|
Vietnamese Standard Code For Information Interchange
VSCII (Vietnamese Standard Code for Information Interchange), also known as TCVN 5712, ISO-IR-180, .VN, ABC or simply the TCVN encodings, is a set of three closely related Vietnamese national standard character encodings for using the Vietnamese language with computers, developed by the TCVN Technical Committee on Information Technology (TCVN/TC1) and first adopted in 1993 (as TCVN 5712:1993). It should not be confused with the similarly-named unofficial VISCII encoding, which was sometimes used by overseas Vietnamese speakers. VISCII was also intended to stand for ''Vietnamese Standard Code for Information Interchange'', but is not related to VSCII. VSCII (TCVN) was used extensively in the north of Vietnam, while VNI was popular in the south. Unicode and the Windows-1258 code page are now used for virtually all Vietnamese computer data, but legacy files or archived messages may need conversion. Encodings All three forms of VSCII keep the 95 printable characters of ASCII un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VISCII
VISCII is an unofficially-defined modified ASCII character encoding for using the Vietnamese language with computers. It should not be confused with the similarly-named officially registered VSCII encoding. VISCII keeps the 95 printable characters of ASCII unmodified, but it replaces 6 of the 33 control characters with printable characters. It adds 128 precomposed characters. Unicode and the Windows-1258 code page are now used for virtually all Vietnamese computer data, but legacy VSCII and VISCII files may need conversion. History and naming VISCII was designed by the Vietnamese Standardization Working Group (Viet-Std Group) led by Christopher Cuong T. Nguyen, Cuong M. Bui, and Hoc D. Ngo based in Silicon Valley, California in 1992 while they were working with the Unicode consortium to include pre-composed Vietnamese characters in the Unicode standard. VISCII, along with VIQR, was first published in a bilingual report in September 1992, in which it was dubbed the "Vietnamese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combining Diacritics
In digital typography, combining characters are characters that are intended to modify other characters. The most common combining characters in the Latin script are the combining diacritical marks (including combining accents). Unicode also contains many precomposed characters, so that in many cases it is possible to use both combining diacritics and precomposed characters, at the user's or application's choice. This leads to a requirement to perform Unicode normalization before comparing two Unicode strings and to carefully design encoding converters to correctly map all of the valid ways to represent a character in Unicode to a legacy encoding to avoid data loss. In Unicode, the main block of combining diacritics for European languages and the International Phonetic Alphabet is U+0300–U+036F. Combining diacritical marks are also present in many other blocks of Unicode characters. In Unicode, diacritics are always added after the main character (in contrast to some older c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
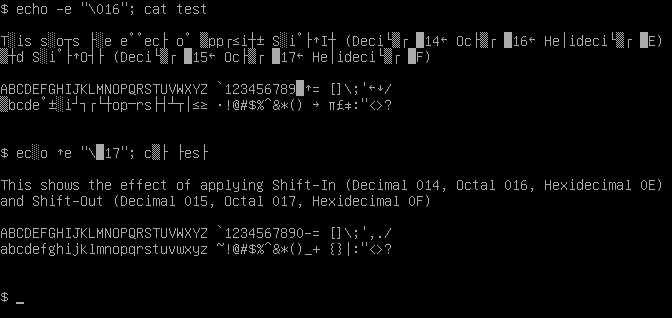
Shift Out
Shift Out (SO) and Shift In (SI) are ASCII control characters 14 and 15, respectively (0x0E and 0x0F). These are sometimes also called "Control-N" and "Control-O". The original meaning of those characters provided a way to shift a coloured ribbon, split longitudinally usually with red and black, up and down to the other colour in an electro-mechanical typewriter or teleprinter, such as the Teletype Model 38, to automate the same function of manual typewriters. Black was the conventional ambient default colour and so was shifted "in" or "out" with the other colour on the ribbon. Later advancements in technology instigated use of this function for switching to a different font or character set and back. This was used, for instance, in the Russian character set known as KOI7-switched, where SO starts printing Russian letters, and SI starts printing Latin letters again. Similarly, they are used for switching between Katakana and Roman letters in the 7-bit version of the Japanese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carriage Return
A carriage return, sometimes known as a cartridge return and often shortened to CR, or return, is a control character or mechanism used to reset a device's position to the beginning of a line of text. It is closely associated with the line feed and newline concepts, although it can be considered separately in its own right. Typewriters Originally, the term "carriage return" referred to a mechanism or lever on a typewriter. For machines where the type element was fixed and the paper held in a moving ''carriage'', this lever was on the left attached to the moving carriage, and operated after typing a line of text to cause the carriage to return to the far right so the type element would be aligned to the left side of the paper. The lever would also usually ''feed'' the paper to advance to the next line. Many electric typewriters such as IBM Electric or Underwood Electric made carriage return to be another key on the keyboard instead of a lever. The key was usually labeled "car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Form Feed
A page break is a marker in an electronic document that tells the document interpreter that the content which follows is part of a new page. A page break causes a form feed to be sent to the printer during spooling of the document to the printer. Thus it is one of the elements that contributes to pagination. Form feed Form feed is a page-breaking ASCII control character. It directs the printer to eject the current page and to continue printing at the top of another. Often, it will also cause a carriage return. The form feed character code is defined as 12 (0xC in hexadecimal), and may be represented as control+L or ^L. In a related use, control+L can be used to clear the screen in Unix shells such as bash. In the C programming language (and other languages derived from C), the form feed character is represented as '\f'. Unicode also provides the character as a printable symbol for a form feed (not as the form feed itself). The form feed character is considered whitespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Tab
The tab key (abbreviation of tabulator key or tabular key) on a keyboard is used to advance the cursor to the next tab stop. History The word ''tab'' derives from the word ''tabulate'', which means "to arrange data in a tabular, or table, form." When a person wanted to type a table (of numbers or text) on a typewriter, there was a lot of time-consuming and repetitive use of the space bar and backspace key. To simplify this, a horizontal bar was placed in the mechanism called the tabulator rack. Pressing the tab key would advance the carriage to the next tabulator stop. The original tabulator stops were adjustable clips that could be arranged by the user on the tabulator rack. Fredric Hillard filed a patent application for such a mechanism in 1900. The tab mechanism came into its own as a rapid and consistent way of uniformly indenting the first line of each paragraph. Often a first tab stop at 5 or 6 characters was used for this, far larger than the indentation used when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Feed
Newline (frequently called line ending, end of line (EOL), next line (NEL) or line break) is a control character or sequence of control characters in character encoding specifications such as ASCII, EBCDIC, Unicode, etc. This character, or a sequence of characters, is used to signify the end of a line of text and the start of a new one. History In the mid-1800s, long before the advent of teleprinters and teletype machines, Morse code operators or telegraphists invented and used Morse code prosigns to encode white space text formatting in formal written text messages. In particular the Morse prosign (mnemonic reak ext) represented by the concatenation of literal textual Morse codes "B" and "T" characters sent without the normal inter-character spacing is used in Morse code to encode and indicate a ''new line'' or ''new section'' in a formal text message. Later, in the age of modern teleprinters, standardized character set control codes were developed to aid in white spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Tab
The tab key (abbreviation of tabulator key or tabular key) on a keyboard is used to advance the cursor to the next tab stop. History The word ''tab'' derives from the word ''tabulate'', which means "to arrange data in a tabular, or table, form." When a person wanted to type a table (of numbers or text) on a typewriter, there was a lot of time-consuming and repetitive use of the space bar and backspace key. To simplify this, a horizontal bar was placed in the mechanism called the tabulator rack. Pressing the tab key would advance the carriage to the next tabulator stop. The original tabulator stops were adjustable clips that could be arranged by the user on the tabulator rack. Fredric Hillard filed a patent application for such a mechanism in 1900. The tab mechanism came into its own as a rapid and consistent way of uniformly indenting the first line of each paragraph. Often a first tab stop at 5 or 6 characters was used for this, far larger than the indentation used when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backspace
Backspace () is the keyboard key that originally pushed the typewriter carriage one position backwards and in modern computer systems moves the display cursor one position backwards,"Backwards" means to the left for left-to-right languages. deletes the character at that position, and shifts back the text after that position by one position. Typewriter In someMany typewriters don't advance accent characters, so that no backspace is needed. However, it is still used e.g. for combining "o" with "/". typewriters, a typist would, for example, type a lowercase letter A with acute accent (á) by typing a lowercase letter A, backspace, and then the acute accent key. This technique (also known as overstrike) is the basis for such spacing modifiers in computer character sets such as the ASCII caret (^, for the circumflex accent). Backspace composition no longer works with typical modern digital displays or typesetting systems.There is no reason why a digital display or typesetting system co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Character
A bell code (sometimes bell character) is a device control code originally sent to ring a small electromechanical bell on tickers and other teleprinters and teletypewriters to alert operators at the other end of the line, often of an incoming message. Though tickers punched the bell codes into their tapes, printers generally do not print a character when the bell code is received. Bell codes are usually represented by the label "BEL". They have been used since 1870 (initially in Baudot code). To maintain backward compatibility, video display terminals (VDTs) that replaced teletypewriters included speakers or buzzers to perform the same function, as did the personal computers that followed. Modern terminal emulators often integrate the warnings to the desktop environment (e.g., the macOS Terminal will play the system warning sound) and also often offer a silent ''visual bell'' feature that flashes the terminal window briefly. Representations In ASCII and Unicode the characte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Of Text
The End-of-Text character (ETX) is a control character used to inform the receiving computer that the end of a record has been reached. This may or may not be an indication that all of the data in a record have been received. In ASCII and in EBCDIC, ETX is code point 0x03, often displayed as {{mono, ^C). It is often used as a "break" character (Control-C) to interrupt a program or process. In TOPS-20, it was used to gain the system's attention before logging in. It is often used in conjunction with Start of Text (STX) and Data Link Escape (DLE), e.g., to distinguish frames in the Data link layer. mIRC uses ETX as the color character escape character. See also * C0 and C1 control codes The C0 and C1 control code or control character sets define control codes for use in text by computer systems that use ASCII and derivatives of ASCII. The codes represent additional information about the text, such as the position of a curso ... Control characters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Null Character
The null character (also null terminator) is a control character with the value zero. It is present in many character sets, including those defined by the Baudot and ITA2 codes, ISO/IEC 646 (or ASCII), the C0 control code, the Universal Coded Character Set (or Unicode), and EBCDIC. It is available in nearly all mainstream programming languages. It is often abbreviated as NUL (or NULL, though in some contexts that term is used for the null pointer). In 8-bit codes, it is known as a null byte. The original meaning of this character was like NOP—when sent to a printer or a terminal, it has no effect (some terminals, however, incorrectly display it as space). When electromechanical teleprinters were used as computer output devices, one or more null characters were sent at the end of each printed line to allow time for the mechanism to return to the first printing position on the next line. On punched tape, the character is represented with no holes at all, so a new unpunched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |