|
WNT4
WNT4 is a secreted protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''WNT4'' gene, found on chromosome 1. It promotes female sex development and represses male sex development. Loss of function may have consequences, such as female to male sex reversal. Function The WNT gene family consists of structurally related genes that encode secreted signaling proteins. These proteins have been implicated in oncogenesis and in several developmental processes, including regulation of cell fate and embryogenesis. Pregnancy WNT4 is involved in many features of pregnancy as a downstream target of BMP2. For example, it regulates endometrial stromal cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation. These processes are all necessary for the development of an embryo. Ablation in female mice results in subfertility, with defects in implantation and decidualization. For instance, there is a decrease in responsiveness to progesterone signaling. Furthermore, postnatal uterine differentiatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSPO1
R-spondin-1 is a secreted protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RSPO1'' gene, found on chromosome 1. In humans, it interacts with WNT4 in the process of female sex development. Loss of function can cause female to male sex reversal. Furthermore, it promotes canonical WNT/β catenin signaling. Structure The protein has two cysteine-rich, furin-like domains and one thrombospondin type 1 domain. Function Sex development Early gonads RSPO1 is required for the early development of gonads, regardless of sex. It has been found in mice only eleven days after fertilization. To induce cell proliferation, it acts synergistically with WNT4. They help stabilize β-catenin, which activates downstream targets. If both are deficient in XY mice, there is less expression of ''SRY'' and a reduction in the amount of SOX9. Moreover, defects in vascularization are found. These occurrences result in testicular hypoplasia. Male to female sex reversal, however, does not occur because Le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramesonephric Duct
The paramesonephric ducts (or Müllerian ducts) are paired ducts of the embryo in the reproductive system of humans and other mammals that run down the lateral sides of the genital ridge and terminate at the sinus tubercle in the primitive urogenital sinus. They form in both sexes during 6th week of fetal development. In the female, go on to form the fallopian tubes/oviducts, uterus, cervix, and the upper one-third of the vagina. In males fetuses, they are normally made to regress by anti-Müllerian hormone which begins to be secreted by the testes during 8th week of fetal development. Each maramesonephric duct is situated just lateral to the mesonephric ducts, mesonephric ducts (Wolffian duct) of the same side. Development The female reproductive system is composed of two embryological segments: the urogenital sinus and the paramesonephric ducts. The two are conjoined at the sinus tubercle. Paramesonephric ducts are present on the embryo of both sexes. Only in females do they d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wnt Signaling Pathway
In cellular biology, the Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt, pronounced "wint", is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling pathways use either nearby cell-cell communication (paracrine) or same-cell communication (autocrine). They are highly evolutionarily conserved in animals, which means they are similar across animal species from fruit flies to humans. Three Wnt signaling pathways have been characterized: the canonical Wnt pathway, the noncanonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the noncanonical Wnt/calcium pathway. All three pathways are activated by the binding of a Wnt-protein ligand to a Frizzled family receptor, which passes the biological signal to the Dishevelled protein inside the cell. The canonical Wnt pathway leads to regulation of gene transcription, and is thought to be negatively regulated in part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows NT 4
Windows NT 4.0 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft, targeting the data server and personal workstation markets. It is the direct successor to Windows NT 3.51, and was released to manufacturing on July 31, 1996, and then to retail in August 24, 1996, with the Server versions released to retail in September 1996. Its most prominent user-facing change was the adoption of Windows 95's user interface, introducing features such as the Start menu and taskbar to the Windows NT product line. It also includes various performance and stability improvements to system-level components, as well as new components such as a cryptography API, DCOM, TAPI 2.0, and the Task Manager, and limited support for DirectX. Over its support lifecycle, NT 4.0 received various updates and service packs offering patches, enhancements to its hardware support, and other new components. Two new editions of NT 4.0 were released post-launch, including a modular v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericyte
Pericytes (formerly called Rouget cells) are multi-functional mural cells of the microcirculation that wrap around the endothelial cells that line the capillaries throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in the basement membrane of blood capillaries, where they communicate with endothelial cells by means of both direct physical contact and paracrine signaling. The morphology, distribution, density and molecular fingerprints of pericytes vary between organs and vascular beds. Pericytes help in the maintainenance of homeostatic and hemostatic functions in the brain, where one of the organs is characterized with a higher pericyte coverage, and also sustain the blood–brain barrier. These cells are also a key component of the neurovascular unit, which includes endothelial cells, astrocytes, and neurons. Pericytes have been postulated to regulate capillary blood flow and the clearance and phagocytosis of cellular debris ''in vitro.'' Pericytes stabilize and monitor the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchymal To Epithelial Transition
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood, or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility, are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical- basal orientation). Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nephron
The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule. The renal tubule extends from the capsule. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of epithelial cells with a lumen. A healthy adult has 1 to 1.5 million nephrons in each kidney. Blood is filtered as it passes through three layers: the endothelial cells of the capillary wall, its basement membrane, and between the podocyte foot processes of the lining of the capsule. The tubule has adjacent peritubular capillaries that run between the descending and ascending portions of the tubule. As the fluid from the capsule flows down into the tubule, it is processed by the epithelial cells lining the tubule: water is reabsorbed and substances are exchanged (some are added, others are removed); first wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic Cell
In cellular biology, a somatic cell (), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Somatic cells compose the body of an organism and divide through mitosis. In contrast, gametes derive from meiosis within the germ cells of the germline and they fuse during sexual reproduction. Stem cells also can divide through mitosis, but are different from somatic in that they differentiate into diverse specialized cell types. In mammals, somatic cells make up all the internal organs, skin, bones, blood and connective tissue, while mammalian germ cells give rise to spermatozoa and ova which fuse during fertilization to produce a cell called a zygote, which divides and differentiates into the cells of an embryo. There are approximately 220 types of somatic cell in the human body. Theoretically, these cells are not germ cells (the source of gametes); they transmit their mut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FGF9
Glia-activating factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGF9'' gene. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This protein was isolated as a secreted factor that exhibits a growth-stimulating effect on cultured glial cells. In nervous system, this protein is produced mainly by neurons and may be important for glial cell development. Expression of the mouse homolog of this gene was found to be dependent on Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling. Mice lacking the homolog gene displayed a male-to-female sex reversal phenotype, which suggested a role in testicular embryogenesis. This gene is involved in the patterning of sex determination, lung development, and skeletal development. Sex de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
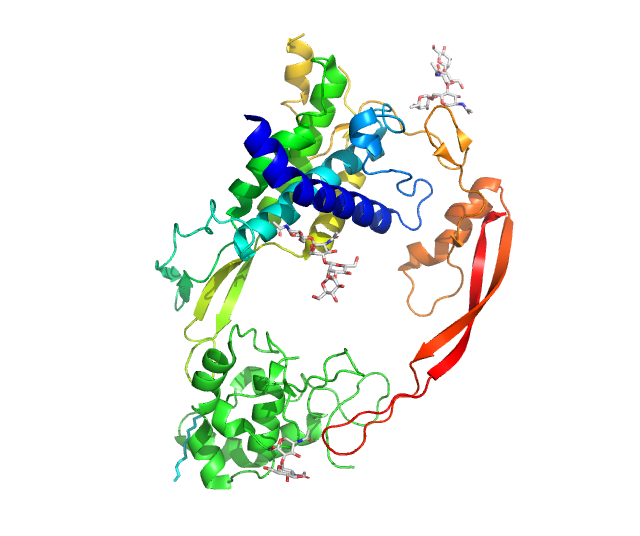
FGFR2
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR-2) also known as CD332 (cluster of differentiation 332) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''FGFR2'' gene residing on chromosome 10. FGFR2 is a receptor for fibroblast growth factor. FGFR-2 is a member of the fibroblast growth factor receptor family, where amino acid sequence is highly conserved between members and throughout evolution. FGFR family members differ from one another in their ligand affinities and tissue distribution. A full-length representative protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin domains, a single hydrophone, hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion of the protein interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and cellular differentiation, differentiation. This particular family member is a high-affinity receptor for acidic, basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibroblast Growth Factor
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) are a family of cell signalling proteins produced by the macrophages. They are involved in a wide variety of processes, most notably as crucial elements for normal development in animal cells. Any irregularities in their function will lead to a range of developmental defects. These growth factors typically act as a systemic or locally circulating molecules of extracellular origin that activate cell surface receptors. A defining property of FGFs is that they bind to heparin and to heparan sulfate. Thus, some are sequestered in the extracellular matrix of tissues that contains heparan sulfate proteoglycans, and released locally upon injury or tissue remodeling. Families In humans, 23 members of the FGF family have been identified, all of which are ''structurally'' related signaling molecules: * Members FGF1 through FGF10 all bind fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). FGF1 is also known as ''acidic fibroblast growth factor'', and FGF2 is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, 5α-DHT, androstanolone or stanolone) is an endogenous androgen sex steroid and hormone primarily involved in the growth and repair of the prostate and the penis, as well as the production of sebum and body hair composition. The enzyme 5α-reductase catalyzes the formation of DHT from testosterone in certain tissues including the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, epididymides, skin, hair follicles, liver, and brain. This enzyme mediates reduction of the C4-5 double bond of testosterone. DHT may also be synthesized from progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone via the androgen backdoor pathway in the absence of testosterone. Relative to testosterone, DHT is considerably more potent as an agonist of the androgen receptor (AR). In addition to its role as a natural hormone, DHT has been used as a medication, for instance in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men; for information on DHT as a medication, see the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |