|
Treaty Of Compiègne (1635)
The Treaty of Compiègne (1635), signed on 30 April 1635, was a mutual defence alliance between the Kingdom of France and Sweden. Prior to 1635, France had supported opponents of its Habsburg rivals in Spain and the Holy Roman Empire, but avoided direct involvement. This included backing the Dutch revolt against Spain, and Swedish intervention in the Thirty Years War. After the Swedish-German Heilbronn League was defeated at Nördlingen in September 1634, France decided to enter the war. In the Treaty of Compiègne, they agreed to continue subsidising Swedish intervention in the Holy Roman Empire, and to declare war on Spain, beginning the 1635 to 1659 Franco-Spanish War. Background A key factor in European politics during the 17th century was the struggle between the Bourbon kings of France and their Habsburg rivals in Spain and the Holy Roman Empire. Habsburg territories in the Spanish Netherlands, Franche-Comté, and the Pyrenees blocked French expansion, and made it vu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Bärwalde
The Treaty of Bärwalde (french: Traité de Barwalde; sv, Fördraget i Bärwalde; german: Vertrag von Bärwalde), signed on 23 January 1631, was an agreement by France to provide Sweden financial support, following its intervention in the Thirty Years' War. This was in line with Cardinal Richelieu's policy of avoiding direct French involvement, but weakening Habsburg Austria by backing its opponents. Under its terms, Gustavus Adolphus agreed to maintain an army of 36,000 troops, in return for an annual payment of 400,000 Reichsthalers, for a period of five years. France continued their support after Gustavus was killed at Lützen in November 1632. When the Swedes were defeated at Nördlingen in September 1634, most of their German allies made peace in the Treaty of Prague. Richelieu decided to intervene directly; in 1635, the Franco-Swedish Treaty of Compiègne replaced that agreed at Bärwalde. Background The Thirty Years War began in 1618 when the Protestant Frederi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axel Oxenstierna
Axel Gustafsson Oxenstierna af Södermöre (; 1583–1654), Count of Södermöre, was a Swedish statesman. He became a member of the Swedish Privy Council in 1609 and served as Lord High Chancellor of Sweden from 1612 until his death. He was a confidant of King Gustavus Adolphus and then Queen Christina, of whom he was at first regent. Oxenstierna is widely considered one of the most influential people in Swedish history. He played an important role during the Thirty Years' War and was appointed Governor-General of occupied Prussia; he is also credited for having laid the foundations of the modern central administrative structure of the State, including the creation of counties ( sv, län). Early life and education Oxenstierna was born on 16 June 1583, at Fånö in Uppland, the son of Gustaf Gabrielsson Oxenstierna (1551–1597) and Barbro Axelsdotter Bielke (1556–1624), as the oldest of nine siblings. His parents belonged to the ancient and influential high noble families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
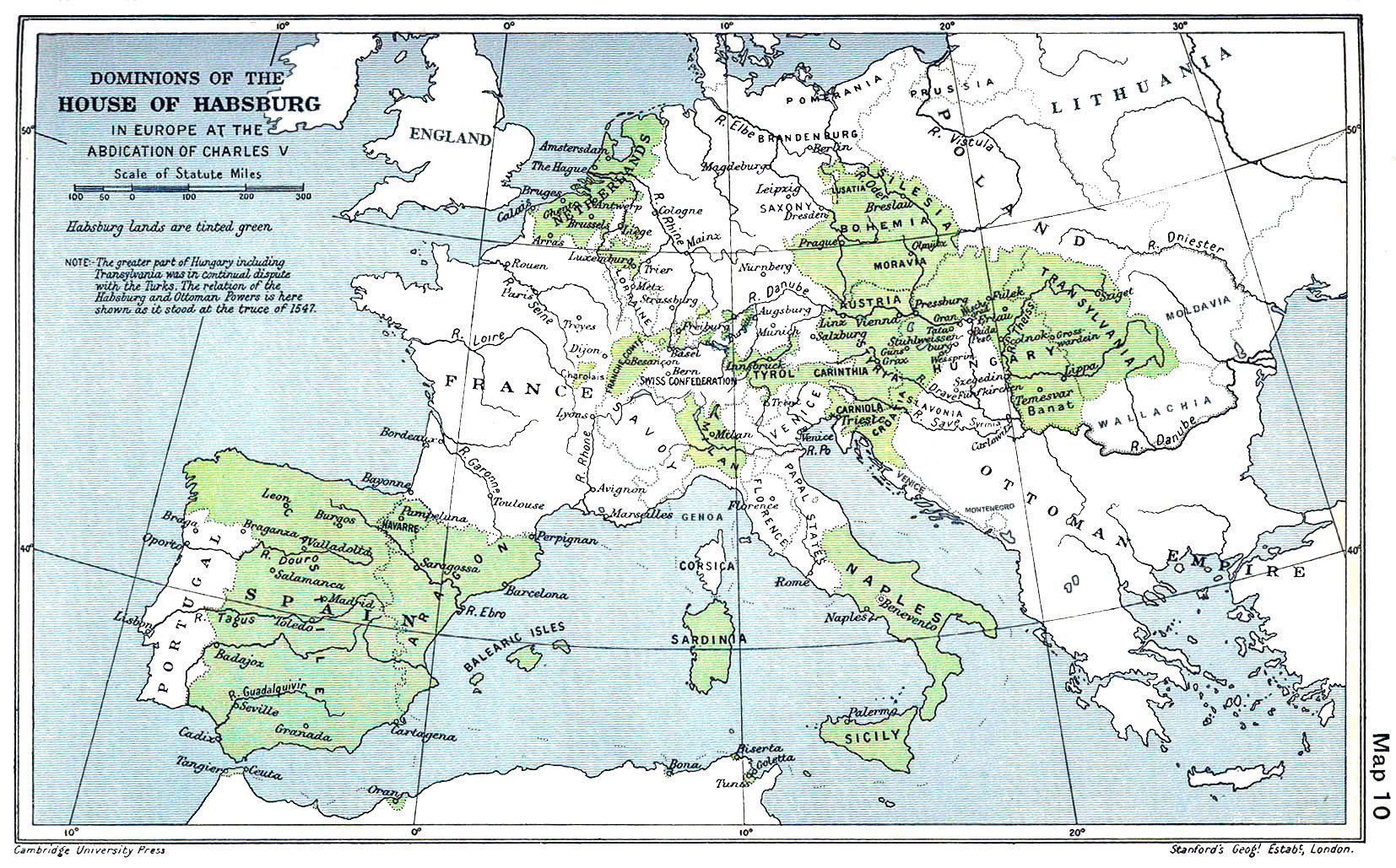
Spanish Netherlands
Spanish Netherlands (Spanish: Países Bajos Españoles; Dutch: Spaanse Nederlanden; French: Pays-Bas espagnols; German: Spanische Niederlande.) (historically in Spanish: ''Flandes'', the name "Flanders" was used as a ''pars pro toto'') was the Habsburg Netherlands ruled by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556 to 1714. They were a collection of States of the Holy Roman Empire in the Low Countries held in personal union by the Spanish Crown (also called Habsburg Spain). This region comprised most of the modern states of Belgium and Luxembourg, as well as parts of northern France, the southern Netherlands, and western Germany with the capital being Brussels. The Army of Flanders was given the task of defending the territory. The Imperial fiefs of the former Burgundian Netherlands had been inherited by the Austrian House of Habsburg from the extinct House of Valois-Burgundy upon the death of Mary of Burgundy in 1482. The Seventeen Provinces formed the core of the Habsbur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breisach
Breisach (formerly Altbreisach; Low Alemannic: ''Alt-Brisach'') is a town with approximately 16,500 inhabitants, situated along the Rhine in the Rhine Valley, in the district Breisgau-Hochschwarzwald, Baden-Württemberg, Germany, about halfway between Freiburg and Colmar — 20 kilometres away from each — and about 60 kilometres north of Basel near the Kaiserstuhl. A bridge leads over the Rhine to Neuf-Brisach, Alsace. Its name is Celtic and means breakwater. The root ''Breis'' can also be found in the French word ''briser'' meaning to break. The hill, on which Breisach came into existence was — at least when there was a flood — in the middle of the Rhine, until the Rhine was straightened by the engineer Johann Gottfried Tulla in the 19th century, thus breaking its surge. History The seat of a Celtic prince was at the hill on which Breisach is built. The Romans maintained an auxiliary castle on Mons Brisiacus (which came from the Celtic word Brisger, which mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the European Parliament. Located at the border with Germany in the historic region of Alsace, it is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin department. In 2019, the city proper had 287,228 inhabitants and both the Eurométropole de Strasbourg (Greater Strasbourg) and the Arrondissement of Strasbourg had 505,272 inhabitants. Strasbourg's metropolitan area had a population of 846,450 in 2018, making it the eighth-largest metro area in France and home to 14% of the Grand Est region's inhabitants. The transnational Eurodistrict Strasbourg-Ortenau had a population of 958,421 inhabitants. Strasbourg is one of the ''de facto'' four main capitals of the European Union (alongside Brussels, Luxembourg and Frankfurt), as it is the seat of several European ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, Fashion capital, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called Caput Mundi#Paris, the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France Regions of France, region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhineland
The Rhineland (german: Rheinland; french: Rhénanie; nl, Rijnland; ksh, Rhingland; Latinised name: ''Rhenania'') is a loosely defined area of Western Germany along the Rhine, chiefly its middle section. Term Historically, the Rhinelands refers (physically speaking) to a loosely defined region embracing the land on the banks of the Rhine in Central Europe, which were settled by Ripuarian and Salian Franks and became part of Frankish Austrasia. In the High Middle Ages, numerous Imperial States along the river emerged from the former stem duchy of Lotharingia, without developing any common political or cultural identity. A "Rhineland" conceptualization can be traced to the period of the Holy Roman Empire from the sixteenth until the eighteenth centuries when the Empire's Imperial Estates (territories) were grouped into regional districts in charge of defence and judicial execution, known as Imperial Circles. Three of the ten circles through which the Rhine flowed r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embassy Of Sweden, Paris
The Embassy of Sweden in Paris is Sweden's diplomatic mission in France. Buildings Chancery In the 1910s, the chancery building was located at 58 Avenue Marceau in Paris. In the late 1930s, the chancery moved around the corner to 25 rue de Bassano and the residence was still at 58 Avenue Marceau. In the late 1960s, the chancery moved to 66 rue Boissière in the 16th arrondissement. In the 1970s, the consulate department was located at 125 Avenue des Champs-Élysées. Since 1974, the chancery and residence is located at 17 rue Barbet de Jouy at Rive Gauche in the 7th arrondissement. The embassy site was bought in 1959 by the Swedish state for 2 million Swedish krona. A Swedish architect was first hired to draw up a proposal for an embassy and ambassadorial residence. When the drawings were not accepted by the French licensing authority, it was instead a Frenchman who came up with the final proposal. The architect André Malizard's proposal has been described as "functional arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland , source1_coordinates= , source1_elevation = , source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein , source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland , source2_coordinates= , source2_elevation = , source_confluence = Reichenau , source_confluence_location = Tamins, Graubünden, Switzerland , source_confluence_coordinates= , source_confluence_elevation = , mouth = North Sea , mouth_location = Netherlands , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = , basin_size = , tributaries_left = , tributaries_right = , custom_label = , custom_data = , extra = The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label= Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label= Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had a population of 1,898,533. Alsatian culture is characterized by a blend of Germanic and French influences. Until 1871, Alsace included the area now known as the Territoire de Belfort, which formed its southernmost part. From 1982 to 2016, Alsace was the smallest administrative ''région'' in metropolitan France, consisting of the Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin departments. Territorial reform passed by the French Parliament in 2014 resulted in the merger of the Alsace administrative region with Champagne-Ardenne and Lorraine to form Grand Est. On 1 January 2021, the departments of Bas-Rhin and Haut-Rhin merged into the new European Collectivity of Alsace but remained part of the region Grand Est. Alsatian is an Alemannic dialect closely related ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Compiègne (1624)
The Treaty of Compiègne, signed on 10 June 1624, was a mutual defence alliance between the Kingdom of France and the Dutch Republic, for an initial period of three years. One of a series of treaties designed to isolate Spain, France agreed to subsidise the Dutch in their War of Independence in return for naval assistance, and trading privileges. It ultimately proved controversial, since its provisions were used to require the Protestant Dutch to help suppress their French co-religionists in La Rochelle. Background The first half of the 17th century in Europe was dominated by the struggle between the Bourbon kings of France and their Habsburg rivals in Spain and in the Holy Roman Empire. Habsburg territories in the Spanish Netherlands, Franche-Comté, and the Pyrenees blocked French expansion, and made it vulnerable to invasion. During the French Wars of Religion, Spain co-operated with the Catholic League in occupying large areas of France, before the succession of Henry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huguenot Rebellions
The Huguenot rebellions, sometimes called the Rohan Wars after the Huguenot leader Henri de Rohan, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which French Calvinist Protestants (Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted against royal authority. The uprising occurred a decade after the death of Henry IV who, himself originally a Huguenot before converting to Catholicism, had protected Protestants through the Edict of Nantes. His successor Louis XIII, under the regency of his Italian Catholic mother Marie de' Medici, became more intolerant of Protestantism. The Huguenots tried to respond by defending themselves, establishing independent political and military structures, establishing diplomatic contacts with foreign powers, and openly revolting against central power. The Huguenot rebellions came after two decades of internal peace under Henry IV, following the intermittent French Wars of Religion of 1562–1598. First Huguenot rebellion (1620–1622) The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |