to the self-defense of organizations as a whole, such as corporate entities or entire nations. Surveillance self-defense is a variant of cyber self-defense and largely overlaps with it. Active and passive cybersecurity measures provide defenders with higher levels of cybersecurity, intrusion detection, incident handling and remediation capabilities. Various sectors and organizations are legally obligated to adhere to cyber security standards. Background Organizations may conduct a penetration test via internal team or hire a third-party organization to audit the organization's systems. Larger organizations may conduct internal attacker-defender scenarios with a " red team" attacking and a "blue team" defending. The defenders, namely threat hunters, system adm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Literacy
Computer literacy is defined as the knowledge and ability to use computers and related technology efficiently, with skill levels ranging from elementary use to computer programming and advanced problem solving. Computer literacy can also refer to the comfort level someone has with using computer programs and applications. Another valuable component is understanding how computers work and operate. An individual's level of computer literacy is measured on the scale of how skilled they are when it comes to using computers and other related tools to achieve a goal. Computer literacy may be distinguished from computer programming, which primarily focuses on the design and coding of computer programs rather than the familiarity and skill in their use. Various countries, including the United Kingdom and the United States, have created initiatives to improve national computer literacy rates. Background Computer literacy differs from digital literacy, which is the ability to communica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Literacy
Digital literacy refers to an individual's ability to find, evaluate, and communicate information through typing and other media on various digital platforms. It is evaluated by an individual's grammar, composition, typing skills and ability to produce text, images, audio and designs using technology. The American Library Association (ALA) defines digital literacy as "the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills." While digital literacy initially focused on digital skills and stand-alone computers, the advent of the internet and use of social media, has resulted in the shift in some of its focus to mobile devices. Similar to other expanding definitions of literacy that recognise cultural and historical ways of making meaning, digital literacy does not replace traditional forms of literacy, but instead builds upon and expands the skills that form the foundation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Literacy
The Association of College & Research Libraries defines information literacy as a "set of integrated abilities encompassing the reflective discovery of information, the understanding of how information is produced and valued and the use of information in creating new knowledge and participating ethically in communities of learning". The 1989 American Library Association (ALA) Presidential Committee on Information Literacy formally defined information literacy (IL) as attributes of an individual, stating that "to be information literate, a person must be able to recognize when information is needed and have the ability to locate, evaluate and use effectively the needed information". In 1990, academic Lori Arp published a paper asking, "Are information literacy instruction and bibliographic instruction the same?" Arp argued that neither term was particularly well defined by theoreticians or practitioners in the field. Further studies were needed to lessen the confusion and continue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, humans in literate societies have sets of practices for producing and consuming writing, and they also have beliefs about these practices. Reading, in this view, is always reading something for some purpose; writing is always writing something for someone for some particular ends. Beliefs about reading and writing and its value for society and for the individual always influence the ways literacy is taught, learned, and practiced over the lifespan. Some researchers suggest that the history of interest in the concept of "literacy" can be divided into two periods. Firstly is the period before 1950, when literacy was understood solely as alphabetical literacy (word and letter recognition). Secondly is the period after 1950, when literacy slowly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing And Society
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology and software engineering. The term "computing" is also synonymous with counting and calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by mechanical computing machines, and before that, to human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. Computing is intimately tied to the representation of numbers, though mathematical concept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |