|
Wave Disk Engine
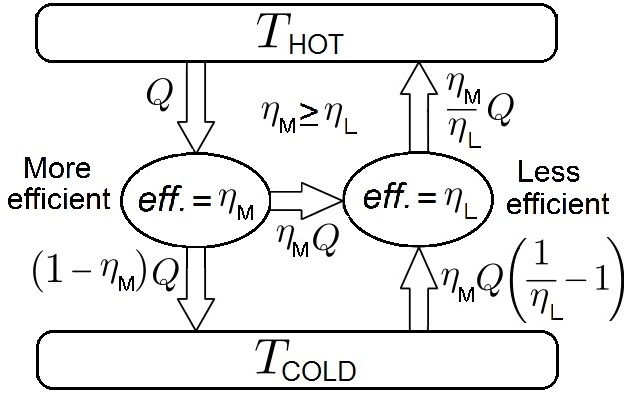
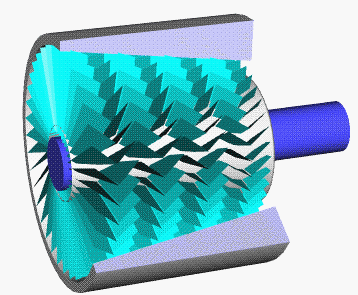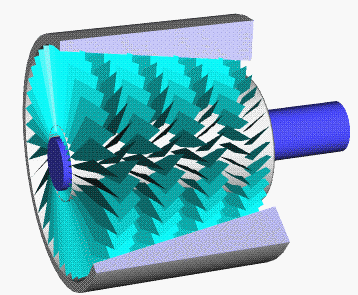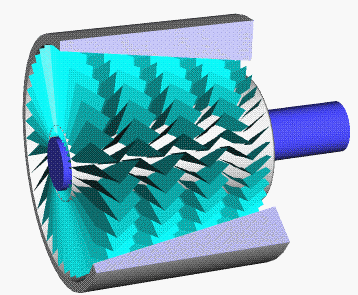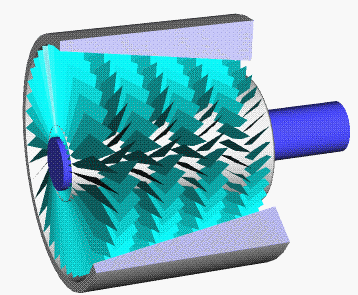
A wave disk engine or wave disk generator is a type of pistonless rotary engine being developed at Michigan State University and Warsaw Institute of Technology. The engine has a spinning disk with curved blades. Once fuel and air enter the engine, the rotation of the disk creates shockwaves that compress the mixture. When ignited, the burning mixture expands, pushing against the blades, causing them to spin. The spinning of the disk itself opens and closes intake and exhaust ports. The proposed concept was called a radial internal combustion wave rotor. Background Wave rotors utilize shock waves to transfer energy between a high-energy fluid to a low-energy fluid, thereby increasing both temperature and pressure of the low-energy fluid (also called pressure wave machines or pressure exchangers). Operational principles As with all heat engines, the efficiency of a wave disk engine is governed by the temperature difference between the hot and cold sides (see Carnot's theorem) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistonless Rotary Engine
A pistonless rotary engine is an internal combustion engine that does not use pistons in the way a reciprocating engine does. Designs vary widely but typically involve one or more rotors, sometimes called rotary pistons. Although many different designs have been constructed, only the Wankel engine has achieved widespread adoption. The term rotary combustion engine has been used as a name for these engines to distinguish them from early (generally up to the early 1920s) aircraft engines and motorcycle engines also known as ''rotary engines''. However, both continue to be called ''rotary engines'' and only the context determines which type is meant, whereas the "pistonless" prefix is less ambiguous. Pistonless rotary engines A pistonless rotary engine replaces the linear reciprocating motion of a piston with more complex compression/expansion motions with the objective of improving some aspect of the engine's operation, such as: higher efficiency thermodynamic cycles, lower mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axial Flow
An axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other rotating compressors such as centrifugal compressor, axi-centrifugal compressors and mixed-flow compressors where the fluid flow will include a "radial component" through the compressor. The energy level of the fluid increases as it flows through the compressor due to the action of the rotor blades which exert a torque on the fluid. The stationary blades slow the fluid, converting the circumferential component of flow into pressure. Compressors are typically driven by an electric motor or a steam or a gas turbine. Axial flow compressors produce a continuous flow of compressed gas, and have the benefits of high efficiency and large mass flow rate, particularly in relation to their size and cross-section. They do, however, require several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistonless Rotary Engine
A pistonless rotary engine is an internal combustion engine that does not use pistons in the way a reciprocating engine does. Designs vary widely but typically involve one or more rotors, sometimes called rotary pistons. Although many different designs have been constructed, only the Wankel engine has achieved widespread adoption. The term rotary combustion engine has been used as a name for these engines to distinguish them from early (generally up to the early 1920s) aircraft engines and motorcycle engines also known as ''rotary engines''. However, both continue to be called ''rotary engines'' and only the context determines which type is meant, whereas the "pistonless" prefix is less ambiguous. Pistonless rotary engines A pistonless rotary engine replaces the linear reciprocating motion of a piston with more complex compression/expansion motions with the objective of improving some aspect of the engine's operation, such as: higher efficiency thermodynamic cycles, lower mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARPA-E
ARPA-E, or Advanced Research Projects Agency–Energy is a United States government agency tasked with promoting and funding research and development of advanced energy technologies. It is modeled after the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). The current Acting Director is ARPA-E Deputy Director for Technology Jennifer Gerbi. History and mission Legislative history ARPA-E was initially conceived by a report by the National Academies entitled ''Rising Above the Gathering Storm: Energizing and Employing America for a Brighter Economic Future''. The report described a need for the US to stimulate innovation and develop clean, affordable, and reliable energy. ARPA-E was officially created by the America COMPETES Act , authored by Congressman Bart Gordon, within the United States Department of Energy (DOE) in 2007, though without a budget. The initial budget of about $400 million was a part of the economic stimulus bill of February 2009. In early January 2011, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States. The DOE oversees the U.S. nuclear weapons program, nuclear reactor production for the United States Navy, energy-related research, and domestic energy production and energy conservation. The DOE was created in 1977 in the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis. It sponsors more physical science research than any other U.S. federal agency, the majority of which is conducted through its system of National Laboratories. The DOE also directs research in genomics, with the Human Genome Project originating from a DOE initiative. The department is headed by the Secretary of Energy, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the Cabinet. The current Secretary of Energy is Jennifer Granholm, who has served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaust Gas
Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack, or propelling nozzle. It often disperses downwind in a pattern called an ''exhaust plume''. It is a major component of motor vehicle emissions (and from stationary internal combustion engines), which can also include crankcase blow-by and evaporation of unused gasoline. Motor vehicle emissions contribute to air pollution and are a major ingredient in the creation of smog in some large cities. A 2013 study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) indicates that 53,000 early deaths occur per year in the United States alone because of vehicle emissions. According to another study from the same university, traffic fumes alone cause the death of 5,000 people every year just in the United Kingdom. Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid Vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is one that uses two or more distinct types of power, such as submarines that use diesel when surfaced and batteries when submerged. Other means to store energy include pressurized fluid in hydraulic hybrids. The basic principle with hybrid vehicles is that the different motors work better at different speeds; the electric motor is more efficient at producing torque, or turning power, and the combustion engine is better for maintaining high speed than a typical electric motor. Switching from one to the other at the proper time while speeding up yields a win-win in terms of energy efficiency, such that it translates into greater fuel efficiency. Vehicle types Two-wheeled and cycle-type vehicles Mopeds, electric bicycles, and even electric kick scooters are a simple form of a hybrid, powered by an internal combustion engine or electric motor and the rider's muscles. Early prototype motorcycles in the late 19th century used the same principle. * In a par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scavenging (automotive)
Scavenging is the process of replacing the exhaust gas in a cylinder of an internal combustion engine with the fresh air/fuel mixture (or fresh air, in the case of direct-injection engines) for the next cycle. If scavenging is incomplete, the remaining exhaust gases can cause improper combustion for the next cycle, leading to reduced power output. Scavenging is equally important for both two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Most modern four-stroke engines use crossflow cylinder heads and valve timing overlap to scavenge the cylinders. Modern two-stroke engines use either Schnuerle scavenging (also known as "loop scavenging") or uniflow scavenging. The scavenge or scavenging port refers to that port through which clean air enters the cylinder, the exhaust port through which it leaves. Origins The first engines deliberately designed to encourage scavenging were gas engines built by Crossley Brothers Ltd in the United Kingdom in the early 1890s. These ''Crossley Otto Scavengin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator.Munson, Bruce Roy, T. H. Okiishi, and Wade W. Huebsch. "Turbomachines." Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics. 6th ed. Hoboken, NJ: J. Wiley & Sons, 2009. Print. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels. Gas, steam, and water turbines have a casing around the blades that contains and controls the working fluid. Credit for invention of the steam turbine is given both to Anglo-Irish engineer Sir Charles Parsons (1854–1931) for invention of the reaction turbine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michigan State University
Michigan State University (Michigan State, MSU) is a public land-grant research university in East Lansing, Michigan. It was founded in 1855 as the Agricultural College of the State of Michigan, the first of its kind in the United States. It is considered a Public Ivy, or a public institution which offers an academic experience similar to that of an Ivy League university. After the introduction of the Morrill Act in 1862, the state designated the college a land-grant institution in 1863, making it the first of the land-grant colleges in the United States. The college became coeducational in 1870. In 1955, the state officially made the college a university, and the current name, Michigan State University, was adopted in 1964. Today, Michigan State has the largest undergraduate enrollment among Michigan's colleges and universities and approximately 634,300 living alums worldwide. The university is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocating Engine
A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.''Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach'' by Yunus A. Cengal and Michael A. Boles Common features in all types There may be one or more pistons. Each piston is inside a cylinder, into which a gas is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnot's Theorem (thermodynamics)
In thermodynamics, Carnot's theorem, developed in 1824 by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot, also called Carnot's rule, is a principle that specifies limits on the maximum efficiency that any heat engine can obtain. Carnot's theorem states that all heat engines operating between the same two thermal or heat reservoirs can't have efficiencies greater than a reversible heat engine operating between the same reservoirs. A corollary of this theorem is that every reversible heat engine operating between a pair of heat reservoirs is equally efficient, regardless of the working substance employed or the operation details. Since a Carnot heat engine is also a reversible engine, the efficiency of all the reversible heat engines is determined as the efficiency of the Carnot heat engine that depends solely on the temperatures of its hot and cold reservoirs. The maximum efficiency (i.e., the Carnot heat engine efficiency) of a heat engine operating between cold and hot reservoirs, denoted as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)