|
Wars Of Castro
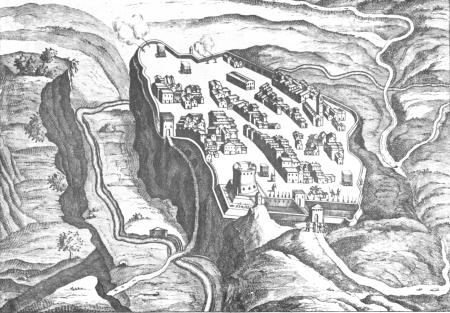
The Wars of Castro were a series of conflicts during the mid-17th century revolving around the ancient city of Castro (located in present-day Lazio, Italy), which eventually resulted in the city's destruction on 2 September 1649. The conflict was a result of a power struggle between the papacy – represented by members of two deeply entrenched Roman families and their popes, the Barberini and Pope Urban VIII and the Pamphili and Pope Innocent X – and the Farnese dukes of Parma, who controlled Castro and its surrounding territories as the Duchy of Castro. Precursors Papal politics of the mid-17th century were complicated, with frequently shifting military and political alliances across the Catholic world. While it is difficult to trace the precise origins of the feud between the duchy of Parma and the papacy, its origins can be looked for in political maneuverings occurring in the years or even decades preceding the start of military action. In 1611 a group of conspir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castro, Lazio
Castro was an ancient city on the west side of Lake Bolsena in the present-day '' comune'' of Ischia di Castro, northern Lazio, Italy. It was destroyed at the conclusion of the Wars of Castro in the 17th century. Early history The settlement of Castro was founded in prehistoric times, and was later the seat of an unspecified Etruscan city, probably Statonia. In the Middle Ages it had a castle (Latin: ''castrum''), hence the name. Although an autonomous commune, it remained nonetheless under papal suzerainty. In 1527 a pro-independence faction assumed power, but they were later ousted by Pier Luigi Farnese, whose family was to rule Castro until the 17th century. In the same year another Farnese, Gian Galeazzo, sacked it in the wake of the Sack of Rome. Ten years later, in 1537, three years after the election of Alessandro Farnese as Pope Paul III, it became the seat of an independent duchy under his son Pier Luigi Farnese. The town, which in the meantime had been reduced t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in the roles of reconnaissance, screening, and skirmishing in many armies, or as heavy cavalry for decisive shock attacks in other armies. An individual soldier in the cavalry is known by a number of designations depending on era and tactics, such as cavalryman, horseman, trooper, cataphract, knight, hussar, uhlan, mamluk, cuirassier, lancer, dragoon, or horse archer. The designation of ''cavalry'' was not usually given to any military forces that used other animals for mounts, such as camels or elephants. Infantry who moved on horseback, but dismounted to fight on foot, were known in the early 17th to the early 18th century as ''dragoons'', a class of mounted infantry which in most armies later evolved into standard cavalry while retain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pamphili
The House of Pamphili (often with the final ''long i'' orthography, Pamphilj) was one of the papal families deeply entrenched in Catholic Church, Roman and Italian politics of the 16th and 17th centuries. Later, the Pamphili family line merged with the Doria and Landi family lines to form the Doria-Pamphili-Landi family line. History The Pamphili surname originated in Gubbio and went to Rome under the pontificate of Pope Innocent VIII (1484–1492). The peak of Pamphili power came with the election of Giovanni Battista Pamphili as Pope Innocent X, who reigned from 1644–1655. Like the reign of his predecessor Pope Urban VIII (of the equally papal Barberini family), Innocent X's rule was littered with examples of nepotism. Members of the Pamphili family did exceptionally well from the Innocent X papacy. The following family members were created cardinals: *Camillo Francesco Maria Pamphili (1644), the Pope's nephew and son of Olimpia Maidalchini, the Pope's sister-in-law and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barberini
The House of Barberini are a family of the Italian nobility that rose to prominence in 17th century Rome. Their influence peaked with the election of Cardinal Maffeo Barberini to the papal throne in 1623, as Pope Urban VIII. Their urban palace, the Palazzo Barberini, completed in 1633 by Bernini, today houses Italy's Galleria Nazionale d'Arte Antica (National Gallery of Ancient Art). Early history The Barberini family were originally a family of minor nobility from the Tuscan town of Barberino Val d'Elsa, who settled in Florence during the early part of the 11th century. This cites: * A. von Reumont, ''Geschichte der Stadt Rom'' (Berlin, 1868), iii. b. 611–612, 615, 617, &c. * ''Almanach de Gotha'' (Gotha, 1902). * J. H. Douglas, ''The Principal Noble Families of Rome'' (Rome, 1905). Carlo Barberini (1488–1566) and his brother Antonio Barberini (1494–1559) were successful Florentine grain, wool and textile merchants. In 1530 Antonio participated in the defense of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 until 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th century until the unification of Italy, between 1859 and 1870. The state had its origins in the rise of Christianity throughout Italy, and with it the rising influence of the Christian Church. By the mid-8th century, with the decline of the Byzantine Empire in Italy, the Papacy became effectively sovereign. Several Christian rulers, including the Frankish kings Charlemagne and Pepin the Short, further donated lands to be governed by the Church. During the Renaissance, the papal territory expanded greatly and the pope became one of Italy's most important secular rulers as well as the head of the Church. At their zenith, the Papal States covered most of the modern Ita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazio
it, Laziale , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +1 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +2 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-62 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €201 billion (2019) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €34,300 (2019) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2019) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.914 · 3rd of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 = ITE , website www ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castro (city)
Castro was an ancient city on the west side of Lake Bolsena in the present-day ''comune'' of Ischia di Castro, northern Lazio, Italy. It was destroyed at the conclusion of the Wars of Castro in the 17th century. Early history The settlement of Castro was founded in prehistoric times, and was later the seat of an unspecified Etruscan city, probably Statonia. In the Middle Ages it had a castle (Latin: ''castrum''), hence the name. Although an autonomous commune, it remained nonetheless under papal suzerainty. In 1527 a pro-independence faction assumed power, but they were later ousted by Pier Luigi Farnese, whose family was to rule Castro until the 17th century. In the same year another Farnese, Gian Galeazzo, sacked it in the wake of the Sack of Rome. Ten years later, in 1537, three years after the election of Alessandro Farnese as Pope Paul III, it became the seat of an independent duchy under his son Pier Luigi Farnese. The town, which in the meantime had been reduced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco I D'Este, Duke Of Modena
Francesco I d'Este (6 September 1610 – 14 October 1658) was Duke of Modena and Reggio from 1629 until his death. The eldest son of Alfonso III d'Este, he became reigning duke after his father's abdication. Biography The pestilence of 1630–1631 killed 70% of Modena's inhabitants. After the outbreak of the Thirty Years' War he sided with Spain and invaded the duchy of Parma, but upon visiting to Spain to claim his reward, he could only acquire Correggio by a payment of 230,000 florins. Later followed the First War of Castro, in which Francesco's Modena joined Venice and Florence and sided with the Dukes of Parma against Barberini Pope Urban VIII, aiming to reconquer Ferrara. The war ended without any particular gain for the Modenese. As again no help had come from Spain, Francesco allied with France through the intercession of Cardinal Mazarin. When he however failed to conquer Cremona, and as the situation of the Thirty Years' War seemed to be favourable for Spain, the Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modena
Modena (, , ; egl, label= Modenese, Mòdna ; ett, Mutna; la, Mutina) is a city and '' comune'' (municipality) on the south side of the Po Valley, in the Province of Modena in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy. A town, and seat of an archbishop, it is known for its car industry since the factories of the famous Italian upper-class sports car makers Ferrari, De Tomaso, Lamborghini, Pagani and Maserati are, or were, located here and all, except Lamborghini, have headquarters in the city or nearby. One of Ferrari's cars, the 360 Modena, was named after the town itself. Ferrari's production plant and Formula One team Scuderia Ferrari are based in Maranello south of the city. The University of Modena, founded in 1175 and expanded by Francesco II d'Este in 1686, focuses on economics, medicine and law, and is the second oldest athenaeum in Italy. Italian military officers are trained at the Military Academy of Modena, and partly housed in the Baroque Ducal Palace. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercenary
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any other official military. Mercenaries fight for money or other forms of payment rather than for political interests. Beginning in the 20th century, mercenaries have increasingly come to be seen as less entitled to protections by rules of war than non-mercenaries. The Geneva Conventions declare that mercenaries are not recognized as legitimate combatants and do not have to be granted the same legal protections as captured service personnel of the armed forces. In practice, whether or not a person is a mercenary may be a matter of degree, as financial and political interests may overlap. Modern mercenary organizations are generally referred to as private military companies or PMCs. Laws of war Protocol Additional GC 1977 (APGC77) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raimondo Montecuccoli
Raimondo Montecuccoli (; 21 February 1609 – 16 October 1680) was an Italian-born professional soldier, military theorist, and diplomat, who served the Habsburg monarchy. Experiencing the Thirty Years' War from scratch as a simple footsoldier, he rose through the ranks into a regiment holder and became an important cavalry commander in the late stages. Serving the Habsburgs as war counsellor and envoy, he commanded their troops in the Second Northern War and the Austro-Turkish War (1663–64), Austro-Turkish War of 1663–64 where he scored an impressive victory in the Battle of Saint Gotthard (1664), Battle of Saint Gotthard. Afterwards, he became president of the Hofkriegsrat and briefly returned as supreme commander of the Imperial forces during the Franco-Dutch War. Montecuccoli was considered the only commander able to compete with the French general Henri de la Tour d'Auvergne, Vicomte de Turenne, Turenne, (1611–1675), and like him, was closely associated with the post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Modena And Reggio
The Duchy of Modena and Reggio ( Emilian: ''Duchêt ed Mòdna e Rèz'', it, Ducato di Modena e Reggio, la, Ducatus Mutinae et Regii) was an Italian state created in 1452 located in Northwestern Italy, in the present day region of Emilia-Romagna. It was ruled since its establishment by the noble House of Este, and since 1814 by the Austria-Este branch of the family. The Este dynasty was a great sponsor of the arts, making the Duchy a cultural reference during the Renaissance and Baroque periods. House of Este In 1452 Emperor Frederick III offered the duchy to Borso d'Este, whose family had ruled the city of Modena and nearby Reggio Emilia for centuries. Borso in 1450 had also succeeded his brother as margrave in the adjacent Papal Duchy of Ferrara, where he received the ducal title in 1471. The Este lands on the southern border of the Holy Roman Empire with the Papal States formed a stabilizing buffer state in the interest of both. The first Este dukes ruled well and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)



