|
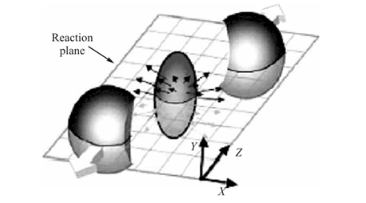
WA93 Experiment
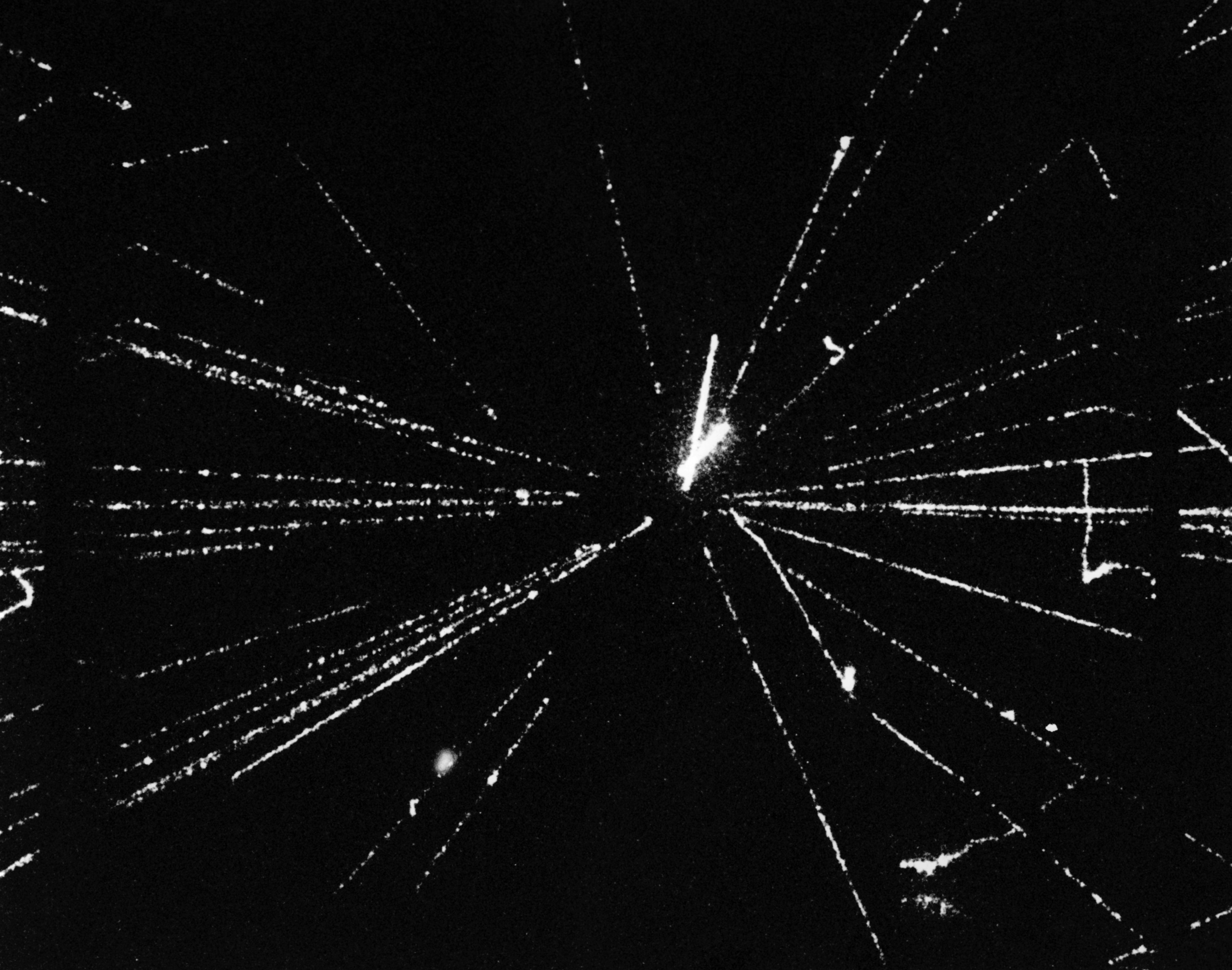
WA93 experiment (''Synonym'': Light Universal Detector or LUD) was a detector experiment conducted at CERN for studying the correlations between photons and charged particles. It was an experimental program of CERN and part of the research programme Super Proton Synchrotron, SPS. The experiment was majorly conducted by the Indian High-Energy Heavy Ion Physics Team at CERN-SPS. For measurement of the multiplicity and the rapidity and azimuthal distributions of photons in ultra-relativistic heavy ion collisions, Photon Multiplicity Detector (PMD), Photon Multiplicity Detector was implemented in the experiment. The experiment was led by Indian physicist Y. P. Viyogi, Y P Viyogi. Hans H. Gutbrod was the spokesperson of the experimental project. The experimental project was approved on 22 November 1990. The experiment was completed on 9 May 2002. Description WA93 experiment was a Particle physics, high-energy physics experiment conducted at CERN's Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS). It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN
The European Organization for Nuclear Research, known as CERN (; ; ), is an intergovernmental organization that operates the largest particle physics laboratory in the world. Established in 1954, it is based in Meyrin, western suburb of Geneva, on the France–Switzerland border. It comprises #Member states and budget, 24 member states. Israel, admitted in 2013, is the only full member geographically out of Europe. CERN is an official United Nations General Assembly observers#Intergovernmental organizations, United Nations General Assembly observer. The acronym CERN is also used to refer to the laboratory; in 2023, it had 2,666 scientific, technical, and administrative staff members, and hosted about 12,370 users from institutions in more than 80 countries. In 2016, CERN generated 49 Byte#Multiple-byte units, petabytes of data. CERN's main function is to provide the particle accelerators and other infrastructure needed for high-energy physics research – consequently, numer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that can move no faster than the speed of light measured in vacuum. The photon belongs to the class of boson particles. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While Planck was trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, he proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charged Particle
In physics, a charged particle is a particle with an electric charge. For example, some elementary particles, like the electron or quarks are charged. Some composite particles like protons are charged particles. An ion, such as a molecule or atom with a surplus or deficit of electrons relative to protons are also charged particles. A Plasma (physics), plasma is a collection of charged particles, atomic nuclei and separated electrons, but can also be a gas containing a significant proportion of charged particles. Charged particles are labeled as either '' positive'' (+) or ''negative'' (-). The designations are arbitrary. Nothing is inherent to a positively charged particle that makes it "positive", and the same goes for negatively charged particles. Examples Positively charged particles * protons * positrons (antielectrons) * positively charged pions * alpha particles * ion, cations Negatively charged particles * electrons * antiprotons * muons * tauons * negative charged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Proton Synchrotron
The Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) is a particle accelerator of the synchrotron type at CERN. It is housed in a circular tunnel, in circumference, straddling the border of France and Switzerland near Geneva, Switzerland. History The SPS was designed by a team led by John Adams (physicist), John Adams, List of Directors General of CERN, director-general of what was then known as Laboratory II. Originally specified as a 300 GeV accelerator, the SPS was actually built to be capable of 400 GeV, an operating energy it achieved on the official commissioning date of 17 June 1976. However, by that time, this energy had been exceeded by Fermilab, which reached an energy of 500 GeV on 14 May of that year. The SPS has been used to accelerate protons and antiprotons, electrons and positrons (for use as the injector for the Large Electron–Positron Collider (LEP)), and quark–gluon plasma, heavy ions. From 1981 to 1991, the SPS operated as a hadron (more precisely, proton–an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon Multiplicity Detector (PMD)
Photon Multiplicity Detector (PMD) is a detector used in the measurement of the multiplicity and spatial distribution of photons produced in nucleus - nucleus collisions. In short form, it is denoted by PMD. It was incorporated in the WA93 experiment. The funding for research and development of the design of PMD was done by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST) of the Government of India. The detector was constructed in the collaboration of Variable Energy Cyclotron Centre in Kolkata, Institute of Physics in Bhubaneswar and group of universities at Chandigarh, Jaipur and Jammu. Description A PMD typically consists of two main layers Veto Detector and Preshower Detector. Veto Detector layer is designed to reject charged particles. Photons pass through a converter in Preshower Detector layer, initiating an electromagnetic shower. The detector then measures the number of cells activated by the shower, providing information about t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Physics
Particle physics or high-energy physics is the study of Elementary particle, fundamental particles and fundamental interaction, forces that constitute matter and radiation. The field also studies combinations of elementary particles up to the scale of protons and neutrons, while the study of combinations of protons and neutrons is called nuclear physics. The fundamental particles in the universe are classified in the Standard Model as fermions (matter particles) and bosons (force-carrying particles). There are three Generation (particle physics), generations of fermions, although ordinary matter is made only from the first fermion generation. The first generation consists of Up quark, up and down quarks which form protons and neutrons, and electrons and electron neutrinos. The three fundamental interactions known to be mediated by bosons are electromagnetism, the weak interaction, and the strong interaction. Quark, Quarks cannot exist on their own but form hadrons. Hadrons that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark–gluon Plasma
Quark–gluon plasma (QGP or quark soup) is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at Thermodynamic equilibrium#Local and global equilibrium, thermal (local kinetic) and (close to) chemical (abundance) equilibrium. The word ''plasma'' signals that free color charges are allowed. In a 1987 summary, Léon Van Hove pointed out the equivalence of the three terms: quark gluon plasma, quark matter and a new state of matter. Since the temperature is above the Hagedorn temperature—and thus above the scale of light u,d-quark mass—the pressure exhibits the relativistic Stefan–Boltzmann law, Stefan–Boltzmann format governed by temperature to the fourth power ( T^) and many practically massless quark and gluon constituents. It can be said that QGP emerges to be the new phase of strongly interacting matter which manifests its physical properties in terms of nearly free dynamics of practically massless gluons and quarks. Both quarks and gluons must be present in conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Bang
The Big Bang is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models based on the Big Bang concept explain a broad range of phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The uniformity of the universe, known as the horizon and flatness problems, is explained through cosmic inflation: a phase of accelerated expansion during the earliest stages. A wide range of empirical evidence strongly favors the Big Bang event, which is now essentially universally accepted.: "At the same time that observations tipped the balance definitely in favor of the relativistic big-bang theory, ..." Detailed measurements of the expansion rate of the universe place the Big Bang singularity at an estimated billion years ago, which is considered the age of the universe. Extrapolating this cosmic expansion backward in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quark–gluon Plasma
Quark–gluon plasma (QGP or quark soup) is an interacting localized assembly of quarks and gluons at Thermodynamic equilibrium#Local and global equilibrium, thermal (local kinetic) and (close to) chemical (abundance) equilibrium. The word ''plasma'' signals that free color charges are allowed. In a 1987 summary, Léon Van Hove pointed out the equivalence of the three terms: quark gluon plasma, quark matter and a new state of matter. Since the temperature is above the Hagedorn temperature—and thus above the scale of light u,d-quark mass—the pressure exhibits the relativistic Stefan–Boltzmann law, Stefan–Boltzmann format governed by temperature to the fourth power ( T^) and many practically massless quark and gluon constituents. It can be said that QGP emerges to be the new phase of strongly interacting matter which manifests its physical properties in terms of nearly free dynamics of practically massless gluons and quarks. Both quarks and gluons must be present in conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur ( American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphur ( Commonwealth spelling) is a chemical element; it has symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with the chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most common on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |