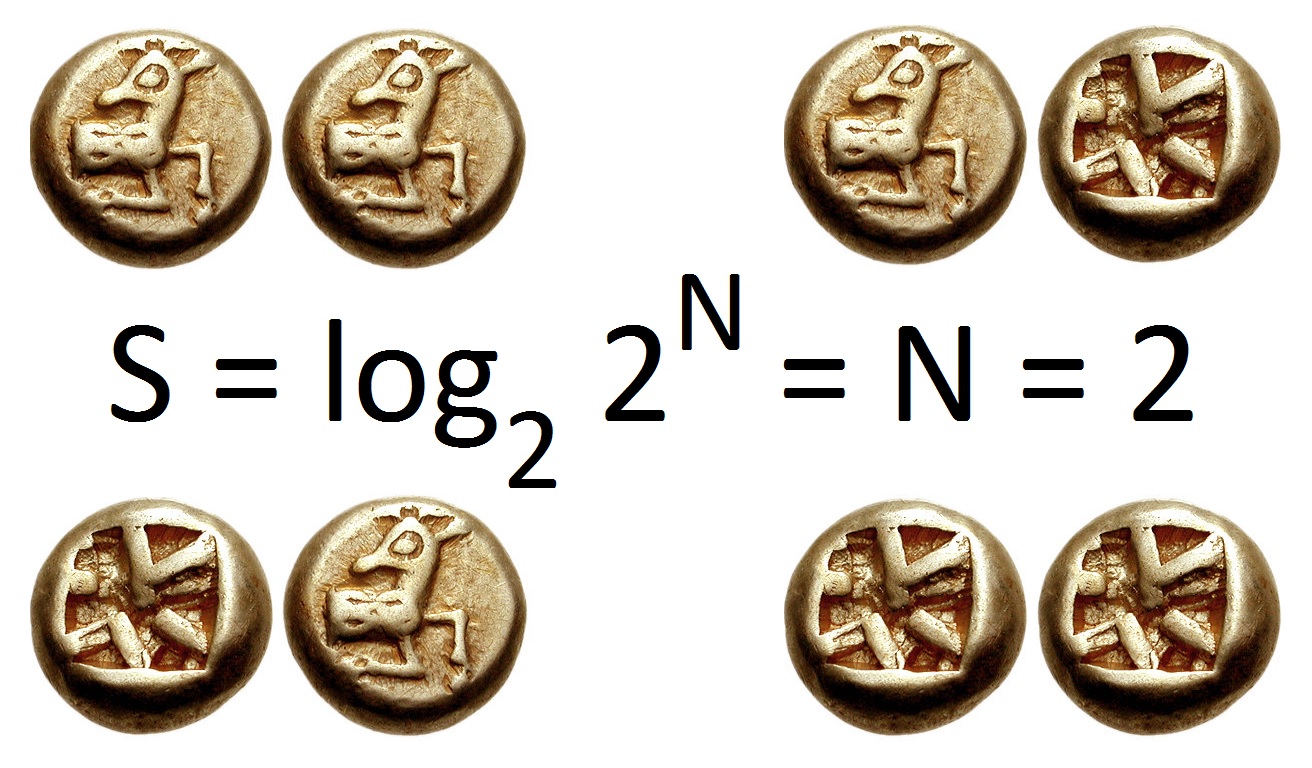|
Variation Of Information
In probability theory and information theory, the variation of information or shared information distance is a measure of the distance between two clusterings ( partitions of elements). It is closely related to mutual information; indeed, it is a simple linear expression involving the mutual information. Unlike the mutual information, however, the variation of information is a true metric, in that it obeys the triangle inequality. Definition Suppose we have two partitions X and Y of a set A, namely X = \ and Y = \. Let: :n = \sum_ , X_, = \sum_ , Y_, =, A, :p_ = , X_, / n and q_ = , Y_, / n :r_ = , X_i\cap Y_, / n Then the variation of information between the two partitions is: :\mathrm(X; Y ) = - \sum_ r_ \left log(r_/p_i)+\log(r_/q_j) \right/math>. This is equivalent to the shared information distance between the random variables ''i'' and ''j'' with respect to the uniform probability measure on A defined by \mu(B):=, B, /n for B\subseteq A. Explicit information ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Theory
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations, probability theory treats the concept in a rigorous mathematical manner by expressing it through a set of axioms of probability, axioms. Typically these axioms formalise probability in terms of a probability space, which assigns a measure (mathematics), measure taking values between 0 and 1, termed the probability measure, to a set of outcomes called the sample space. Any specified subset of the sample space is called an event (probability theory), event. Central subjects in probability theory include discrete and continuous random variables, probability distributions, and stochastic processes (which provide mathematical abstractions of determinism, non-deterministic or uncertain processes or measured Quantity, quantities that may either be single occurrences or evolve over time in a random fashion). Although it is no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, Neuroscience, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a Fair coin, fair coin flip (which has two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy, less uncertainty) than identifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (which has six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of A Set
In mathematics, a partition of a set is a grouping of its elements into Empty set, non-empty subsets, in such a way that every element is included in exactly one subset. Every equivalence relation on a Set (mathematics), set defines a partition of this set, and every partition defines an equivalence relation. A set equipped with an equivalence relation or a partition is sometimes called a setoid, typically in type theory and proof theory. Definition and notation A partition of a set ''X'' is a set of non-empty subsets of ''X'' such that every element ''x'' in ''X'' is in exactly one of these subsets (i.e., the subsets are nonempty mutually disjoint sets). Equivalently, a family of sets ''P'' is a partition of ''X'' if and only if all of the following conditions hold: *The family ''P'' does not contain the empty set (that is \emptyset \notin P). *The union (set theory), union of the sets in ''P'' is equal to ''X'' (that is \textstyle\bigcup_ A = X). The sets in ''P'' are said ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information (MI) of two random variables is a measure of the mutual Statistical dependence, dependence between the two variables. More specifically, it quantifies the "Information content, amount of information" (in Units of information, units such as shannon (unit), shannons (bits), Nat (unit), nats or Hartley (unit), hartleys) obtained about one random variable by observing the other random variable. The concept of mutual information is intimately linked to that of Entropy (information theory), entropy of a random variable, a fundamental notion in information theory that quantifies the expected "amount of information" held in a random variable. Not limited to real-valued random variables and linear dependence like the Pearson correlation coefficient, correlation coefficient, MI is more general and determines how different the joint distribution of the pair (X,Y) is from the product of the marginal distributions of X and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric (mathematics)
In mathematics, a metric space is a set together with a notion of ''distance'' between its elements, usually called points. The distance is measured by a function called a metric or distance function. Metric spaces are a general setting for studying many of the concepts of mathematical analysis and geometry. The most familiar example of a metric space is 3-dimensional Euclidean space with its usual notion of distance. Other well-known examples are a sphere equipped with the angular distance and the hyperbolic plane. A metric may correspond to a metaphorical, rather than physical, notion of distance: for example, the set of 100-character Unicode strings can be equipped with the Hamming distance, which measures the number of characters that need to be changed to get from one string to another. Since they are very general, metric spaces are a tool used in many different branches of mathematics. Many types of mathematical objects have a natural notion of distance and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Inequality
In mathematics, the triangle inequality states that for any triangle, the sum of the lengths of any two sides must be greater than or equal to the length of the remaining side. This statement permits the inclusion of Degeneracy (mathematics)#Triangle, degenerate triangles, but some authors, especially those writing about elementary geometry, will exclude this possibility, thus leaving out the possibility of equality. If , , and are the lengths of the sides of a triangle then the triangle inequality states that :c \leq a + b , with equality only in the degenerate case of a triangle with zero area. In Euclidean geometry and some other geometries, the triangle inequality is a theorem about vectors and vector lengths (Norm (mathematics), norms): :\, \mathbf u + \mathbf v\, \leq \, \mathbf u\, + \, \mathbf v\, , where the length of the third side has been replaced by the length of the vector sum . When and are real numbers, they can be viewed as vectors in \R^1, and the triang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set (mathematics)
In mathematics, a set is a collection of different things; the things are '' elements'' or ''members'' of the set and are typically mathematical objects: numbers, symbols, points in space, lines, other geometric shapes, variables, or other sets. A set may be finite or infinite. There is a unique set with no elements, called the empty set; a set with a single element is a singleton. Sets are ubiquitous in modern mathematics. Indeed, set theory, more specifically Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, has been the standard way to provide rigorous foundations for all branches of mathematics since the first half of the 20th century. Context Before the end of the 19th century, sets were not studied specifically, and were not clearly distinguished from sequences. Most mathematicians considered infinity as potentialmeaning that it is the result of an endless processand were reluctant to consider infinite sets, that is sets whose number of members is not a natural number. Specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutual Information
In probability theory and information theory, the mutual information (MI) of two random variables is a measure of the mutual Statistical dependence, dependence between the two variables. More specifically, it quantifies the "Information content, amount of information" (in Units of information, units such as shannon (unit), shannons (bits), Nat (unit), nats or Hartley (unit), hartleys) obtained about one random variable by observing the other random variable. The concept of mutual information is intimately linked to that of Entropy (information theory), entropy of a random variable, a fundamental notion in information theory that quantifies the expected "amount of information" held in a random variable. Not limited to real-valued random variables and linear dependence like the Pearson correlation coefficient, correlation coefficient, MI is more general and determines how different the joint distribution of the pair (X,Y) is from the product of the marginal distributions of X and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lattice (order)
A lattice is an abstract structure studied in the mathematical subdisciplines of order theory and abstract algebra. It consists of a partially ordered set in which every pair of elements has a unique supremum (also called a least upper bound or join (mathematics), join) and a unique infimum (also called a greatest lower bound or meet (mathematics), meet). An example is given by the power set of a set, partially ordered by Subset, inclusion, for which the supremum is the Union (set theory), union and the infimum is the Intersection (set theory), intersection. Another example is given by the natural numbers, partially ordered by divisibility, for which the supremum is the least common multiple and the infimum is the greatest common divisor. Lattices can also be characterized as algebraic structures satisfying certain axiomatic Identity (mathematics), identities. Since the two definitions are equivalent, lattice theory draws on both order theory and universal algebra. Semilatti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasse Diagram
In order theory, a Hasse diagram (; ) is a type of mathematical diagram used to represent a finite partially ordered set, in the form of a drawing of its transitive reduction. Concretely, for a partially ordered set (S,\le) one represents each element of S as a vertex in the plane and draws a line segment or curve that goes ''upward'' from one vertex x to another vertex y whenever y covers x (that is, whenever x\ne y, x\le y and there is no z distinct from x and y with x\le z\le y). These curves may cross each other but must not touch any vertices other than their endpoints. Such a diagram, with labeled vertices, uniquely determines its partial order. Hasse diagrams are named after Helmut Hasse (1898–1979); according to Garrett Birkhoff, they are so called because of the effective use Hasse made of them. However, Hasse was not the first to use these diagrams. One example that predates Hasse can be found in an 1895 work by Henri Gustave Vogt. Although Hasse diagrams were orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy (information Theory)
In information theory, the entropy of a random variable quantifies the average level of uncertainty or information associated with the variable's potential states or possible outcomes. This measures the expected amount of information needed to describe the state of the variable, considering the distribution of probabilities across all potential states. Given a discrete random variable X, which may be any member x within the set \mathcal and is distributed according to p\colon \mathcal\to[0, 1], the entropy is \Eta(X) := -\sum_ p(x) \log p(x), where \Sigma denotes the sum over the variable's possible values. The choice of base for \log, the logarithm, varies for different applications. Base 2 gives the unit of bits (or "shannon (unit), shannons"), while base Euler's number, ''e'' gives "natural units" nat (unit), nat, and base 10 gives units of "dits", "bans", or "Hartley (unit), hartleys". An equivalent definition of entropy is the expected value of the self-information of a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |