|
Transit Of Asteroids
A transit of a minor planet takes place when a minor planet passes directly between an observer and another heavenly body, obscuring a small part of that body's disc. From the perspective of observers on Earth, transits of the Sun and Moon by minor planets are very rare, as the minor planets orbiting between the Earth and those bodies are few and very small. Transits of the Sun would be more visible from the outer planets. Transits should be distinguished from occultations, in which the minor planet entirely blocks out the light from the other body. Asteroids Most asteroids orbit in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. For this reason, transits of the Sun by asteroids are rare from Earth's perspective, but would not be uncommon from the perspective of Jupiter. Still, the high inclination of many asteroid orbits would make this less common that it would be otherwise. One example of a forthcoming asteroid transit visible from Jupiter will be that of 4 Vesta, which will trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet
According to the International Astronomical Union (IAU), a minor planet is an astronomical object in direct orbit around the Sun that is exclusively classified as neither a planet nor a comet. Before 2006, the IAU officially used the term ''minor planet'', but that year's meeting reclassified minor planets and comets into dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies (SSSBs).Press release, IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes International Astronomical Union, August 24, 2006. Accessed May 5, 2008. Minor planets include asteroids ( |
Angular Diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it is the angular aperture (of a lens). The angular diameter can alternatively be thought of as the angular displacement through which an eye or camera must rotate to look from one side of an apparent circle to the opposite side. Humans can resolve with their naked eyes diameters of up to about 1 arcminute (approximately 0.017° or 0.0003 radians). This corresponds to 0.3 m at a 1 km distance, or to perceiving Venus as a disk under optimal conditions. Formula The angular diameter of a circle whose plane is perpendicular to the displacement vector between the point of view and the center of said circle can be calculated using the formula :\delta = 2\arctan \left(\frac\right), in which \delta is the angular diameter, and d is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit Of Venus
frameless, upright=0.5 A transit of Venus across the Sun takes place when the planet Venus passes directly between the Sun and a superior planet, becoming visible against (and hence obscuring a small portion of) the solar disk. During a transit, Venus can be seen from Earth as a small black dot moving across the face of the Sun. The duration of such transits is usually several hours (the transit of 2012 lasted 6 hours and 40 minutes). A transit is similar to a solar eclipse by the Moon. While the diameter of Venus is more than three times that of the Moon, Venus appears smaller, and travels more slowly across the face of the Sun, because it is much farther away from Earth. Transits of Venus are among the rarest of predictable astronomical phenomena. They occur in a pattern that generally repeats every 243 years, with pairs of transits eight years apart separated by long gaps of 121.5 years and 105.5 years. The periodicity is a reflection of the fact that the orbital period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transit Of Mercury
frameless, upright=0.5 A transit of Mercury across the Sun takes place when the planet Mercury passes directly between the Sun and a superior planet. During a transit, Mercury appears as a tiny black dot moving across the Sun as the planet obscures a small portion of the solar disk. Because of orbital alignments, transits viewed from Earth occur in May or November. The last four such transits occurred on May 7, 2003; November 8, 2006; May 9, 2016; and November 11, 2019. The next will occur on November 13, 2032. A typical transit lasts several hours. Mercury transits are much more frequent than transits of Venus, with about 13 or 14 per century, primarily because Mercury is closer to the Sun and orbits it more rapidly. On June 3, 2014, the Mars rover ''Curiosity'' observed the planet Mercury transiting the Sun, marking the first time a planetary transit has been observed from a celestial body besides Earth. Scientific investigation The orbit of the planet Mercury lies interi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
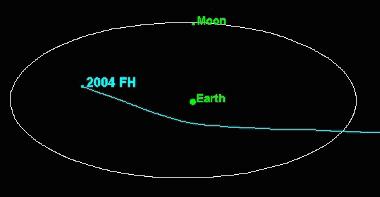
2004 FH
2004 FH is a micro-asteroid and near-Earth object of the Aten group, approximately 30 meters in diameter, that passed just above the Earth's surface on 18 March 2004, at 22:08 UTC. It was the 11th closest approach to Earth recorded . The asteroid was first observed on 16 March 2004, by astronomers of the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico. Orbit and classification is an Aten asteroid. It passed 43,000 km from the Earth on 18 March 2004. For comparison, geostationary satellites orbit Earth at 35,790 kilometers. Despite its small size, it is still the fourth largest asteroid detected coming closer to the Earth than the Moon. Had this object hit Earth, it would probably have detonated high in the atmosphere. It might have produced a blast measured in hundreds of kilotons of TNT, but may not have produced any effect on the ground. It could also have been an Earth-grazing fireball if it had been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Notable Asteroids
The following is a collection of lists of asteroids of the Solar System that are exceptional in some way, such as their size or orbit. For the purposes of this article, "asteroid" refers to minor planets out to the orbit of Neptune, and includes the dwarf planet 1 Ceres, the Jupiter trojans and the centaur (small Solar System body), centaurs, but not trans-Neptunian objects (objects in the Kuiper belt, scattered disc or inner Oort cloud). For a complete list of minor planets in numerical order, see List of minor planets. Background Asteroids are given minor planet numbers, but not all minor planets are asteroids. Minor planet numbers are also given to objects of the Kuiper belt, which is similar to the asteroid belt but farther out (around 30–60 AU), whereas asteroids are mostly between 2–3 AU from the Sun and at the orbit of Jupiter 5 AU from the Sun. Also, comets are not typically included under minor planet numbers, and have their own Astronomical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/1819 N1
The Great Comet of 1819, officially designated as C/1819 N1, also known as Comet Tralles, was an exceptionally bright and easily visible comet, approaching an apparent magnitude of 1–2, discovered July 1, 1819 by the German astronomer Johann Georg Tralles in Berlin. It was the first comet analyzed using polarimetry, by French mathematician François Arago. Discovery On July 1, 1819, Johann Georg Tralles in Berlin observed a brilliant comet low in the sky during the evening twilight. It was confirmed the next night by the astronomer Johann Elert Bode, also in Berlin. Observations On July 2, Tralles found the comet to have a coma of 40″. On July 3, Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve measured the nucleus at 8″ with a tail of several degrees. Heinrich Wilhelm Matthias Olbers reported that the nucleus had an apparent magnitude of 1–2 and a tail about 7–8° long. The comet was last sighted by Struve on October 25. Also on July 3, François Arago used a polarimeter of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comet Halley
Halley's Comet or Comet Halley, officially designated 1P/Halley, is a short-period comet visible from Earth every 75–79 years. Halley is the only known short-period comet that is regularly visible to the naked eye from Earth, and thus the only naked-eye comet that can appear twice in a human lifetime. Halley last appeared in the inner parts of the Solar System in 1986 and will next appear in mid-2061. Halley's periodic returns to the inner Solar System have been observed and recorded by astronomers around the world since at least 240 BC. But it was not until 1705 that the English astronomer Edmond Halley understood that these appearances were reappearances of the same comet. As a result of this discovery, the comet is named after Halley. During its 1986 visit to the inner Solar System, Halley's Comet became the first comet to be observed in detail by spacecraft, providing the first observational data on the structure of a comet nucleus and the mechanism of coma and tail fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-Earth Asteroid
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun ( perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). If a NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but a small fraction are comets. There are over 30,503 known near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) and over a hundred known short-period near-Earth comets (NECs). A number of solar-orbiting meteoroids were large enough to be tracked in space before striking the Earth. It is now widely accepted that collisions in the past have had a significant role in shaping the geological and biological history of the Earth. Asteroids as small as in diameter can cause significant damage to the local environment and human populations. Larger asteroids penetrate the atmosphere to the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2101 Adonis
2101 Adonis, ''provisional designation'': , is an asteroid on an extremely eccentric orbit, classified as potentially hazardous asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group. ''Adonis'' measures approximately in diameter. Discovered by Eugène Delporte at Uccle in 1936, it became a lost asteroid until 1977. It may also be an extinct comet and a source of meteor showers. It was named after Adonis from Greek mythology. Discovery ''Adonis'' was discovered on 12 February 1936, by Belgian astronomer Eugène Delporte at the Royal Observatory of Belgium in Uccle. After its initial discovery, which happened during a close approach with Earth, the asteroid was observed for two months, before it became a lost asteroid, as not enough observations could be made to calculate a sufficiently accurate orbit. It took 41 years until it was finally rediscovered by the American astronomer Charles Kowal in 1977, based on mathematical predictions made by Dr. Brian Marsden. Orbit and classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Second
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is of an arcminute, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcsecond (mas) and microarcsecond (μas), for instance, are commonly used in astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_(cropped).jpg)

