|
Volterra Equations
Volterra (; Latin: ''Volaterrae'') is a walled mountaintop town in the Tuscany region of Italy. Its history dates from before the 8th century BC and it has substantial structures from the Etruscan, Roman, and Medieval periods. History Volterra, known to the ancient Etruscans as ''Velathri'' or ''Vlathri'' and to the Romans as ''Volaterrae'', is a town and ''comune'' in the Tuscany region of Italy. The site is believed to have been continuously inhabited as a city since at least the end of the 8th century BC. The town was a Bronze Age settlement of the Proto-Villanovan culture. It became an important Etruscan centre as one of the "twelve cities" of the Etruscan League. It was allied to Rome at the end of the 3rd century BC and became a municipium. The wealthy Caecina family lived here and Gaius Caecina Largus and the eminent Aulus Caecina Severus (consul 2–1 BC) built the theatre and probably other monuments. Other important families here were the Persii and the Lael ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscany
Tuscany ( ; ) is a Regions of Italy, region in central Italy with an area of about and a population of 3,660,834 inhabitants as of 2025. The capital city is Florence. Tuscany is known for its landscapes, history, artistic legacy, and its influence on high culture. It is regarded as the birthplace of the Italian Renaissance and of the foundations of the Italian language. The prestige established by the Tuscan dialect's use in literature by Dante Alighieri, Petrarch, Giovanni Boccaccio, Niccolò Machiavelli and Francesco Guicciardini led to its subsequent elaboration as the language of culture throughout Italy. It has been home to many figures influential in the history of art and science, and contains well-known museums such as the Uffizi and the Palazzo Pitti. Tuscany is also known for its wines, including Chianti, Vino Nobile di Montepulciano, Morellino di Scansano, Brunello di Montalcino and white Vernaccia di San Gimignano. Having a strong linguistic and cultural identity, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. After adjacent lands had been conquered its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto and western Campania. A large body of literature has flourished on the origins of the Etruscans, but the consensus among modern scholars is that the Etruscans were an indigenous population. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900 BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany (; ) was an Italian monarchy located in Central Italy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1860, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In the 19th century the population of the Grand Duchy was about 1,815,000 inhabitants. Having brought nearly all Tuscany under his control after conquering the Republic of Siena, Cosimo I de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, Cosimo I de' Medici, was elevated by a papal bull of Pope Pius V to Grand Duke of Tuscany on 27 August 1569. The Grand Duchy was ruled by the House of Medici until the extinction of its senior branch in 1737. While not as internationally renowned as the old republic, the grand duchy thrived under the Medici and it bore witness to unprecedented economic and military success under Cosimo I and his sons, until the reign of Ferdinando II de' Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany, Ferdinando II, which saw the beginning of the state's long economic decline. That econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medici
The House of Medici ( , ; ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first consolidated power in the Republic of Florence under Cosimo de' Medici and his grandson Lorenzo "the Magnificent" during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Mugello region of Tuscany, and prospered gradually in trade until it was able to fund the Medici Bank. This bank was the largest in Europe in the 15th century and facilitated the Medicis' rise to political power in Florence, although they officially remained citizens rather than monarchs until the 16th century. In 1532, the family acquired the hereditary title Duke of Florence. In 1569, the duchy was elevated to the Grand Duchy of Tuscany after territorial expansion. The Medici ruled the Grand Duchy from its inception under the builder Cosimo I until 1737, with the death of Gian Gastone de' Medici. The Medici produced four popes of the Catholic Church— Pope Leo X (1513–1521), Pope Clement VI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Florence
The Republic of Florence (; Old Italian: ), known officially as the Florentine Republic, was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany, Italy. The republic originated in 1115, when the Florentine people rebelled against the Margraviate of Tuscany upon the death of Matilda of Tuscany, who controlled vast territories that included Florence. The Florentines formed a commune in Rabodo's (Matilda’s successor) successors' place. The republic was ruled by a council known as the Signoria of Florence. The signoria was chosen by the (titular ruler of the city), who was elected every two months by Florentine guild members. During the Republic's history, Florence was an important cultural, economic, political and artistic force in Europe. Its coin, the florin, was the dominant trade coin of Western Europe for large scale transactions and became widely imitated throughout the continent. During the Republican period, Florence was al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , such that is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium or ammonium. By itself, "alum" often refers to potassium alum, with the formula . Other alums are named after the monovalent ion, such as sodium alum and ammonium alum. The name "alum" is also used, more generally, for salts with the same formula and structure, except that aluminium is replaced by another Valence (chemistry), trivalent metal ion like chromium#Chromium(III), chromium, or sulfur is replaced by another chalcogen like selenium. The most common of these analogs is chrome alum . In most industries, the name "alum" (or "papermaker's alum") is used to refer to aluminium sulfate, , which is used for most industrial flocculation (the variable is an integer whose size depends on the amount of water absorbed into the alum). For medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
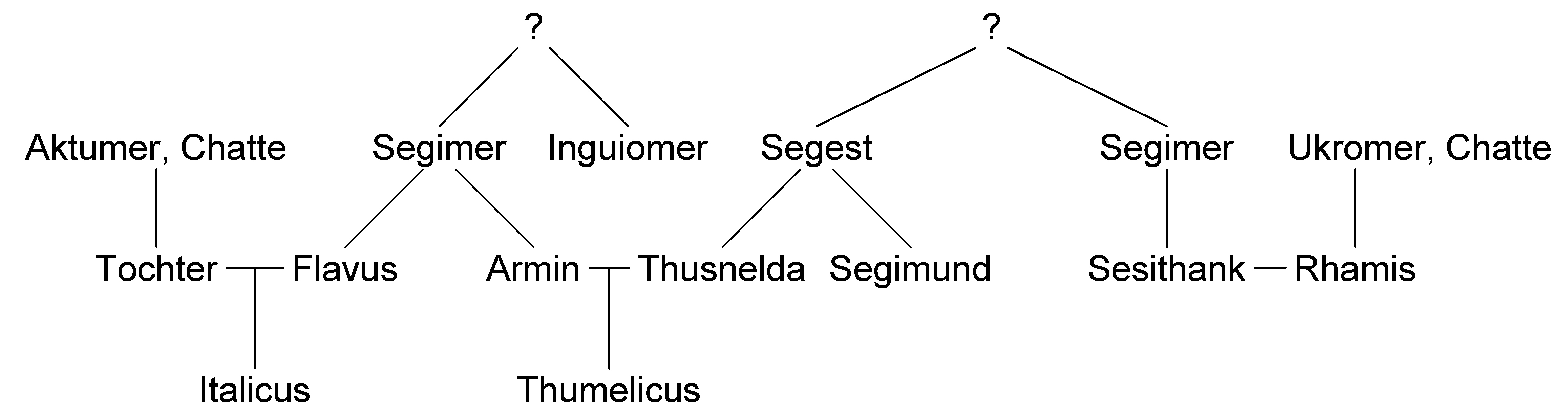
Arminius
Arminius (; 18/17 BC–AD 21) was a chieftain of the Germanic peoples, Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in AD 9, in which three Roman legions under the command of general and governor Publius Quinctilius Varus were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest precipitated the Roman Empire's permanent strategic withdrawal and the deprovincialization of Germania Magna, and modern historians regard it as one of Imperial Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization (cultural), Romanization of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history. Born a prince of the Cherusci tribe, Arminius was part of the Roman-friendly faction of the tribe. He learned Latin and served in the Roman military, which gained him Roman citizenship, and the rank of Equites, ''eques''. After serving with distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; ) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River. As a Roman domain Moesia was administered at first by the governor of Noricum as 'Civitates of Moesia and Triballia'. It included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Albania, northern parts of North Macedonia (Moesia Superior), Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobruja and small parts of Southern Ukraine (Moesia Inferior). Geography In ancient geographical sources, Moesia was bounded to the south by the Haemus (Balkan Mountains) and Scardus (Šar) mountains, to the west by the Drinus (Drina) river, on the north by the Donaris (Danube) and on the east by the Euxine (Black Sea). History The region of Moesia was inhabited chiefly by Thracian, Illyrian, and Thraco-Illyrian peoples. The name of the region comes from Moesi, the Latin name of a Thracian tribe who lived there before the Roman conquest. Parts of Moes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propraetor
In ancient Rome, a promagistrate () was a person who was granted the power via '' prorogation'' to act in place of an ordinary magistrate in the field. This was normally ''pro consule'' or ''pro praetore'', that is, in place of a consul or praetor, respectively. This was an expedient development, starting in 327 BC and becoming regular by 241 BC, that was meant to allow consuls and praetors to continue their activities in the field without disruption. By allowing veteran commanders to stay in the field rather than being rotated out for someone who may not have had much experience in the theatre, the practice helped increase the chances of victory. Whether a commander, however, would be kept was largely decided politically and often motivated by commanders' ambitions. However, the effect of prorogation was to allow commanders to retain their positions as long as political support existed, weakening the republican check of the annual magistracy (and the rotation that imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aulus Caecina Severus
Aulus Caecina Severus was a Roman politician and general who was consul in 1 BC. He was Emperor Augustus' representative in Moesia when the Great Illyrian Revolt broke out. As a result, he spent 4 years in heavy fighting against the Illyrian tribes before the revolt was suppressed by the Romans. In 14 AD he was in charge of several legions on the lower Rhine which mutinied on the death of Augustus. He was recorded as having handled this poorly, with the situation only being salvaged by the intervention of his commander-in-chief, Germanicus. Over the next two years, while campaigning in Germany, Caecina led his legions with skill and verve. At the conclusion of one hard-fought battle he famously routed the army of Arminius, who seven years earlier had destroyed three Roman legions. He was eulogised by the chroniclers for his exploits. On his return to Rome he was awarded triumph honours. Biography Aulus Caecina Severus was descended from a distinguished Volaterran family of Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caecinia Gens
The gens Caecinia was a plebeian family of Etruscan origin at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are first mentioned in the time of Cicero, and they remained prominent through the first century of the Empire, before fading into obscurity in the time of the Flavian emperors. A family of this name rose to prominence once more at the beginning of the fifth century.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. I, p. 529 (" Caecina"). Origin The Etruscan roots of the Caecinae are indicated by the form of their nomen, which in the masculine form ends in ', typical of Etruscan names. The feminine form, ''Caecinia'', is formed as though the masculine form were ''Caecinius'', which is also encountered, though rarely, in inscriptions. The Caecinae seem either to have derived their name from, or given it to, the river Caecina, which flows by the town of Volaterrae, one of the ancient cities of Etruria. A sepulchre belonging to the Caecinae has been discovered near Vol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (: ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ('duty holders'), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privileges and protections of citizenship. Every citizen was a . The distinction of was not made in the Roman Kingdom; instead, the immediate neighbours of the city were invited or compelled to transfer their populations to the urban structure of Rome, where they took up residence in neighbourhoods and became Romans . Under the Roman Republic the practical considerations of incorporating communities into the city-state of Rome forced the Romans to devise the concept of , a distinct state under the jurisdiction of Rome. It was necessary to distinguish various types of and other settlements, such as the colony. In the early Roman Empire these distinctions began to disappear; for example, when Pliny the Elder served in the Roman army, the distinctio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |