|
Venetian Bombardments Of The Beylik Of Tunis (1784–1788)
The Venetian bombardments of the Beylik of Tunis were a series of naval bombardments of the capital and various port cities of the Beylik of Tunis by the Venetian navy in order to force Bey Hammuda ibn Ali to resume the treaty that protected Venetian-flagged shipping from harassment by Barbary pirates. The campaign lasted from 1784 to 1786, with the Venetian navy under Angelo Emo bombarding the harbour towns of Tunisia. The conflict dragged on until 1792, but no major naval actions were undertaken after the winter of 1786/87. Background War broke out between the Beylik of Tunis and the Republic of Venice after a Venetian-flagged merchant ship laden with goods from the Barbary coast was burned by the authorities in Malta due to it being infected with the plague. The Bey of Tunis demanded compensation, but received none, and his demands for an increased annual payment went unheeded. As a result, he declared war on Venice. A Venetian squadron under the Andrea Querini was already o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbary States
The Barbary Coast (also Barbary, Berbery, or Berber Coast) were the coastal regions of central and western North Africa, more specifically, the Maghreb and the Ottoman borderlands consisting of the regencies in Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli, as well as the Sultanate of Morocco from the 16th to 19th centuries. The term originates from an exonym for the Berbers. Political Diversity Barbary was not always a unified political entity. From the 16th century onward, it was divided into four political entities—from west to east—the Alawi Sultanate, the Regency of Algiers, the Regency of Tunis, and the Regency of Tripoli. Major rulers and petty monarchs during the times of the Barbary states' plundering parties included the sultan of Morocco, the dey of Algiers, bey of Tunis, and pasha of Tripoli, respectively. The slave trade The slave trade was not just an economic lifeline to the Barbary States, but was often justified as a form of jihad against Christian states. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bubonic Plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of Plague (disease), plague caused by the Bacteria, bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well as Lymphadenopathy, swollen and painful lymph nodes occurring in the area closest to where the bacteria entered the skin. Acral necrosis, the dark discoloration of skin, is another symptom. Occasionally, swollen lymph nodes, known as "buboes", may break open. The three types of plague are the result of the route of infection: bubonic plague, septicemic plague, and pneumonic plague. Bubonic plague is mainly spread by infected fleas from small animals. It may also result from exposure to the body fluids from a dead plague-infected animal. Mammals such as rabbits, hares, and some cat species are susceptible to bubonic plague, and typically die upon contraction. In the bubonic form of plague, the bacteria enter through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Farina
Cape Farina () is a headland in Bizerte Governorate, Tunisia. It forms the northwestern end of the Gulf of Tunis. The Tunisian towns of Ghar el-Melh (the ancient Castra Delia), Rafraf, Lahmeri, and the beach of Plage Sidi Ali Mekki Est are located along the peninsula. Names The cape was known to the Phoenicians and Punics, Carthaginians as , meaning the , a healing god in the Phoenician pantheon whom the ancient Greeks, Greeks and ancient Romans, Romans variously Interpretatio graeca, interpreted as Asclepius or Apollo. From this, the cape's name was interpreted by Greco-Roman authors as Rusucmona and was known under Roman rule as the () or ('). Its modern Arabic language, Arabic names are ''Ras et-Tarf'' or ''Ras Sidi Ali el-Mekki''. Geography The extremity of Cape Farina forms the northwestern end of the Gulf of Tunis. The geological formation responsible for Cape Farina continues underwater before rising to form Plane Island offshore. History Under Roman Empire, Roman r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
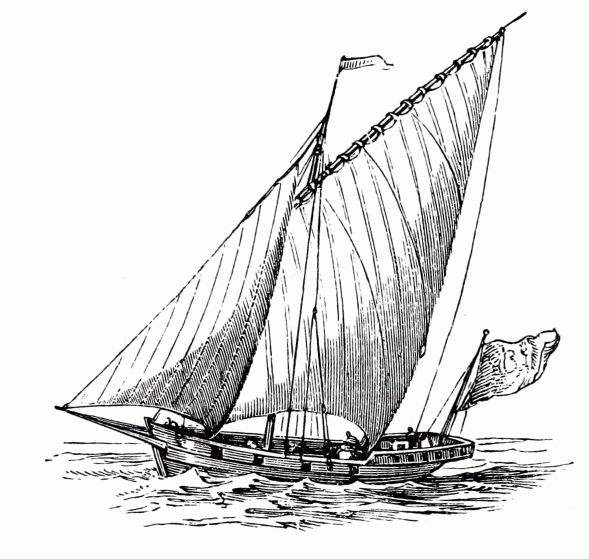
Tartana
A tartane (also tartan, tartana) was a small ship used both as a fishing ship and for coastal trading in the Mediterranean. They were in use for over 300 years until the late 19th century. A tartane had a single mast on which was rigged a large lateen sail, and with a bowsprit and fore-sail. When the wind was aft a square sail Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which a sailing vessel's primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars that are perpendicular (or square) to the median plane of the keel and masts of the vessel. These sp ... was generally hoisted like a cross jack. References * * * Merchant sailing ship types {{ship-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malta
Malta, officially the Republic of Malta, is an island country in Southern Europe located in the Mediterranean Sea, between Sicily and North Africa. It consists of an archipelago south of Italy, east of Tunisia, and north of Libya. The two official languages are Maltese language, Maltese and English language, English. The country's capital is Valletta, which is the smallest capital city in the EU by both area and population. It was also the first World Heritage Site, World Heritage City in Europe to become a European Capital of Culture in 2018. With a population of about 542,000 over an area of , Malta is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, tenth-smallest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population density, ninth-most densely populated. Various sources consider the country to consist of a single urban region, for which it is often described as a city-state. Malta has been inhabited since at least 6500 BC, during the Mesolith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4.7 million inhabitants, including 1.2 million in and around the capital city of Palermo, it is both the largest and most populous island in the Mediterranean Sea. Sicily is named after the Sicels, who inhabited the eastern part of the island during the Iron Age. Sicily has a rich and unique culture in #Art and architecture, arts, Music of Sicily, music, #Literature, literature, Sicilian cuisine, cuisine, and Sicilian Baroque, architecture. Its most prominent landmark is Mount Etna, the tallest active volcano in Europe, and one of the most active in the world, currently high. The island has a typical Mediterranean climate. It is separated from Calabria by the Strait of Messina. It is one of the five Regions of Italy#Autonomous regions with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galiot
A galiot, galliot or galiote, was a small galley boat propelled by sail or oars. There are three different types of naval galiots that sailed on different seas. A ''galiote'' was a type of French flat-bottom river boat or barge and also a flat-bottomed boat with a simple sail for transporting wine. Naval vessels * Mediterranean (16th–17th centuries) : Historically, a galiot was a type of ship with oars, also known as a half-galley, then, from the 17th century forward, a ship with sails and oars. As used by the Barbary pirates against the Republic of Venice, a galiot had two masts and about 16 pairs of oars. Warships of the type typically carried between two and ten cannons of small caliber, and between 50 and 150 men. It was a Barbary galiot, captained by Barbarossa I, that captured two Papal vessels in 1504. * North Sea (17th–19th centuries) : A galiot was a type of Dutch or German merchant ship of 20 to 400 tons ( bm), similar to a ketch, with a rounded fore and aft li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomb-vessel
A bomb vessel, bomb ship, bomb ketch, or simply bomb was a type of wooden sailing naval ship. Its primary armament was not cannons ( long guns or carronades) – although bomb vessels carried a few cannons for self-defence – but mortars mounted forward near the bow and elevated to a high angle, and projecting their fire in a ballistic arc. Explosive shells (also called ''bombs'' at the time) or carcasses were employed rather than solid shot. Bomb vessels were specialized ships designed for bombarding (hence the name) fixed positions on land. In the 20th century, this naval gunfire support role was carried out by the most similar purpose-built World War I- and II-era monitors, but also by other warships now firing long-range explosive shells. Development The first recorded deployment of bomb vessels by the English was for the siege of Calais in 1347 when Edward III deployed single-deck ships with bombardes and other artillery. The first specialised bomb vessels were built t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xebec
A xebec ( or ), also spelled zebec, was a Mediterranean sailing ship that originated in the barbary states (Algeria), it was used mostly for trading. Xebecs had a long overhanging bowsprit and aft-set mizzen mast. The term can also refer to a small, fast vessel of the sixteenth to nineteenth centuries, used almost exclusively in the Mediterranean Sea. Description Xebecs were ships similar to galleys primarily used by Barbary pirates, which have both lateen sails and oars for propulsion. Early xebecs had two masts while later ships had three. Xebecs featured a distinctive hull with pronounced overhanging bow and stern, and rarely displaced more than 200 tons, making them slightly smaller and with slightly fewer guns than frigates of the period. Use by Barbary corsairs These ships were easy to produce and were cheap, and thus nearly every corsair captain ('' Raïs'') had at least one xebec in his fleet. They could be of varying sizes. Some ships had only three guns w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetian Ship Palma
Venetian often means from or related to: * Venice, a city in Italy * Veneto, a region of Italy * Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area Venetians might refer to: * Masters of Venetian painting in 15th-16th centuries * City dwellers of Venice Venetian and the like may also refer to: * Venetian language, a Romance language spoken mostly in the Veneto region * Venice, Florida, a city in Sarasota County, United States *The Venetian Las Vegas, a resort hotel and casino in Las Vegas, Nevada *The Venetian Macao, a hotel and casino in Macau, China *Venetian blind, or Venetian, a common type of window blind similar to Persian blind *Venetian curtain, a type of theater front curtain *''The Venetian Woman'', ''The Venetian Comedy'', or ''The Venetian'' originally ''La veniexiana'' (play), a comedy in Venetian language, 1535-1537 *''The Venetians'', an 1892 novel by Mary Elizabeth Braddon * ''The Venetian'' (play), a work by Clifford Bax * ''The Venetian'' (film), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetian Ship Forza
''Forza'' was a first-rank ship of the line of the Venetian navy, serving from 1774 to 1784, although it was originally laid down in 1719. ''Forza'' was laid down in April 1719 as part of the initial series of the . Her chief architect, Francesco Da Ponte, fled to Russia to seek employment in the new Russian fleet, and her construction was entrusted to another, unknown, architect. With the end of the Ottoman–Venetian Wars after 1718, naval construction was largely suspended and ''Forza'' was only completed to 75% ('18 carats' in Venetian nomenclature) and mothballed in the Arsenal of Venice. She was completed to 87.5% ('21 carats') between 1740 and 1746, but not finished until February 1774, under the auspices of Pietro Paresi. With 55 years, she holds the record for length of time between being laid down and completed at the Arsenal of Venice. When finished, ''Forza'' had a length of slightly over , a displacement of tons, and armed with 70 cannon, although normally, in peaceti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |