|
Transverse Facial Artery
The transverse facial artery is an artery that branches from the superficial temporal artery and runs across the face. Course The transverse facial artery is given off from the superficial temporal artery before that vessel leaves the parotid gland; running forward through the substance of the gland, it passes transversely across the side of the face, between the parotid duct and the lower border of the zygomatic arch, and divides into numerous branches, which supply the parotid gland and parotid duct, the masseter muscle, and the integument, and anastomose with the facial artery, the masseteric artery, the buccinator artery, and the infraorbital artery. This vessel rests on the masseter, and is accompanied by one or two branches of the facial nerve. Additional images File:Gray507.png, Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries See also * Facial artery The facial artery (external maxillary artery in older texts) is a br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraorbital Artery
The supraorbital artery is a branch of the ophthalmic artery. It passes anteriorly within the orbit to exit the orbit through the supraorbital foramen or notch alongside the supraorbital nerve, splitting into two terminal branches which go on to form anastomoses with arteries of the head. Structure Origin The supraorbital artery arises from the ophthalmic artery. Course and relations It travels anteriorly in the orbit by passing superior to the eye and medial to the superior rectus and levator palpebrae superioris. It then joins the supraorbital nerve to jointly pass between the periosteum of the roof of the orbit and the levator palpebrae superioris towards the supraorbital foramen or notch. After passing through the supraorbital foramen or notch, it often splits into a superficial branch and a deep branch. Distribution The supraorbital artery contributes arterial supply to: the superior rectus muscle, superior oblique muscle, levator palpebrae muscles, periorbita, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parotid Gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands. Etymology The word ''parotid'' literally means "beside the ear". From Greek παρωτίς (stem παρωτιδ-) : (gland) behind the ear < παρά - pará : in front, and οὖς - ous (stem ὠτ-, ōt-) : ear. Structure The parotid glands are a pair of mainly |
Facial Artery
The facial artery (external maxillary artery in older texts) is a branch of the external carotid artery that supplies structures of the superficial face. Structure The facial artery arises in the carotid triangle from the external carotid artery, a little above the lingual artery and, sheltered by the ramus of the mandible. It passes obliquely up beneath the digastric and stylohyoid muscles, over which it arches to enter a groove on the posterior surface of the submandibular gland. It then curves upward over the body of the mandible at the antero-inferior angle of the masseter; passes forward and upward across the cheek to the angle of the mouth, then ascends along the side of the nose, and ends at the medial commissure of the eye, under the name of the angular artery. The facial artery is remarkably tortuous. This is to accommodate itself to neck movements such as those of the pharynx in deglutition; and facial movements such as those of the mandible, lips, and cheeks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subclavian Artery
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery. The usual branches of the subclavian on both sides of the body are the vertebral artery, the internal thoracic artery, the thyrocervical trunk, the costocervical trunk and the dorsal scapular artery, which may branch off the transverse cervical artery, which is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. The subclavian becomes the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib. Structure From its origin, the subclavian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotid Artery , an artery on each side of the head and neck supplying blood to the brain
{{SIA ...
Carotid artery may refer to: * Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery * External carotid artery, an artery on each side of the head and neck supplying blood to the face, scalp, skull, neck and meninges * Internal carotid artery The internal carotid artery (Latin: arteria carotis interna) is an artery in the neck which supplies the anterior circulation of the brain. In human anatomy, the internal and external carotids arise from the common carotid arteries, where these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Facial Nerve
The facial nerve, also known as the seventh cranial nerve, cranial nerve VII, or simply CN VII, is a cranial nerve that emerges from the pons of the brainstem, controls the muscles of facial expression, and functions in the conveyance of taste sensations from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. The nerve typically travels from the pons through the facial canal in the temporal bone and exits the skull at the stylomastoid foramen. It arises from the brainstem from an area posterior to the cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve) and anterior to cranial nerve VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve). The facial nerve also supplies preganglionic parasympathetic fibers to several head and neck ganglia. The facial and intermediate nerves can be collectively referred to as the nervus intermediofacialis. The path of the facial nerve can be divided into six segments: # intracranial (cisternal) segment # meatal (canalicular) segment (within the internal auditory canal) # labyrinthine segment (i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masseter
In human anatomy, the masseter is one of the muscles of mastication. Found only in mammals, it is particularly powerful in herbivores to facilitate chewing of plant matter. The most obvious muscle of mastication is the masseter muscle, since it is the most superficial and one of the strongest. Structure The masseter is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral muscle, consisting of three heads, superficial, deep and coronoid. The fibers of superficial and deep heads are continuous at their insertion. Superficial head The superficial head, the larger, arises by a thick, tendinous aponeurosis from the temporal process of the zygomatic bone, and from the anterior two-thirds of the inferior border of the zygomatic arch. Its fibers pass inferior and posterior, to be inserted into the angle of the mandible and inferior half of the lateral surface of the ramus of the mandible. Deep head The deep head is much smaller, and more muscular in texture. It arises from the posterior third of the lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
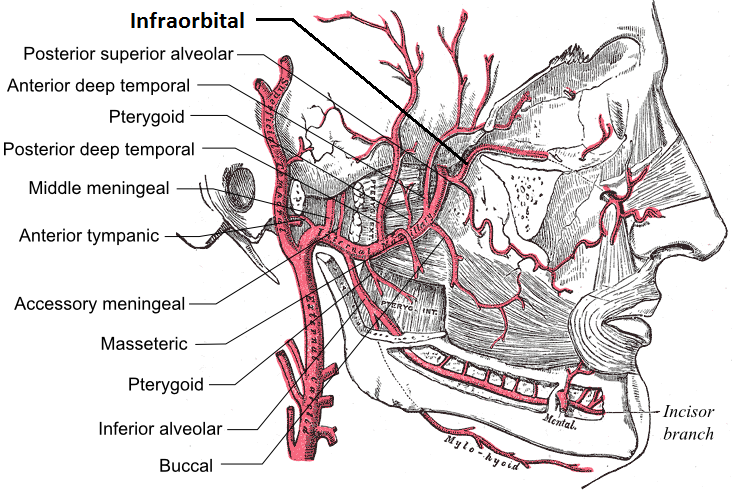
Infraorbital Artery
The infraorbital artery is an artery in the head that branches off the maxillary artery, emerging through the infraorbital foramen, just under the orbit of the eye. Course The infraorbital artery appears, from its direction, to be the continuation of the trunk of the maxillary artery, but often arises in conjunction with the posterior superior alveolar artery. It runs along the infraorbital groove and canal with the infraorbital nerve, and emerges on the face through the infraorbital foramen, beneath the infraorbital head of the levator labii superioris muscle. Branches While in the canal, it gives off * (a) orbital branches which assist in supplying the inferior rectus and inferior oblique and the lacrimal sac, and * (b) anterior superior alveolar arteries - branches which descend through the anterior alveolar canals to supply the upper incisor and canine teeth and the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus. On the face, some branches pass upward to the medial angle of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buccinator Artery
The buccal artery (buccinator artery) is a small artery in the head. It branches off the second part of the maxillary artery and supplies the cheek and buccinator muscle. Course It runs obliquely forward, between the pterygoideus internus The medial pterygoid muscle (or internal pterygoid muscle), is a thick, quadrilateral muscle of the face. It is supplied by the mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (V). It is important in mastication (chewing). Structure The medial pteryg ... and the insertion of the temporalis, to the outer surface of the buccinator, to which it is distributed, anastomosing with branches of the facial artery and with the Infraorbital artery, infraorbital. From the infraorbital area, it descends bilaterally in the superficial face along the lateral margin of the nose, then running anti-parallel to the facial artery across the lateral oral region. Additional images file:Gray508.png, The arteries of the face and scalp. References External links < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masseteric Artery
The masseteric artery is small and passes laterally through the mandibular notch to the deep surface of the masseter muscle, which it supplies. It anastomoses with the masseteric branches of the external maxillary artery and with the transverse facial artery The transverse facial artery is an artery that branches from the superficial temporal artery and runs across the face. Course The transverse facial artery is given off from the superficial temporal artery before that vessel leaves the parotid glan .... See also * Masseteric nerve References Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygomatic Arch
In anatomy, the zygomatic arch, or cheek bone, is a part of the skull formed by the zygomatic process of the temporal bone (a bone extending forward from the side of the skull, over the opening of the ear) and the temporal process of the zygomatic bone (the side of the cheekbone), the two being united by an oblique suture (the zygomaticotemporal suture); the tendon of the temporal muscle passes medial to (i.e. through the middle of) the arch, to gain insertion into the coronoid process of the mandible (jawbone). The jugal point is the point at the anterior (towards face) end of the upper border of the zygomatic arch where the masseteric and maxillary edges meet at an angle, and where it meets the process of the zygomatic bone. The arch is typical of '' Synapsida'' (“fused arch”), a clade of amniotes that includes mammals and their extinct relatives, such as '' Moschops'' and '' Dimetrodon''. Structure The zygomatic process of the temporal arises by two roots: * an '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parotid Gland
The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands. Etymology The word ''parotid'' literally means "beside the ear". From Greek παρωτίς (stem παρωτιδ-) : (gland) behind the ear < παρά - pará : in front, and οὖς - ous (stem ὠτ-, ōt-) : ear. Structure The parotid glands are a pair of mainly |