|
Uncrewed NASA Missions
Since 1958, NASA has overseen more than 1,000 Uncrewed spacecraft, uncrewed missions into Earth orbit or beyond. It has both launched its own missions and provided funding for private-sector missions. A number of NASA missions, including the #Explorers Program (1958–present), Explorers Program, #Voyager program (1977–present), Voyager program, and #New Frontiers program (2006–present), New Frontiers program, are ongoing. List of missions Explorers Program (1958–present) The Explorer program has launched more than 90 missions since it began more than five decades ago. It has matured into one of NASA's lower-cost mission programs. The program started as a U.S. Army proposal to place a scientific satellite into orbit during the International Geophysical Year (1957–58). However, that proposal was rejected in favor of the U.S. Navy's Project Vanguard. The Explorer program was later reestablished to catch up with the Soviet Union after the launch of ''Sputnik 1'' in Octo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer 11
''Pioneer 11'' (also known as ''Pioneer G'') is a NASA robotic space probe launched on April 5, 1973, to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, the solar wind, and cosmic rays. It was the first probe to Exploration of Saturn, encounter Saturn, the second to fly through the Asteroid belt#Exploration, asteroid belt, and the second to fly by Jupiter. Later, ''Pioneer 11'' became the List of artificial objects leaving the Solar System, second of five artificial objects to achieve an escape velocity allowing it to Solar System#Farthest regions, leave the Solar System. Due to power constraints and the vast distance to the probe, the last routine contact with the spacecraft was on September 30, 1995, and the last good engineering data was received on November 24, 1995. Mission background History Approved in February 1969, ''Pioneer 11'' and its twin probe, ''Pioneer 10'', were the first to be designed for exploring the outer Solar System. Yielding to multip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delta Rocket
The Delta rocket family was a versatile range of American rocket-powered expendable launch systems that provided space launch capability in the United States from 1960 to 2024. Japan also launched license-built derivatives (N-I (rocket), N-I, N-II (rocket), N-II, and H-I) from 1975 to 1992. More than 300 Delta rockets were launched with a 95% success rate. The series was phased out in favor of the Vulcan Centaur, with the Delta IV Heavy, Delta IV Heavy rocket's last launch occurring on April 9, 2024. Origins The original Delta rockets used a modified version of the PGM-17 Thor, the first ballistic missile deployed by the United States Air Force (USAF), as their Multistage rocket, first stage. The Thor had been designed in the mid-1950s to reach Moscow from bases in Britain or similar allied nations, and the first wholly successful Thor launch had occurred in September 1957. Subsequent satellite and space probe flights soon followed, using a Thor first stage with several di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northfield, Minnesota
Northfield is a city in Dakota County, Minnesota, Dakota and Rice County, Minnesota, Rice counties in the U.S. state, state of Minnesota. It is mostly in Rice County, with a small portion in Dakota County. The population was 20,790 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. Northfield is south of the downtowns of Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota, St. Paul and is an exurb of the Minneapolis-St. Paul metropolitan area. History Northfield was platted in October 1855 by John W. North. Northfield was founded by settlers from New England known as "Yankees" as part of New England's colonization of what was then the far west. It was an early agricultural center with many wheat and corn farms. The town also supported lumber and flour mills powered by the Cannon River (Minnesota), Cannon River. As the "wheat frontier" moved west, dairy operations and diversified farms replaced wheat-based agriculture. The region has since moved away from dairy and beef operations, and it produce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilmore Schjeldahl
Gilmore Tilmen Schjeldahl (June 1, 1912March 10, 2002) was an American businessman and inventor in plastics, adhesives and circuitry. He was awarded 16 US patents and may be best known for inventing the plastic-lined airsickness bag. He also founded the Schjeldahl Company, which designed and built Echo I, and worked on Echo II, Project Stargazer, Stratascope II, and PAGEOS. He had five children, including Peter Schjeldahl, a notable art critic, poet, and educator. Schjeldahl died on March 10, 2002, at his home in Lenox, Massachusetts, after battling Alzheimer's disease for many years. Biography Early life and education Gilmore Tilmen Schjeldahl was born in Esmond, North Dakota, to Norwegian immigrants. His father was a railroad worker. He grew up in Northwood, North Dakota, and did not graduate from high school, but took courses at North Dakota State College of Science and North Dakota State University before being drafted into the U.S. Army to serve during World War II. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mission And Spacecraft Library
Mission and Spacecraft Library (MSL) is a reference web site, maintained by NASA, containing information about satellites. It contains a catalog of several hundreds of satellites from different countries. The site was founded by Jet Propulsion Laboratory employee Mike Evans, who had a vision of building a database that would be publicly accessible via the World Wide Web The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis .... The site has not been updated since 1999. References External links Mission and Spacecraft Library American educational websites Online databases Government databases in the United States NASA online Spaceflight {{space-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, broadly construed. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 30 cm and 3 mm), or between 1 and 3000 GHz (30 cm and 0.1 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire super high frequency, super high frequency (SHF) band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. The boundaries between far infrared, terahertz radiation, microwaves, and ultra-high-frequency (UHF) are fairly arbitrary and differ between different fields of study. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' indicates that microwaves are small (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used in prior radio technology. Frequencies in the micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection (physics)
Reflection is the change in direction of a wavefront at an interface between two different media so that the wavefront returns into the medium from which it originated. Common examples include the reflection of light, sound and water waves. The ''law of reflection'' says that for specular reflection (for example at a mirror) the angle at which the wave is incident on the surface equals the angle at which it is reflected. In acoustics, reflection causes echoes and is used in sonar. In geology, it is important in the study of seismic waves. Reflection is observed with surface waves in bodies of water. Reflection is observed with many types of electromagnetic wave, besides visible light. Reflection of VHF and higher frequencies is important for radio transmission and for radar. Even hard X-rays and gamma rays can be reflected at shallow angles with special "grazing" mirrors. Reflection of light Reflection of light is either '' specular'' (mirror-like) or '' diffuse'' (retai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balloon Satellite
A balloon satellite, sometimes referred to as a "satelloon", is a satellite inflated with gas after it has been put into orbit. Echo 1 and Echo 2 balloon satellites The first flying body of this type was Echo 1, which was launched into a high orbit on August 12, 1960, by the United States. It originally had a spherical shape measuring , with a thin metal-coated plastic shell made of Mylar. It served for testing as a "passive" communication satellite, communication and geodesy, geodetic satellite. One of the first radio contacts using the satellite was successful at a distance of nearly (between the east coast of the US and California). By the time Echo 1 burned up in 1968, the measurements of its orbit by several dozen Earth station (communications), earth stations had improved our knowledge of the precise shape of the planet by nearly a factor of ten. Its successor was the similarly built Echo satellite, Echo 2 (1964 to about 1970). This satellite circled the Earth about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications Satellite
A communications satellite is an artificial satellite that relays and amplifies radio telecommunication signals via a Transponder (satellite communications), transponder; it creates a communication channel between a source transmitter and a Radio receiver, receiver at different locations on Earth. Communications satellites are used for television, telephone, radio, internet, and military applications. Many communications satellites are in geostationary orbit above the equator, so that the satellite appears stationary at the same point in the sky; therefore the satellite dish antennas of ground stations can be aimed permanently at that spot and do not have to move to track the satellite. Others form satellite constellations in low Earth orbit, where antennas on the ground have to follow the position of the satellites and switch between satellites frequently. The radio waves used for telecommunications links travel by Line-of-sight propagation, line of sight and so are obstructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echo II
{{Disambig ...
Echo II or Echo 2 or ''variant'', may refer to: * ''Echo II''-class submarine of the Soviet Navy * Echo 2 (satellite), a 1964 NASA communications satellite * Echo II (expansion card), a speech synthesizer card for the Apple II See also * EchoStar II, a 1990s communications satellite * Echo (other) An echo is a reflection of sound. Echo may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Echo (DC Comics), various different characters * Echo (''Dollhouse''), the protagonist of the TV series ''Dollhouse'' * Echo (Marvel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
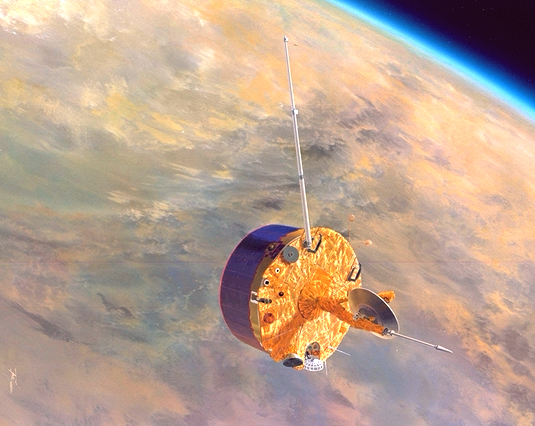
Pioneer Venus Project
The Pioneer Venus project was part of the Pioneer program consisting of two spacecraft, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, launched to Venus in 1978. The program was managed by NASA's Ames Research Center. The Pioneer Venus Orbiter entered orbit around Venus on December 4, 1978, and performed observations to characterize the atmosphere and surface of Venus. It continued to transmit data until October 1992. The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe deployed four small probes into the Venusian atmosphere on December 9, 1978. All four probes transmitted data throughout their descent to the surface. One probe survived the landing and transmitted data from the surface for over an hour. Overview The Pioneer mission consisted of two components, launched separately: an orbiter and a multiprobe. Orbiter The orbiter was launched on May 20, 1978 on an Atlas-Centaur rocket. The orbiter's mass was . The Pioneer Venus Orbiter was inserted into an elliptical orbit around V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |