|
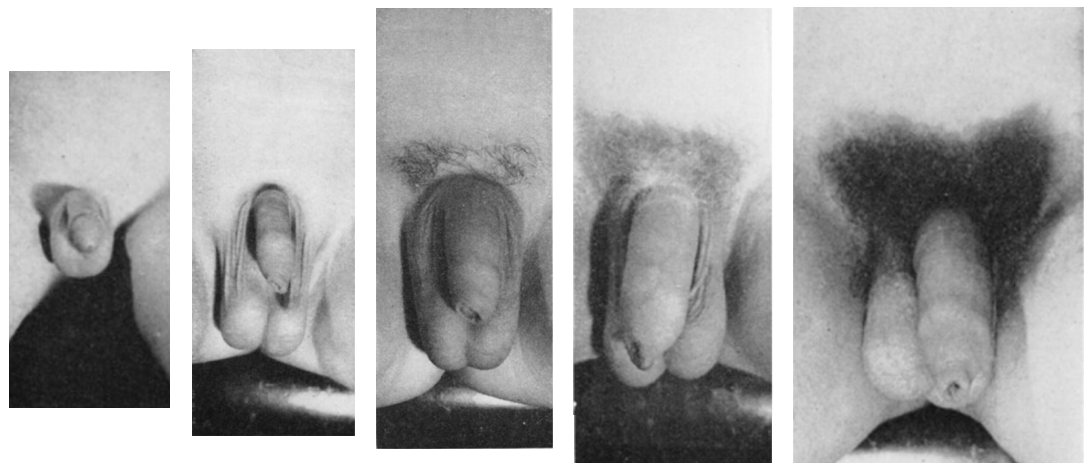
Voice Change
A voice change or voice mutation, sometimes referred to as a voice break or voice crack, commonly refers to the deepening of the voice of men as they reach puberty. Before puberty both sexes have roughly similar vocal pitches, but during puberty the male voice typically deepens an octave, while the female voice usually deepens only by a few tones. A similar effect is a "voice crack", during which a person's voice suddenly and unintentionally enters a higher register (usually falsetto) for a brief period of time. This may be caused by singing or talking at a pitch outside the person's natural vocal range, stress, fatigue, emotional tension, or the physical changes associated with puberty. An instance of a voice crack (when associated with puberty) lasts for only a moment and generally occurs less frequently as a person grows into maturity. Anatomical changes Most of the voice change begins around puberty. Adult pitch is reached 2–3 years later, but the voice does not stabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles in a male. In response to the signals, the gonads produce hormones that stimulate libido and the growth, function, and transformation of the brain, bones, muscle, blood, skin, hair, breasts, and sex organs. Physical growth—height and weight—accelerates in the first half of puberty and is completed when an adult body has been developed. Before puberty, the external sex organs, known as primary sexual characteristics, are sex characteristics that distinguish males and females. Puberty leads to sexual dimorphism through the development of the secondary sex characteristics, which further distinguish the sexes. On average, females begin puberty at age 10½ and complete puberty at ages 15-17; males begin at ages 11½-12 and complete pube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( ; ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions to musical form have led him to be called "Father of the Symphony" and "Father of the String quartet". Haydn arose from humble origins, the child of working people in a rural village. He established his career first by serving as a chorister at St. Stephen's Cathedral, Vienna, then through an arduous period as a freelance musician. Eventually he found career success, spending much of his working life as Kapellmeister, music director for the wealthy Esterházy family at their palace of Eszterháza in rural Hungary. Though he had his own orchestra there, it isolated him from other composers and trends in music so that he was, as he put it, "forced to become original". During this period his music circulated widely in publication, eventuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish instruments in the same category (e.g., an oboe and a clarinet, both woodwinds). In simple terms, timbre is what makes a particular musical instrument or human voice have a different sound from another, even when they play or sing the same note. For instance, it is the difference in sound between a guitar and a piano playing the same note at the same volume. Both instruments can sound equally tuned in relation to each other as they play the same note, and while playing at the same amplitude level each instrument will still sound distinctive with its own unique tone color. Musicians distinguish instruments based on their varied timbres, even instruments playing notes at the same pitch and volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messiah (Handel)
''Messiah'' (HWV 56) is an English-language oratorio composed in 1741 by George Frideric Handel. The text was compiled from the King James Bible and the Coverdale Bible, Coverdale Psalter by Charles Jennens. It was first performed in Dublin on 13 April 1742 and received its London premiere a year later. After an initially modest public reception, the oratorio gained in popularity, eventually becoming one of the best-known and most frequently performed choral works in Western culture#Music, Western music. Handel's reputation in England, where he had lived since 1712, had been established through his compositions of Italian opera. He turned to English oratorio in the 1730s in response to changes in public taste; ''Messiah'' was his sixth work in this genre. Although its Structure of Handel's Messiah, structure resembles that of Opera#The Baroque era, opera, it is not in dramatic form; there are no impersonations of characters and no direct speech. Instead, Jennens's text is an ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti. Born in Halle, Germany, Handel spent his early life in Hamburg and Italy before settling in London in 1712, where he spent the bulk of his career and became a naturalised British subject in 1727. He was strongly influenced both by the middle-German polyphonic choral tradition and by composers of the Italian Baroque. In turn, Handel's music forms one of the peaks of the "high baroque" style, bringing Italian opera to its highest development, creating the genres of English oratorio and organ concerto, and introducing a new style into English church music. He is consistently recognized as one of the greatest composers of his age. Handel started three commercial opera companies to supply the English nobility with Italian opera. In 1737, he had a physical breakdown, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorio Allegri
Gregorio Allegri (17 February 1652) was an Italian Catholic priest and composer of the Roman School and brother of Domenico Allegri; he was also a singer. He was born"Allegri, Gregorio" in '' Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 271. and died in Rome. He is chiefly known for his '' Miserere'' for two choirs. Life He studied music as a ''puer'' (boy chorister) at San Luigi dei Francesi, under the '' maestro di cappella'' Giovanni Bernardino Nanino, brother of Giovanni Maria Nanino. Being intended for the Church, he obtained a benefice in the cathedral of Fermo. Here he composed a large number of motets and other sacred music, which, being brought to the notice of Pope Urban VIII, obtained for him an appointment in the choir of the Sistine Chapel at Rome as a contralto. He held this from 6 December 1629 until his death. Allegri is said to have been a virtuous man, as well as good-natured and generous to the poor and to prisoners. Among Alle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exultate Jubilate
(Exult, rejoice), K. 165, is a 1773 motet by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart. History This religious solo motet was composed when Mozart was staying in Milan during the production of his opera '' Lucio Silla'' which was being performed there in the Teatro Regio Ducale. It was written for the castrato Venanzio Rauzzini, who had sung the part of the '' primo uomo'' Cecilio in ''Lucio Silla'' the previous year. While waiting for the end of the run (from 26 December 1772 to 25 January 1773), Mozart composed the motet for his singer, whose technical excellence he admired. Its first performance took place at the Theatine Church on 17 January 1773, while Rauzzini was still singing in Mozart's opera at night. Mozart made some revisions around 1780. On 30 May 1779, a Trinity Sunday, a revised version was performed by Francesco Ceccarelli at the Holy Trinity Church, Salzburg. Another revised version was intended for Christmas. The manuscripts of the two Salzburg versions were discovered in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age resulted in List of compositions by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, more than 800 works representing virtually every Western classical genre of his time. Many of these compositions are acknowledged as pinnacles of the symphony, symphonic, concerto, concertante, chamber music, chamber, operatic, and choir, choral repertoires. Mozart is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Classical music, Western music, with his music admired for its "melodic beauty, its formal elegance and its richness of harmony and texture". Born in Salzburg, Mozart showed Child prodigy, prodigious ability from his earliest childhood. At age five, he was already competent on keyboard and violin, had begun to compose, and performed before European r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Rosselli (historian)
John Rosselli (8 June 1927, Florence – 16 January 2001, Cambridge) was an Italian-born British historian, academic, journalist, music critic, and writer on music. He earned degrees in history from Swarthmore College in the United States and the University of Cambridge in England; studying under Herbert Butterfield at the latter institution from 1948 through 1951. After completing his education, he worked as a features writer, editor, and critic for ''The Guardian''; rising to the post of deputy London editor. He left the paper in 1964 to join the faculty of University of Sussex where he became a reader and taught history until 1989. He wrote extensively on the history of Italian music, particularly opera. His books include ''The Opera Industry in Italy from Cimarosa to Verdi: The Role of the Impresario'' (Cambridge University Press, 1984), ''Music and Musicians in Nineteenth-Century Italy'' (1991, Batsford Books Batsford Books is an independent British book publisher. Batsford ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castrato
A castrato (Italian; : castrati) is a male singer who underwent castration before puberty in order to retain a singing voice equivalent to that of a soprano, mezzo-soprano, or contralto. The voice can also occur in one who, due to an endocrinological condition, never reaches sexual maturity. Castration before puberty (or in its early stages) prevents the larynx from being transformed by the normal physiological events of puberty. As a result, the vocal range of prepubescence (shared by both sexes) is largely retained, and the voice develops into adulthood in a unique way. Prepubescent castration for this purpose diminished greatly in the late 18th century. Methods of castration used to terminate the onset of puberty varied. Methods involved using opium to medically induce a coma, then submerging the boy into an ice or milk bath where the procedure of either twisting the testicles until they atrophied, or complete removal via surgical cutting was performed (however the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castration
Castration is any action, surgery, surgical, chemical substance, chemical, or otherwise, by which a male loses use of the testicles: the male gonad. Surgical castration is bilateral orchiectomy (excision of both testicles), while chemical castration uses pharmaceutical drugs to deactivate the testes. Some forms of castration cause sterilization (medicine), sterilization (permanently preventing the castrated person or animal from reproduction, reproducing); it also greatly reduces the production of hormones, such as testosterone and estrogen. Surgical castration in animals is often called neutering. #Other animals, Castration of animals is intended to favor a desired development of the animal or of its habits, as an anaphrodisiac or to prevent overpopulation. The parallel of castration for female animals is spaying. Castration may also refer medically to oophorectomy in female humans and animals. The term ''castration'' may also be sometimes used to refer to emasculation where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countertenors
A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a specific kind of countertenor) may match the soprano's range of around C4 to C6.A sopranist is a term, widely used falsely, used to describe a countertenor whose vocal range is so high it is equivalent to that of a soprano. Countertenors often have tenor or baritone chest voices, but sing in falsetto or head voice much more often than they do in their chest voice. The nature of the countertenor voice has radically changed throughout musical history, from a modal voice, to a modal and falsetto voice, to the primarily falsetto voice that is denoted by the term today. This is partly because of changes in human physiology ( increase in body height) and partly because of fluctuations in pitch. The term first came into use in England during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |