|
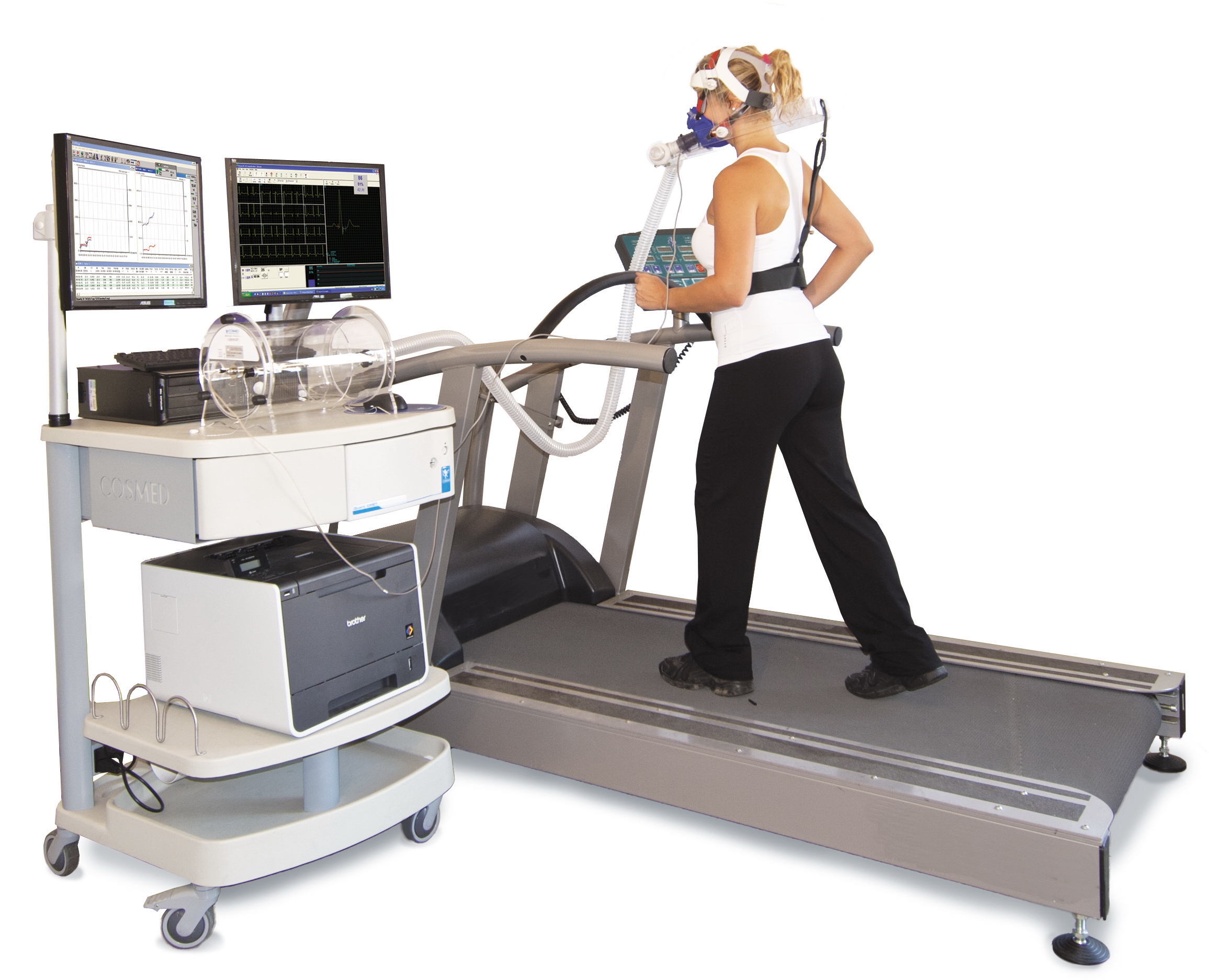
Ventilatory Threshold
{{Multiple issues, {{more footnotes, date=December 2014{{cleanup, date=December 2014, reason=Wikipedia Markup fixes. In kinesiology, the ventilatory threshold (VT1) refers to the point during exercise at which ventilation starts to increase at a faster rate than VO2 (V – volume, O2 – oxygen). One's threshold is said to reflect levels of anaerobiosis and lactate accumulation. As the intensity level of the activity being performed increases, breathing becomes faster; more steadily first and then more rapid as the intensity increases. When breathing surpasses normal ventilation rate, one has reached ventilatory threshold. For most people this threshold lies at exercise intensities between 50% and 75% of VO2 max. A major factor affecting one's ventilatory threshold is their maximal ventilation (amount of air entering and exiting lungs). This is dependent on their personal experience with the activity and how physically fit the person is. Comparison studies of more athletic people ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesiology
Kinesiology () is the scientific study of human body movement. Kinesiology addresses physiological, anatomical, biomechanical, pathological, neuropsychological principles and mechanisms of movement. Applications of kinesiology to human health include biomechanics and orthopedics; strength and conditioning; sport psychology; motor control; skill acquisition and motor learning; methods of rehabilitation, such as physical and occupational therapy; and sport and exercise physiology. Studies of human and animal motion include measures from motion tracking systems, electrophysiology of muscle and brain activity, various methods for monitoring physiological function, and other behavioral and cognitive research techniques. Basics Kinesiology studies the science of human movement, performance, and function by applying the fundamental sciences of Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Chemistry, Biochemistry, Biophysics, Biomechanics, Biomathematics, Biostatistics, Physiology, Exerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greg Lemond
Gregory James LeMond (born June 26, 1961) is an American former professional road racing cyclist, entrepreneur, and anti-doping advocate. A two-time winner of the Road Race World Championship (1983 and 1989) and a three-time winner of the Tour de France (1986, 1989, and 1990). LeMond is the only American male to win the Tour de France and is considered by many to be the greatest American cyclist of all time, one of the great all-round cyclists of the modern era, and an icon of the sport's globalisation. LeMond began his professional cycling career in 1981. In 1983, he became the first American male cyclist to win the Road World Championship. LeMond won the Tour de France in 1986; he is the first non-European professional cyclist to win the men's Tour. He was accidentally shot with pellets and seriously injured while hunting in 1987. Following the shooting, he underwent two surgeries and missed the next two Tours. At the 1989 Tour, he completed an improbable comeback to win i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Indurain
--> Miguel is a given name and surname, the Portuguese and Spanish form of the Hebrew name Michael. It may refer to: Places * Pedro Miguel, a parish in the municipality of Horta and the island of Faial in the Azores Islands * São Miguel (other), various locations in Azores, Portugal, Brazil and Cape Verde People * Miguel (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media *Miguel (singer) (born 1985), Miguel Jontel Pimentel, American recording artist *Miguel Bosé (born 1956), Spanish pop new wave musician and actor *Miguel Calderón (born 1971), artist and writer * Miguel Cancel (born 1968), former American singer *Miguel Córcega (1929–2008), Mexican actor and director *Miguel de Cervantes (1547–1616), Spanish author * Miguel Delibes (1920–2010), Spanish novelist * Miguel Ferrer (1955–2017), American actor * Miguel Galván (1957–2008), Mexican actor *Miguel Gómez (photographer) (born 1974), Colombian / American photographer. *Miguel Ángel Landa (born 1936), Venez ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steve Prefontaine
Steve Roland "Pre" Prefontaine (January 25, 1951 – May 30, 1975) was an American long-distance runner who from 1973 to 1975 set American records at every distance from 2,000 to 10,000 meters. He competed in the 1972 Summer Olympics, and was preparing for the 1976 Olympics with the Oregon Track Club at the time of his death in 1975. Prefontaine's career, alongside those of Jim Ryun, Frank Shorter, and Bill Rodgers, generated considerable media coverage, which helped inspire the 1970s "running boom." He died at age 24 in an automobile crash near his residence in Eugene, Oregon. One of the premier track meets in the world, the Prefontaine Classic, is held annually in Eugene in his honor. Prefontaine's celebrity and charisma later resulted in two 1990s feature films about his short life. Early life Prefontaine was born on January 25, 1951, in Coos Bay, Oregon. His father, Raymond George Prefontaine (November 11, 1919 – December 21, 2004), was a welder who served in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Exercise
Anaerobic exercise is a type of exercise that breaks down glucose in the body without using oxygen; ''anaerobic'' means "without oxygen". In practical terms, this means that anaerobic exercise is more intense, but shorter in duration than aerobic exercise. The biochemistry of anaerobic exercise involves a process called glycolysis, in which glucose is converted to adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the primary source of energy for cellular reactions. This type of exercise leads to a buildup of lactic acid. Anaerobic exercise may be used to help build endurance, muscle strength, and power. Metabolism Anaerobic metabolism is a natural part of metabolic energy expenditure. Fast twitch muscles (as compared to slow twitch muscles) operate using anaerobic metabolic systems, such that any use of fast twitch muscle fibers leads to an increased anaerobic energy expenditure. Intense exercise lasting upwards of four minutes (e.g. a mile race) may still have considerable ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactate Threshold
Lactate inflection point (LIP), is the exercise intensity at which the blood concentration of lactate and/or lactic acid begins to increase rapidly. It is often expressed as 85% of maximum heart rate or 75% of maximum oxygen intake. When exercising at or below the lactate threshold, any lactate produced by the muscles is removed by the body without it building up. The onset of blood lactate accumulation (OBLA) is often confused with the lactate threshold. With an exercise intensity higher than the threshold the lactate production exceeds the rate at which it can be broken down. The blood lactate concentration will show an increase equal to 4.0mM; it then accumulates in the muscle and then moves to the bloodstream. Regular endurance exercise leads to adaptations in skeletal muscle which raises the threshold at which lactate levels will rise. This is mediated via activation of PGC-1α, which alters the isoenzyme composition of the LDH complex and decreases the activity of the lactat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VO2 Max
VO2 max (also maximal oxygen consumption, maximal oxygen uptake or maximal aerobic capacity) is the maximum rate of oxygen consumption attainable during physical exertion. The name is derived from three abbreviations: "V̇" for volume (the dot appears over the V to indicate "per unit of time"), "O2" for oxygen, and "max" for maximum. A similar measure is VO2 peak (peak oxygen consumption), which is the measurable value from a session of physical exercise, be it incremental or otherwise. It could match or underestimate the actual VO2 max. Confusion between the values in older and popular fitness literature is common. The measurement of V̇O2 max in the laboratory provides a quantitative value of endurance fitness for comparison of individual training effects and between people in endurance training. Maximal oxygen consumption reflects cardiorespiratory fitness and endurance capacity in exercise performance. Elite athletes, such as competitive distance runners, racing cyclists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise professionals and utilise education, lifestyle intervention and specific forms of exercise to rehabilitate and manage acute and chronic injuries and conditions. Understanding the effect of exercise involves studying specific changes in muscular, cardiovascular, and neurohumoral systems that lead to changes in functional capacity and strength due to endurance training or strength training. The effect of training on the body has been defined as the reaction to the adaptive responses of the body arising from exercise or as "an elevation of metabolism produced by exercise". Exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. History Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Physiology
In physiology, respiration is the movement of oxygen from the outside environment to the cells within tissues, and the removal of carbon dioxide in the opposite direction that's to the environment. The physiological definition of respiration differs from the biochemical definition, which refers to a metabolic process by which an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP and NADPH) by oxidizing nutrients and releasing waste products. Although physiologic respiration is necessary to sustain cellular respiration and thus life in animals, the processes are distinct: cellular respiration takes place in individual cells of the organism, while physiologic respiration concerns the diffusion and transport of metabolites between the organism and the external environment. Gas exchanges in the lung occurs by ventilation and perfusion. Ventilation refers to the in and out movement of air of the lungs and perfusion is the circulation of blood in the pulmonary capillaries. In mammals, physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |