|
Trias Greenfinch
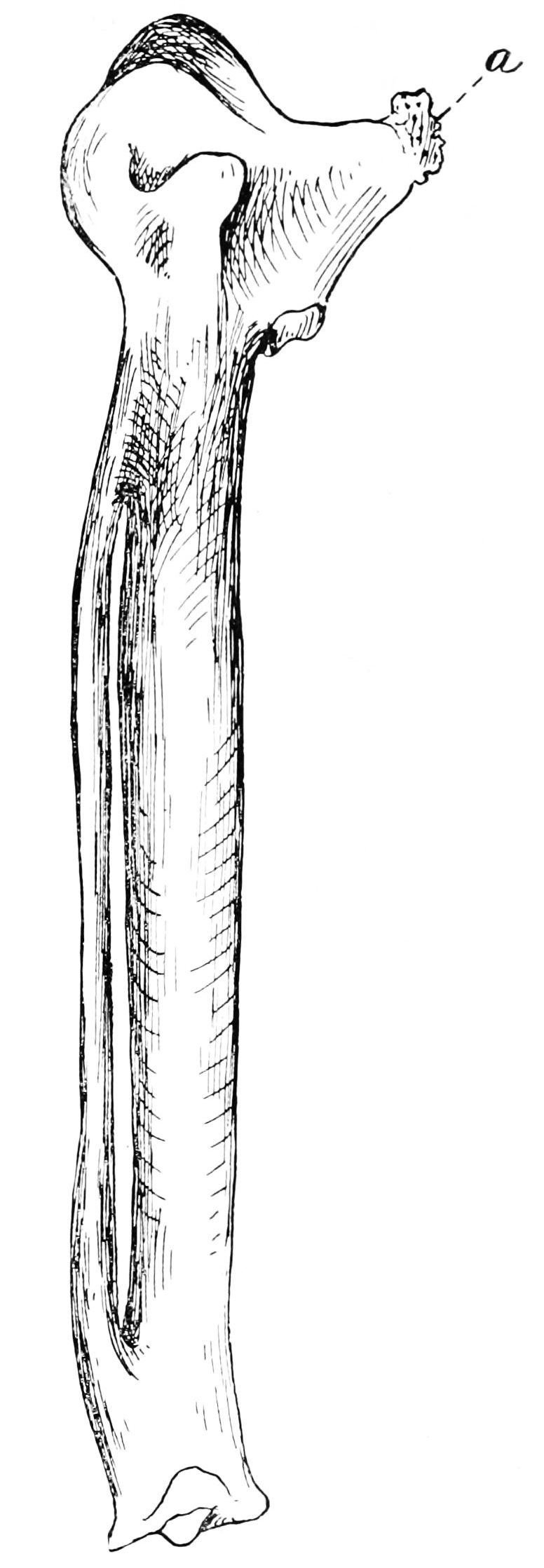
The Trias greenfinch (''Chloris triasi'') is an extinct passerine from the family of finches (Fringillidae). The fossil remains were unearthed in the Cuevas de los Murciélagos near San Andrés y Sauces in the north of La Palma, Canary Islands. The species epithet commemorates Spanish palaeontologist Miquel Trías who collected the holotype together with Josep Antoni Alcover in July 1985. Description The holotype is an almost complete cranium with both pterygoids but lacking mandible, quadrate bones, and the palatine process of maxilla. The paratypes include a proximal fragment of a right humerus, a distal fragment of a right humerus with a prominent fragmented epicondyle, a left ulna lacking the epiphyseal plate, an almost complete right ulna lacking the olecranon and a complete left carpometacarpus. The cranium length is 34,89 mm, the cranium width is 17,47 mm and the cranium height is 14,31 mm. The maxilla length is 19,10 mm, the maxilla width is 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently defined as the time between c. 129,000 and c. 11,700 years ago. The Late Pleistocene equates to the proposed Tarantian Age of the geologic time scale, preceded by the officially ratified Chibanian (formerly known as Middle Pleistocene) and succeeded by the officially ratified Greenlandian. The estimated beginning of the Tarantian is the start of the Eemian interglacial period ( Marine Isotope Stage 5). It is held to end with the termination of the Younger Dryas, some 11,700 years ago when the Holocene Epoch began. The term Upper Pleistocene is currently in use as a provisional or "quasi-formal" designation by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS). Although the three olde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicondyle
An epicondyle () is a rounded eminence on a bone that lies upon a condyle ('' epi-'', "upon" + ''condyle'', from a root meaning "knuckle" or "rounded articular area"). There are various epicondyles in the human skeleton, each named by its anatomic Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ... site. They include the following: Skeletal system {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene Extinctions
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of globa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds Of The Canary Islands
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. Bird ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Quaternary Prehistoric Birds
Late Quaternary prehistoric birds are avian taxa that became extinct during the Late Quaternary – the Holocene or Late Pleistocene – and before recorded history, or more precisely, before they could be studied alive by ornithological science. They became extinct before the period of global scientific exploration that started in the late 15th century. In other words, this list basically deals with extinctions between 40,000 BC and 1500 AD. For the purposes of this article, a "bird" is any member of the clade Neornithes, that is, any descendant of the most recent common ancestor of all currently living birds. The birds are known from their remains, which are subfossil (not fossilized, or not completely fossilized). Some are also known from folk memory, as in the case of Haast's eagle in New Zealand. As the remains are not completely fossilized, they may yield organic material for molecular analyses to provide additional clues for resolving their taxonomic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloris (bird)
The greenfinches are small passerine birds in the genus ''Chloris'' in the subfamily Carduelinae within the Fringillidae. The species have a Eurasian distribution except for the European greenfinch, which also occurs in North Africa. These finches all have large conical bills and yellow patches on the wing feathers. The greenfinches were formerly placed in the genus '' Carduelis''. Molecular phylogenetic studies showed that the greenfinches form a monophyletic group that is not closely related to the species in ''Carduelis'' and instead is sister to a clade containing the desert finch (''Rhodospiza obsoleta'') and the Socotra golden-winged grosbeak (''Rhynchostruthus socotranus''). The greenfinches were therefore moved to the resurrected genus ''Chloris'' which had originally been introduced by the French naturalist Georges Cuvier in 1800 with the European greenfinch as the type species. The name is from Ancient Greek ''khloris'', the European greenfinch, from ''khloros'', "gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurel Forest
Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elongated leaves, known as "laurophyll" or "lauroid". Plants from the laurel family (Lauraceae) may or may not be present, depending on the location. Ecology Laurel and laurophyll forests have a patchy distribution in warm temperate regions, often occupying topographic refugia where the moisture from the ocean condenses so that it falls as rain or fog and soils have high moisture levels.Abstract at NASA – MODIS: Izquierdo, T; de las Heras, P; Marquez, A (2011). Vegetation indices changes in the cloud forest of La Gomera Island (Canary Islands) and their hydrological implications". ''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Greenfinch
The European greenfinch or simply the greenfinch (''Chloris chloris'') is a small passerine bird in the finch family Fringillidae. This bird is widespread throughout Europe, North Africa and Southwest Asia. It is mainly resident, but some northernmost populations migrate further south. The greenfinch has also been introduced into Australia, New Zealand, Uruguay, and Argentina. Taxonomy The greenfinch was described by Carl Linnaeus in his landmark 1758 10th edition of ''Systema Naturae'' under the binomial name ''Loxia chloris''. The specific epithet is from ''khloris'', the Ancient Greek name for this bird, from ''khloros'', "green". The finch family, Fringillidae, is divided into two subfamilies, the Carduelinae, containing around 28 genera with 141 species and the Fringillinae containing a single genus, ''Fringilla'', with four species. The finch family are all seed-eaters with stout conical bills. They have similar skull morphologies, nine large primaries, 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpometacarpus
The carpometacarpus is a bone found in the hands of birds. It results from the fusion of the carpal and metacarpal bone, and is essentially a single fused bone between the wrist and the knuckles. It is a smallish bone in most birds, generally flattened and with a large hole in the middle. In flightless birds, however, its shape may be slightly different, or it might be absent entirely. It forms the tip of the wing skeleton in birds. To it, most of the primary remiges attach. The alula, by contrast, is formed by the thumb, which does not completely fuse with the other hand-bones. Likewise, the tipmost primaries attach to the phalanx bones. To non-biologists the carpometacarpus may be best known from buffalo wings. Buffalo wings come in two basic sizes, a large angled one containing three major bones, and a smaller flat one containing only two. The bone missing in the latter is the carpometacarpus. See also * Carpometacarpal joint The carpometacarpal (CMC) joints are five jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olecranon
The olecranon (, ), is a large, thick, curved bony eminence of the ulna, a long bone in the forearm that projects behind the elbow. It forms the most pointed portion of the elbow and is opposite to the cubital fossa or elbow pit. The olecranon serves as a lever for the extensor muscles that straighten the elbow joint. Structure The olecranon is situated at the proximal end of the ulna, one of the two bones in the forearm. When the hand faces forward (supination) the olecranon faces towards the back (posteriorly). It is bent forward at the summit so as to present a prominent lip which is received into the olecranon fossa of the humerus during extension of the forearm. Its base is contracted where it joins the body and the narrowest part of the upper end of the ulna. Its posterior surface, directed backward, is triangular, smooth, subcutaneous, and covered by a bursa. Its superior surface is of quadrilateral form, marked behind by a rough impression for the insertion of the Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiphyseal Plate
The epiphyseal plate (or epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with maintenance remodeling throughout its existing bone tissue, but the growth plate is the place where the long bone grows longer (adds length). The plate is only found in children and adolescents; in adults, who have stopped growing, the plate is replaced by an epiphyseal line. This replacement is known as epiphyseal closure or growth plate fusion. Complete fusion can occur as early as 12 for girls (with the most common being 14-15 years for girls) and as early as 14 for boys (with the most common being 15–17 years for boys). Structure Development Endochondral ossification is responsible for the initial bone development from cartilage in utero and infants and the longitudinal growth of long bones in the epiphyseal plate. The plate's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)