|
William Lacy (Catholic Priest)
William Lacy (Lacey) (died 1582) was an English Catholic priest and martyr. He and fellow priest Richard Kirkman were executed at York on 22 August 1582. Biography William was born at Houghton (or Tosside, West Riding). He married a widow, named Creswell, whose sons, Arthur and Joseph, became Jesuits. Little is related of his family by his biographers. He had a brother Ralph of Preston, a sister Barbara, and nephews (apparently her sons) Robert and William (Cal. S. P., Dom. add. 1566-79, London, 1871, p. 562). He held a position of emolument under the Crown, possibly as coroner, till about 1565. One of this name, probably a relative, was a coroner for the West Riding in 1581-2 (Dasent, "Acts of the Privy Council", xiii, 358).Wainewright, John. "Bl. William Lacy." The Catholic Encyclopedia< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
13 Eliz
Thirteen or 13 may refer to: * 13 (number) * Any of the years 13 BC, AD 13, 1913, or 2013 Music Albums * ''13'' (Black Sabbath album), 2013 * ''13'' (Blur album), 1999 * ''13'' (Borgeous album), 2016 * ''13'' (Brian Setzer album), 2006 * ''13'' (Die Ärzte album), 1998 * ''13'' (The Doors album), 1970 * ''13'' (Havoc album), 2013 * ''13'' (HLAH album), 1993 * ''13'' (Indochine album), 2017 * ''13'' (Marta Savić album), 2011 * ''13'' (Norman Westberg album), 2015 * ''13'' (Ozark Mountain Daredevils album), 1997 * ''13'' (Six Feet Under album), 2005 * ''13'' (Suicidal Tendencies album), 2013 * ''13'' (Solace album), 2003 * ''13'' (Second Coming album), 2003 * 13 (Timati album), 2013 * ''13'' (Ces Cru EP), 2012 * ''13'' (Denzel Curry EP), 2017 * ''Thirteen'' (CJ & The Satellites album), 2007 * ''Thirteen'' (Emmylou Harris album), 1986 * ''Thirteen'' (Harem Scarem album), 2014 * ''Thirteen'' (James Reyne album), 2012 * ''Thirteen'' (Megadeth album), 2011 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakefield
Wakefield is a cathedral city in West Yorkshire, England located on the River Calder. The city had a population of 109,766 in the 2021 census, up from 99,251 in the 2011 census. The city is the administrative centre of the wider Metropolitan Borough of Wakefield, which had a population of , the most populous district in England. It is part of the West Yorkshire Built-up Area and the Yorkshire and the Humber region. In 1888, it gained city status due to its cathedral. The city has a town hall and is home to the county hall, which was the former administrative centre of the city's county borough and metropolitan borough as well as county town for the West Riding of Yorkshire. The Battle of Wakefield took place in the Wars of the Roses, and the city was a Royalist stronghold in the Civil War. Wakefield became an important market town and centre for wool, exploiting its position on the navigable River Calder to become an inland port. In the 18th century, Wakefie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recusancy
Recusancy (from ) was the state of those who remained loyal to the Catholic Church and refused to attend Church of England services after the English Reformation. The 1558 Recusancy Acts passed in the reign of Elizabeth I, and temporarily repealed in the Interregnum (1649–1660), remained on the statute books until 1888. They imposed punishments such as fines, property confiscation and imprisonment on recusants. The suspension under Oliver Cromwell was mainly intended to give relief to Nonconformist Protestants rather than to Catholics, to whom some restrictions applied into the 1920s, through the Act of Settlement 1701, despite the 1828–1829 Catholic emancipation. In some cases those adhering to Catholicism faced capital punishment, and some English and Welsh Catholics who were executed in the 16th and 17th centuries have been canonised by the Catholic Church as martyrs of the English Reformation. Today, ''recusant'' applies to the descendants of Catholic families of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
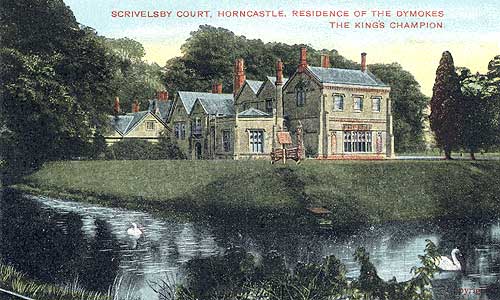
Scrivelsby
Scrivelsby is a village and ecclesiastical parish in the East Lindsey district of the County of Lincolnshire, England. It is situated south of Horncastle and is on the B1183 road east from the A153 road. It is administered by the civil parish of Mareham on the Hill. Historically the manor was held by grand serjeanty, a form of feudal tenure which required the performance of a ceremonial service rather than a money payment – in this case as the King's Champion. History The manor of Scrivelsby is listed in the Domesday Book of 1086 as "Scrivelesbi" and was held in chief from the king. It then comprised 89 households, 16 villagers, 11 smallholders and 30 freemen, with 8.5 ploughlands, a meadow of , woodland of , a mill and a church. In 1086 the manor was held by ''Robert Dispensator'' (Latin) ("Robert the Bursar"). Robert was succeeded by his brother Urse d'Abetot, Burke's Genealogical and Heraldic History of the Landed Gentry, 15th Edition, ed. Pirie-Gordon, H., Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hereditary Champion Of England
The Honourable The King's (or Queen's) Champion is an honorary and Inheritance, hereditary office in the Royal Household of the British sovereign. The champion's original role at the coronation of a British monarch was to challenge anyone who contested the new monarch's entitlement to the throne to trial by combat. Although this function was last enacted at the coronation of George IV in 1821, the office continues to descend through the Dymoke family. The Lord of the manor, Lord of the Manor of Scrivelsby in Lincolnshire, England, has, since the Norman Conquest in 1066, held the manor from the Crown by grand serjeanty of being the King's or Queen's Champion. Such person is also the Standard Bearer of England. The current King's Champion is a member of the Dymoke family, which has included many Champions. The 35th Champion was the 34th Lord of the Manor of Scrivelsby, Thornton, Lincolnshire, Thornton and Dalderby and patron of the living of Scrivelsby-cum-Dalderby, Francis John Fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Dymoke
Robert Dymoke, Dymock or Dymocke, of Scrivelsby, Lincolnshire (born 1531; died at Lincoln, England, 11 September 1580) was Queen's Champion of England and a devout Catholic recusant who was named a martyr after his death. Life In 1579 Dymoke received the Catholic priest, Richard Kirkman, at his manor of Scrivelsby, and maintained him as a schoolmaster to his sons. He was himself, at the time, an occasional conformist to the Anglican state religion. He was reconciled to the Catholic Church in 1580, either by Kirkman or by Edmund Campion. In July 1580, Dymoke and his wife were indicted for hearing Mass and for recusancy. He was by then quite helpless owing to paralysis. Dymoke was ordered by Thomas Cooper, Bishop of Lincoln, to be carried off to gaol in Lincoln, where he was visited in his last hours by Protestant ministers, while he was dying there. Family He was the son of Sir Edward Dymoke, of Scrivelsby, Lincolnshire (d. 1566), Hereditary King's Champion. The office ran in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Briant
Alexander Briant, SJ (17 August 1556 – 1 December 1581) was an English Jesuit and martyr, executed at Tyburn. Life He was born in Somerset, and entered Hart Hall, Oxford (now Hertford College), at an early age. While there, he became a pupil of Robert Parsons, and he completed his studies with him at Balliol College, which, along with his association with Richard Holtby, led to his conversion. After leaving university, he entered the English College at Reims then went to the English College, Douai, and was ordained priest on 29 March 1578. Assigned to the English mission in August of the following year, he laboured with zeal in his own county of Somerset.Saxton, Eugene. "Blessed Alexander Briant." The Catholic Encyclopedia Vol. 1. New York: Robert Appleton Company, 1907. 1 F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Thirkeld
Richard Thirkeld (died 29 May 1583) was an English Roman Catholic priest. He is a Catholic martyr beatified by Pope Leo XIII in 1886. Life Thirkeld was born at Coniscliffe, Durham, England. From Queen's College, Oxford, where he was in 1564–5, he went to Reims, where he was ordained priest, 18 April 1579. He left 23 May for the English mission, where he ministered in or about York, and acted as confessor to Margaret Clitheroe. On the eve of the Annunciation, 1583, he was arrested while visiting one of the Catholic prisoners in the Kidcote on Ouse bridge. He at once confessed his priesthood, both to the pursuivants, who arrested him, and to the mayor before whom he was brought, and for the night was lodged in the house of the high sheriff. The next day his trial took place, at which he managed to appear in his cassock, which made him appear all the more venerable. The charge was one of having reconciled the Queen's subjects to the Church of Rome. He was found guilty on 27 Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douai
Douai ( , , ; ; ; formerly spelled Douay or Doway in English) is a city in the Nord (French department), Nord département in northern France. It is a Subprefectures in France, sub-prefecture of the department. Located on the river Scarpe (river), Scarpe some from Lille and from Arras, Douai is home to one of the region's most impressive belfry (architecture), belfries. History Its site probably corresponds to that of a 4th-century Roman fortress known as Duacum. From the 10th century, the town was a Romance languages, romance fiefdom of the Count of Flanders, counts of County of Flanders, Flanders. The town became a flourishing textile market centre during the Middle Ages, historically known as Douay or Doway in English. In 1384, the county of Flanders passed into the domains of the Dukes of Burgundy and thence in 1477 into Habsburg possessions. In 1667, Douai was taken by the troops of Louis XIV of France, and by the 1668 Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1668), Treaty of Aix-la-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |