|
Trinomial Triangle
The trinomial triangle is a variation of Pascal's triangle. The difference between the two is that an entry in the trinomial triangle is the sum of the ''three'' (rather than the ''two'' in Pascal's triangle) entries above it: \begin & & & & 1\\ & & & 1& 1&1\\ & & 1& 2& 3&2&1\\ &1& 3& 6& 7&6&3&1\\ 1&4&10&16&19&16&10&4&1\end The k-th entry of the n-th row is denoted by : _2. Rows are counted starting from 0. The entries of the n-th row are indexed starting with -n from the left, and the middle entry has index 0. The symmetry of the entries of a row about the middle entry is expressed by the relationship : _2=_2 Properties The n-th row corresponds to the coefficients in the polynomial expansion of the expansion of the trinomial (1 + x + x^2) raised to the n-th power: :\left(1+x+x^2\right)^n= \sum _^_2 x^=\sum _^_2 x^ or, symmetrically, :\left(1+x+1/x\right)^n=\sum_^_2 x^k, hence the alternative name trinomial coefficients because of their relationship to the multino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pascal's Triangle
In mathematics, Pascal's triangle is a triangular array of the binomial coefficients that arises in probability theory, combinatorics, and algebra. In much of the Western world, it is named after the French mathematician Blaise Pascal, although other mathematicians studied it centuries before him in India, Persia, China, Germany, and Italy. The rows of Pascal's triangle are conventionally enumerated starting with row n = 0 at the top (the 0th row). The entries in each row are numbered from the left beginning with k = 0 and are usually staggered relative to the numbers in the adjacent rows. The triangle may be constructed in the following manner: In row 0 (the topmost row), there is a unique nonzero entry 1. Each entry of each subsequent row is constructed by adding the number above and to the left with the number above and to the right, treating blank entries as 0. For example, the initial number of row 1 (or any other row) is 1 (the sum of 0 and 1), whereas the numbers 1 and 3 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
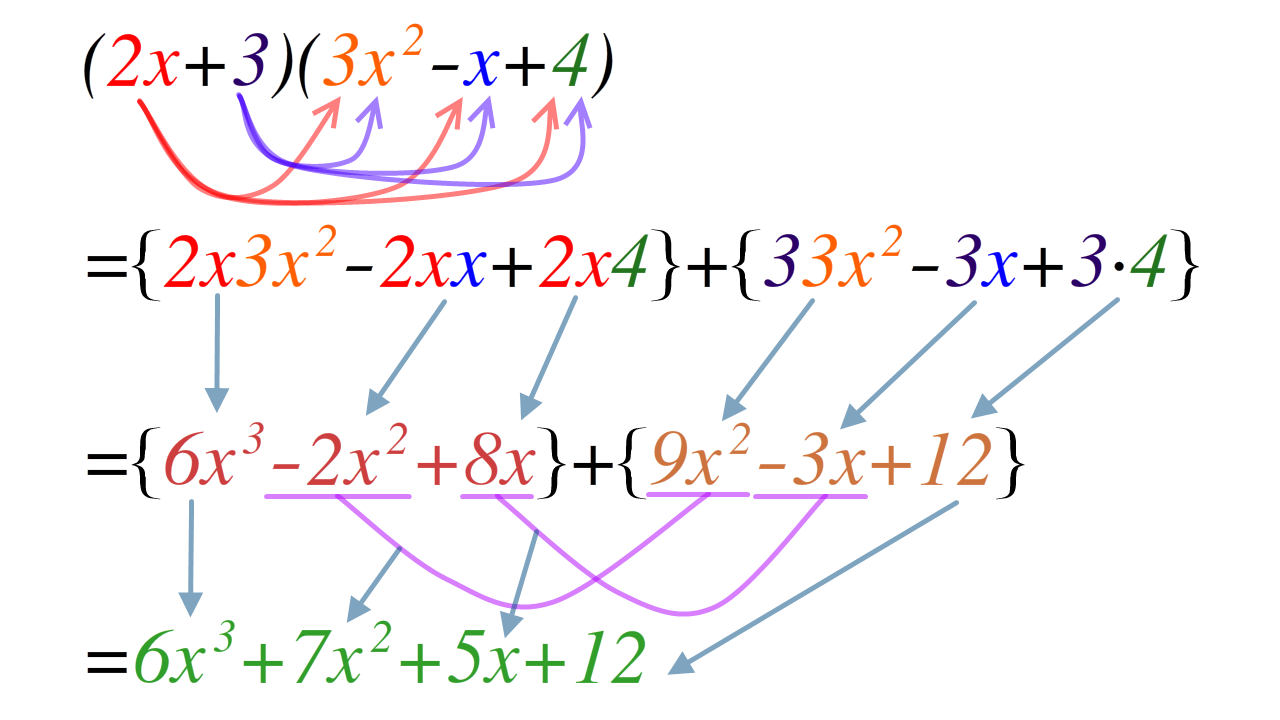
Polynomial Expansion
In mathematics, an expansion of a product of sums expresses it as a sum of products by using the fact that multiplication distributes over addition. Expansion of a polynomial expression can be obtained by repeatedly replacing subexpressions that multiply two other subexpressions, at least one of which is an addition, by the equivalent sum of products, continuing until the expression becomes a sum of (repeated) products. During the expansion, simplifications such as grouping of like terms or cancellations of terms may also be applied. Instead of multiplications, the expansion steps could also involve replacing powers of a sum of terms by the equivalent expression obtained from the binomial formula; this is a shortened form of what would happen if the power were treated as a repeated multiplication, and expanded repeatedly. It is customary to reintroduce powers in the final result when terms involve products of identical symbols. Simple examples of polynomial expansions are the we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinomial
In elementary algebra, a trinomial is a polynomial consisting of three terms or monomials. Examples of trinomial expressions # 3x + 5y + 8z with x, y, z variables # 3t + 9s^2 + 3y^3 with t, s, y variables # 3ts + 9t + 5s with t, s variables # ax^2+bx+c, the quadratic expression in standard form with a,b,c variables. # A x^a y^b z^c + B t + C s with x, y, z, t, s variables, a, b, c nonnegative integers and A, B, C any constants. # Px^a + Qx^b + Rx^c where x is variable and constants a, b, c are nonnegative integers and P, Q, R any constants. Trinomial equation A trinomial equation is a polynomial equation involving three terms. An example is the equation x = q + x^m studied by Johann Heinrich Lambert in the 18th century. Some notable trinomials * The quadratic trinomial in standard form (as from above): ax^2+bx+c See also *Trinomial expansion *Monomial *Binomial * Multinomial *Simple expression In mathematics, a monomial is, roughly speaking, a polynomial which has on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multinomial Coefficients
In mathematics, the multinomial theorem describes how to expand a power of a sum in terms of powers of the terms in that sum. It is the generalization of the binomial theorem from binomials to multinomials. Theorem For any positive integer and any non-negative integer , the multinomial formula describes how a sum with terms expands when raised to an arbitrary power : :(x_1 + x_2 + \cdots + x_m)^n = \sum_ \prod_^m x_t^\,, where : = \frac is a multinomial coefficient. The sum is taken over all combinations of nonnegative integer indices through such that the sum of all is . That is, for each term in the expansion, the exponents of the must add up to . Also, as with the binomial theorem, quantities of the form that appear are taken to equal 1 ( even when equals zero). In the case , this statement reduces to that of the binomial theorem. Example The third power of the trinomial is given by :(a+b+c)^3 = a^3 + b^3 + c^3 + 3 a^2 b + 3 a^2 c + 3 b^2 a + 3 b^2 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangular Numbers
A triangular number or triangle number counts objects arranged in an equilateral triangle. Triangular numbers are a type of figurate number, other examples being square numbers and cube numbers. The th triangular number is the number of dots in the triangular arrangement with dots on each side, and is equal to the sum of the natural numbers from 1 to . The sequence of triangular numbers, starting with the 0th triangular number, is (This sequence is included in the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences .) Formula The triangular numbers are given by the following explicit formulas: T_n= \sum_^n k = 1+2+3+ \dotsb +n = \frac = , where \textstyle is a binomial coefficient. It represents the number of distinct pairs that can be selected from objects, and it is read aloud as " plus one choose two". The first equation can be illustrated using a visual proof. For every triangular number T_n, imagine a "half-square" arrangement of objects corresponding to the triangular n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recurrence Formula
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a parameter k that is independent of n; this number k is called the ''order'' of the relation. If the values of the first k numbers in the sequence have been given, the rest of the sequence can be calculated by repeatedly applying the equation. In ''linear recurrences'', the th term is equated to a linear function of the k previous terms. A famous example is the recurrence for the Fibonacci numbers, F_n=F_+F_ where the order k is two and the linear function merely adds the two previous terms. This example is a linear recurrence with constant coefficients, because the coefficients of the linear function (1 and 1) are constants that do not depend on n. For these recurrences, one can express the general term of the sequence as a closed-form expression ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonhard Euler
Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in many other branches of mathematics such as analytic number theory, complex analysis, and infinitesimal calculus. He introduced much of modern mathematical terminology and notation, including the notion of a mathematical function. He is also known for his work in mechanics, fluid dynamics, optics, astronomy and music theory. Euler is held to be one of the greatest mathematicians in history and the greatest of the 18th century. A statement attributed to Pierre-Simon Laplace expresses Euler's influence on mathematics: "Read Euler, read Euler, he is the master of us all." Carl Friedrich Gauss remarked: "The study of Euler's works will remain the best school for the different fields of mathematics, and nothing else can replace it." Euler i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generating Function
In mathematics, a generating function is a way of encoding an infinite sequence of numbers () by treating them as the coefficients of a formal power series. This series is called the generating function of the sequence. Unlike an ordinary series, the ''formal'' power series is not required to converge: in fact, the generating function is not actually regarded as a function, and the "variable" remains an indeterminate. Generating functions were first introduced by Abraham de Moivre in 1730, in order to solve the general linear recurrence problem. One can generalize to formal power series in more than one indeterminate, to encode information about infinite multi-dimensional arrays of numbers. There are various types of generating functions, including ordinary generating functions, exponential generating functions, Lambert series, Bell series, and Dirichlet series; definitions and examples are given below. Every sequence in principle has a generating function of each type (excep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibonacci Number
In mathematics, the Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted , form a sequence, the Fibonacci sequence, in which each number is the sum of the two preceding ones. The sequence commonly starts from 0 and 1, although some authors start the sequence from 1 and 1 or sometimes (as did Fibonacci) from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the first few values in the sequence are: :0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144. The Fibonacci numbers were first described in Indian mathematics, as early as 200 BC in work by Pingala on enumerating possible patterns of Sanskrit poetry formed from syllables of two lengths. They are named after the Italian mathematician Leonardo of Pisa, later known as Fibonacci, who introduced the sequence to Western European mathematics in his 1202 book '' Liber Abaci''. Fibonacci numbers appear unexpectedly often in mathematics, so much so that there is an entire journal dedicated to their study, the '' Fibonacci Quarterly''. Applications of Fibonacci numbers includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Andrews (mathematician)
George Eyre Andrews (born December 4, 1938) is an American mathematician working in special functions, number theory, analysis and combinatorics. Education and career He is currently an Evan Pugh Professor of Mathematics at Pennsylvania State University. He did his undergraduate studies at Oregon State University and received his PhD in 1964 at the University of Pennsylvania where his advisor was Hans Rademacher. During 2008–2009 he was president of the American Mathematical Society. Contributions Andrews's contributions include several monographs and over 250 research and popular articles on q-series, special functions, combinatorics and applications. He is considered to be the world's leading expert in the theory of integer partitions. In 1976 he discovered Ramanujan's Lost Notebook. He is highly interested in mathematical pedagogy. His book ''The Theory of Partitions'' is the standard reference on the subject of integer partitions. He has advanced mathematics in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King (chess)
The king (♔, ♚) is the most important piece in the game of chess. It may move to any adjoining square; it may also perform a move known as castling. If a player's king is threatened with capture, it is said to be in check, and the player must remove the threat of on the next move. If this cannot be done, the king is said to be in checkmate, resulting in a loss for that player. A player cannot make any move that places their own king in check. Despite this, the king can become a strong offensive piece in the endgame or, rarely, the middlegame. In algebraic notation, the king is abbreviated by the letter K among English speakers. The white king starts the game on e1; the black king starts on e8. Unlike all other pieces, only one king per player can be on the board at any time, and the kings are never removed from the board during the game. Placement and movement The white king starts on e1, on the first to the right of the queen from White's perspective. The black k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chess
Chess is a board game for two players, called White and Black, each controlling an army of chess pieces in their color, with the objective to checkmate the opponent's king. It is sometimes called international chess or Western chess to distinguish it from related games, such as xiangqi (Chinese chess) and shogi (Japanese chess). The recorded history of chess goes back at least to the emergence of a similar game, chaturanga, in seventh-century India. The rules of chess as we know them today emerged in Europe at the end of the 15th century, with standardization and universal acceptance by the end of the 19th century. Today, chess is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide. Chess is an abstract strategy game that involves no hidden information and no use of dice or cards. It is played on a chessboard with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. At the start, each player controls sixteen pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |