|
Vilsmaier Reagent
The Vilsmeier reagent is an organic compound with the formula CH3)2NCHCll. It is a salt consisting of the N,N-dimethyliminium cation ( CH3)2N=CHClsup>+) and chloride anion. Depending on the particular reaction, the anion can vary. In typical POCl3-based reactions, the anion is PO2Cl2−. The iminium cation CH3)2N=CHClsup>+ is the reactive component of interest. This iminium species is a derivative of the imidoyl chloride CH3N=CHCl. Analogues of this particular reagent are generated when tertiary amides other than DMF are treated with POCl3. The salt is a white solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Vilsmeier reagent is the active intermediate in the formylation reactions, the Vilsmeier reaction or Vilsmeier-Haack reaction that use mixtures of dimethylformamide and phosphorus oxychloride Phosphoryl chloride (commonly called phosphorus oxychloride) is a colourless liquid with the formula . It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
Some chemical authorities define an organic compound as a chemical compound that contains a carbon–hydrogen or carbon–carbon bond; others consider an organic compound to be any chemical compound that contains carbon. For example, carbon-containing compounds such as alkanes (e.g. methane ) and its derivatives are universally considered organic, but many others are sometimes considered inorganic, such as certain compounds of carbon with nitrogen and oxygen (e.g. cyanide ion , hydrogen cyanide , chloroformic acid , carbon dioxide , and carbonate ion ). Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, and even ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iminium Cation
In organic chemistry, an iminium cation is a polyatomic ion with the general structure . They are common in synthetic chemistry and biology. Structure Iminium cations adopt alkene-like geometries: the central C=N unit is nearly coplanar with all four substituents. Unsymmetrical iminium cations can exist as cis and trans isomers. The C=N bonds, which are near 129 picometers in length, are shorter than C-N single bonds. Cis/trans isomers are observed. The C=N distance is slightly shorter in iminium cations than in the parent imine, and computational studies indicate that the C=N bonding is also stronger in iminium vs imine, although the C=N distance contracts only slightly. These results indicate that the barrier for rotation is higher than in the parent imines. Formation Iminium cations are obtained by protonation and alkylation of imines: : : They also are generated by the condensation of secondary amines with ketones or aldehydes: : This rapid, reversible reaction is one st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
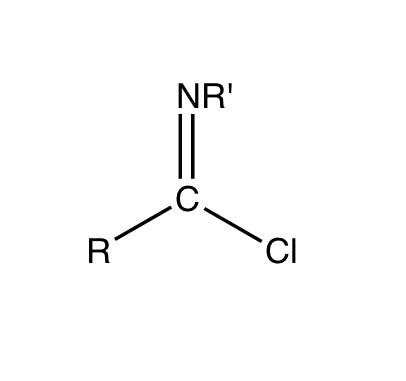
Imidoyl Chloride
Imidoyl chlorides are organic compounds that contain the functional group RC(NR')Cl. A double bond exist between the R'N and the carbon centre. These compounds are analogues of acyl chloride. Imidoyl chlorides tend to be highly reactive and are more commonly found as intermediates in a wide variety of synthetic procedures. Such procedures include Gattermann aldehyde synthesis, Houben-Hoesch reaction, Houben-Hoesch ketone synthesis, and the Beckmann rearrangement. Their chemistry is related to that of enamines and their tautomers when the α hydrogen is next to the C=N bond.Ulrich, H. The Chemistry of Imidoyl Halides; Plenum Press: New York, 1968; pp. 55–112. Many chlorinated N-heterocycles are formally imidoyl chlorides, e.g. 2-Chloropyridine, 2-chloropyridine, 2, 4, and 6-chloropyrimidines. Synthesis and properties Imidoyl halides are synthesized by combining amides and halogenating agents. The structure of the carboxylic acid amides plays a role in the outcome of the synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide, DMF is an organic compound with the chemical formula . Its structure is . Commonly abbreviated as DMF (although this initialism is sometimes used for 2,5-dimethylfuran, dimethylfuran, or dimethyl fumarate), this colourless liquid is Miscibility, miscible with Water (molecule), water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions. Dimethylformamide is odorless, but chemical purity, technical-grade or degraded samples often have a fishy smell due to impurity of dimethylamine. Dimethylamine degradation impurities can be removed by Sparging (chemistry), sparging samples with an inert gas such as argon or by sonication, sonicating the samples under reduced pressure. As its name indicates, it is structurally related to formamide, having two methyl groups in the place of the two hydrogens. DMF is a polar molecule, polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent with a high boiling point. It facilitates reactions that follow polar mechanisms, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus Oxychloride
Phosphoryl chloride (commonly called phosphorus oxychloride) is a colourless liquid with the formula . It hydrolyses in moist air releasing phosphoric acid and fumes of hydrogen chloride. It is manufactured industrially on a large scale from phosphorus trichloride and oxygen or phosphorus pentoxide. It is mainly used to make phosphate esters. Structure Like phosphate, is tetrahedral in shape. It features three P−Cl bonds and one strong P–O bond, with an estimated bond dissociation energy of 533.5 kJ/mol. Unlike in the case of , the Schomaker-Stevenson rule predicts appropriate bond length for the P–O bond only if the P–O bond is treated as a double bond, P=O. More modern treatments explain the tight P–O bond as a combination of lone pair transfer from the phosphorus to the oxygen atom and a dative ''π'' back-bond that produces an effective + −configuration. Phosphoryl chloride exists as neutral molecules in the solid, liquid and gas states. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eschenmoser's Salt
In organic chemistry, Eschenmoser's salt (named for Albert Eschenmoser) is the ionic, organic compound . It is the iodide salt of the dimethylaminomethylene cation . The dimethylaminomethylene cation is a strong dimethylaminomethylating agent, used to prepare derivatives of the type .E. F. Kleinman in "Dimethylmethyleneammonium Iodide and Chloride" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. Enolates, silyl enol ethers, and even more acidic ketones undergo efficient dimethylaminomethylation. Once prepared, such tertiary amines can be further methylated and then subjected to base-induced elimination to afford methylidenated ketones. The salt was first prepared by the group of Albert Eschenmoser after whom the reagent is named. Structure and bonding Dimethylaminomethylene cation is described as a resonance hybrid of the carbocation and an iminium cation: : The atoms are coplanar. The cation is isoelectronic with isob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |