|
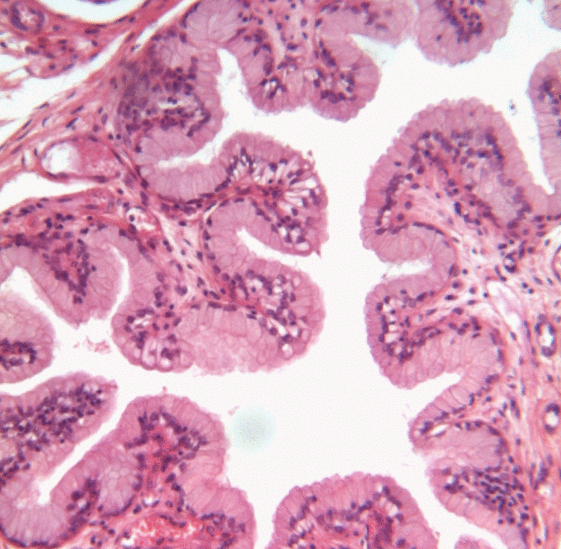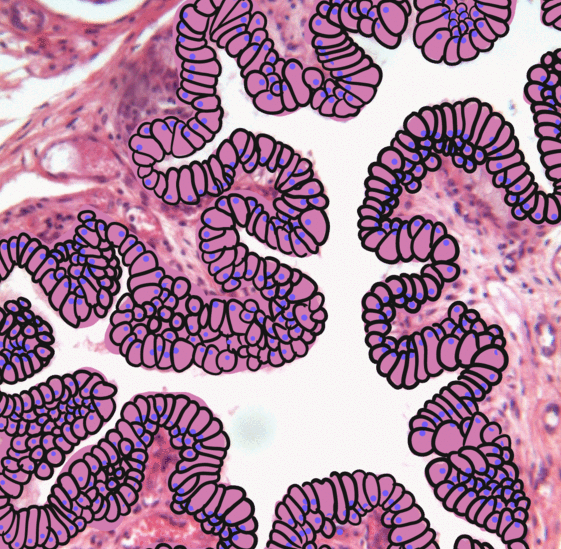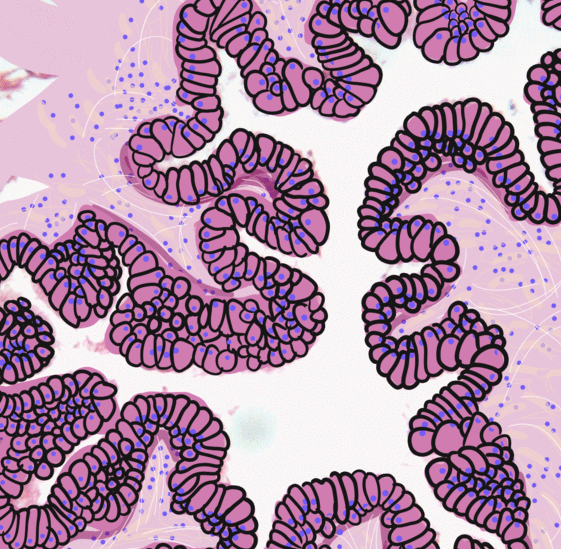
Urothelium
Transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched. This tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urinary system and is known here as urothelium (: urothelia). The bladder, for example, has a need for great distension. Structure The appearance of transitional epithelium differs according to its cell layer. Cells of the basal layer are cuboidal (cube-shaped), or columnar (column-shaped), while the cells of the superficial layer vary in appearance depending on the degree of distension. These cells appear to be cuboidal with a domed apex when the organ or the tube in which they reside is not stretched. When the organ or tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
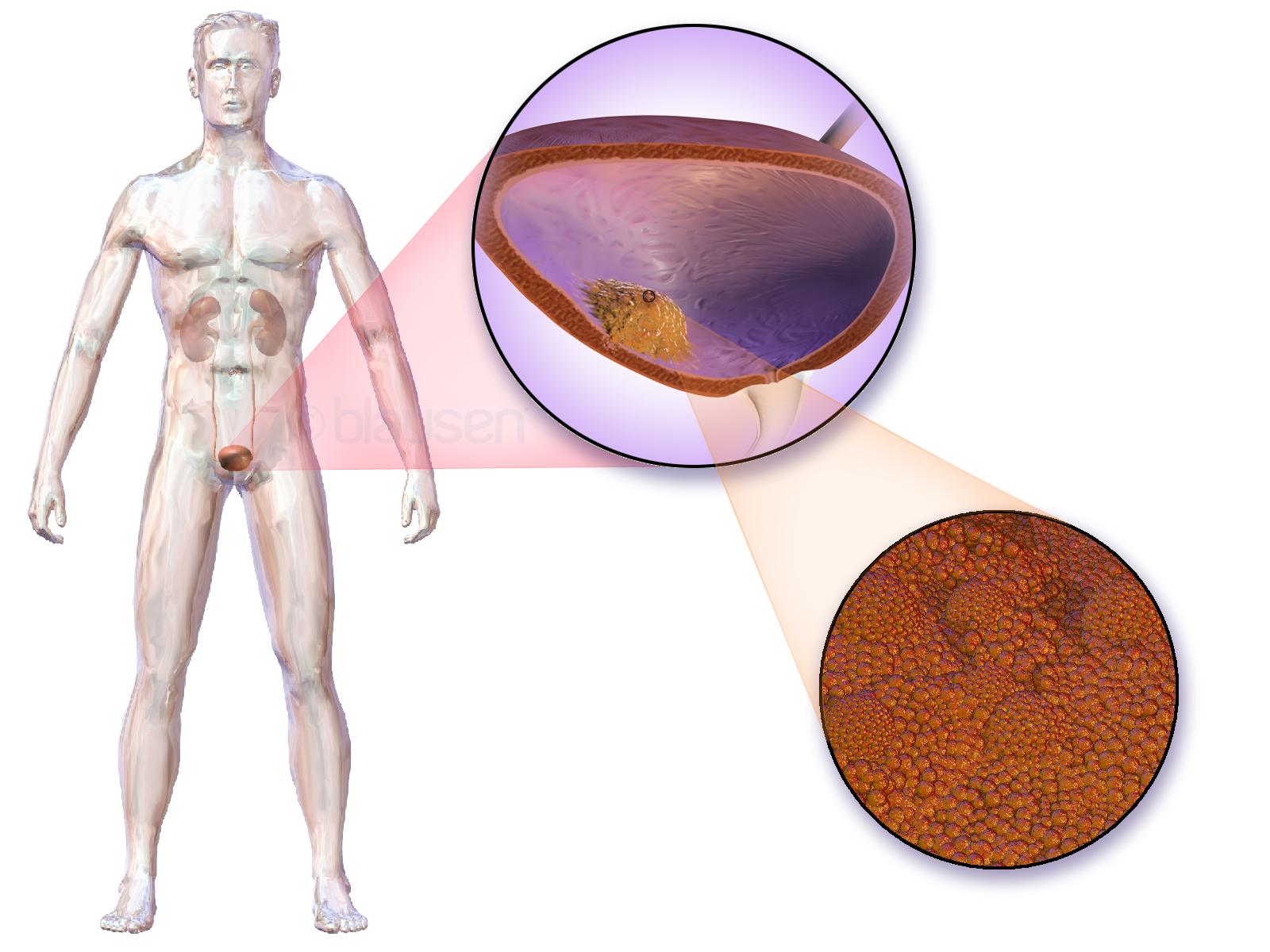
Bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor. The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and (10 and ) before the urge to empty occurs, but can hold considerably more. The Latin phrase for "urinary bladder" is ''vesica urinaria'', and the term ''vesical'' or prefix ''vesico-'' appear in connection with associated structures such as vesical veins. The modern Latin word for "bladder" – ''cystis'' – appears in associated terms such as cystitis (inflammation of the bladder). Structure In humans, the bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated at the base of the pelvis. In gross anatomy, the bladder can be divided into a broad (base), a body, an apex, and a neck. The apex (also called the vertex) is directed forward toward th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facet Cell
Facet cells (also known as umbrella cells, capping cells, superficial urotheliocytes) are a type of cells located in the renal pelvis, the ureters, and the urethra. Umbrella cells form the outermost layer of the urothelium, which is a special type of epithelium found in the renal pelvis, the ureters, and the urethra. Umbrella cells are special in that they can contain multiple nuclei. Their apical membrane contains numerous invaginations, which allows the cells to stretch during urination. Umbrella cells are linked together with tight junctions which: * prevents urine from leaking through the epithelium. * creates an osmotic barrier. Urine osmolarity can range from 50 to 1200 mmol/ L while the normal body osmolarity is 290 mmol/L. The difference between the two could lead to fluid entering or exiting the ureter due to the osmotic pressure Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a Solution (chemistry), solution to prevent the inward flo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Transitional cell carcinoma is a type of cancer that arises from the transitional epithelium, a tissue lining the inner surface of these hollow organs. It typically occurs in the urothelium of the urinary system; in that case, it is also called urothelial carcinoma. It is the most common type of bladder cancer and cancer of the ureter, urethra, and urachus. Symptoms of urothelial carcinoma in the bladder include hematuria (blood in the urine). Diagnosis includes urine analysis and imaging of the urinary tract (cystoscopy). It accounts for 95% of bladder cancer cases and bladder cancer is in the top 10 most common malignancy disease in the world and is associated with approximately 200,000 deaths per year in the United States alone. It is the second most common type of kidney cancer, but accounts for only five to 10 percent of all primary renal malignant tumors. Men and older people have a higher rate of urothelial carcinomas. Other risk factors include smoking and exposure to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the bladder. These cells can grow to form a tumor, which eventually spreads, damaging the bladder and other organs. Most people with bladder cancer are diagnosed after noticing blood in their urine. Those suspected of having bladder cancer typically have their bladder inspected by a thin medical camera, a procedure called cystoscopy. Suspected tumors are removed and examined to determine if they are cancerous. Based on how far the tumor has spread, the cancer case is assigned a stage 0 to 4; a higher stage indicates a more widespread and dangerous disease. Those whose bladder tumors have not spread outside the bladder have the best prognoses. These tumors are typically surgically removed, and the person is treated with chemotherapy or one of several immune-stimulating therapies. Those whose tumors continue to grow, or whose tumors have penetrated the bladder muscle, often have their bladder surgically removed ( radical cy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
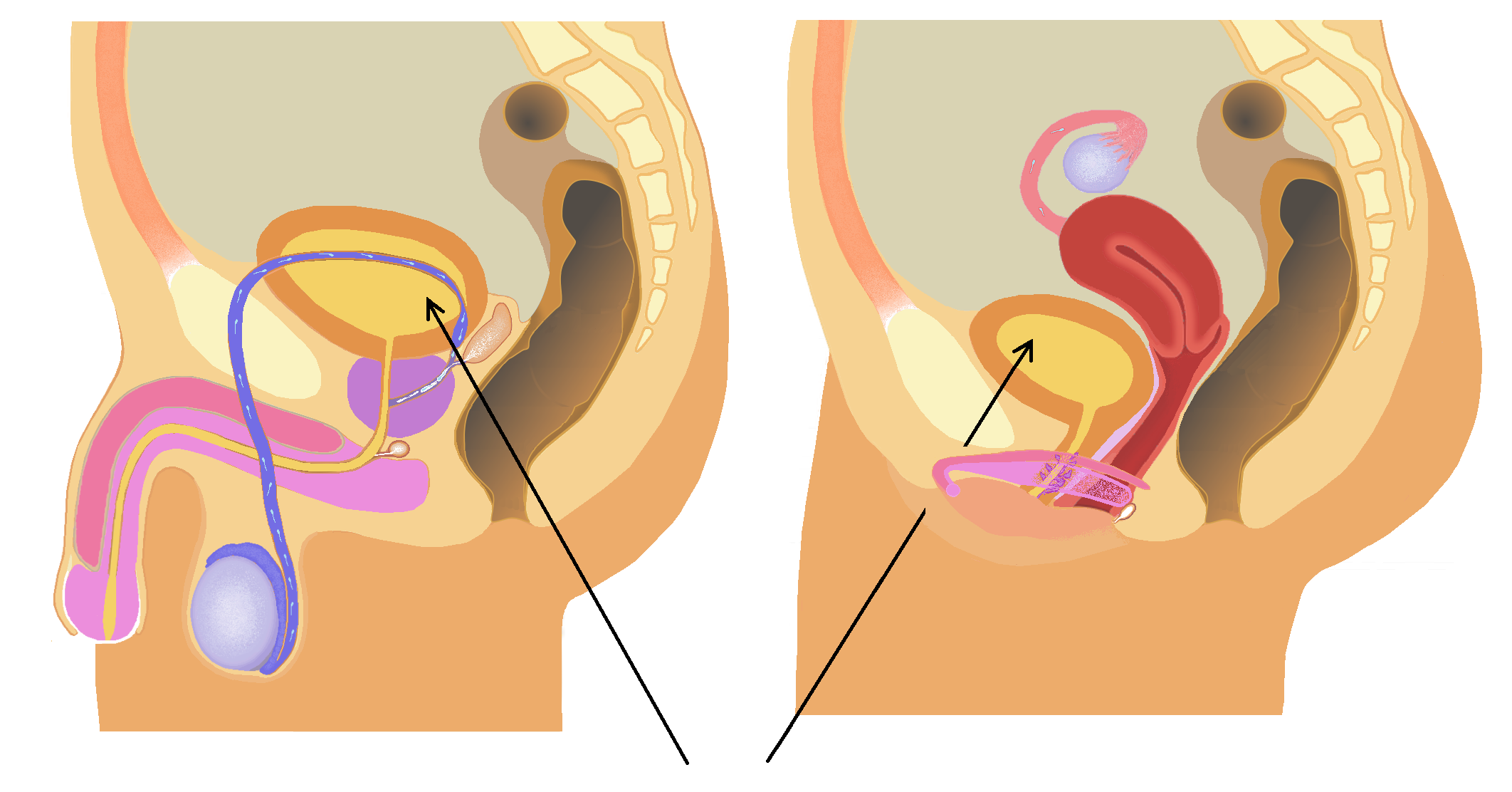
Urinary System
The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of Electrolyte, electrolytes and Metabolite, metabolites, and regulate Acid–base homeostasis, blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the Renal artery, renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, waste (in the form of urine) exits the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuboidal
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of many internal organs, the corresponding inner surfaces of body cavities, and the inner surfaces of blood vessels. Epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. These tissues also lack blood or lymph supply. The tissue is supplied by nerves. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either simple squamous, simple columnar, or simple cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary System
The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of Electrolyte, electrolytes and Metabolite, metabolites, and regulate Acid–base homeostasis, blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the Renal artery, renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, waste (in the form of urine) exits the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |