|
Train Protection System
A train protection system is a railway technical installation to ensure safe operation in the event of human error. Development Train stops The earliest systems were train stops, as still used by the New York City Subway, the Toronto subway, the London Underground, the Moscow Subway (only on the older lines) and the Berlin S-Bahn. Beside every signal is a moveable arm. If the signal is red, levers connected to valves on any passing train hit the arm, opening the brake line, applying the emergency brake, If the signal shows green, the arm is turned away from the levers and there is no contact. The Great Western Railway in the UK introduced its ' automatic train control' system in the early years of the 20th century. Each distant signal had before it a ramp between the running rails. If the signal showed green, the ramp was energised with a low voltage current which was passed to the locomotive when a shoe came into contact with the ramp. A bell rang in the locomotive's ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Error
Human error refers to something having been done that was " not intended by the actor; not desired by a set of rules or an external observer; or that led the task or system outside its acceptable limits".Senders, J.W. and Moray, N.P. (1991) Human Error: Cause, Prediction, and Reduction'. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, p.25. . Human error has been cited as a primary cause contributing factor in disasters and accidents in industries as diverse as nuclear power (e.g., the Three Mile Island accident), aviation (see pilot error), space exploration (e.g., the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster and Space Shuttle Columbia disaster), and medicine (see medical error). Prevention of human error is generally seen as a major contributor to reliability and safety of (complex) systems. Human error is one of the many contributing causes of risk events. Definition Human error refers to something having been done that was "not intended by the actor; not desired by a set of rules or an external obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
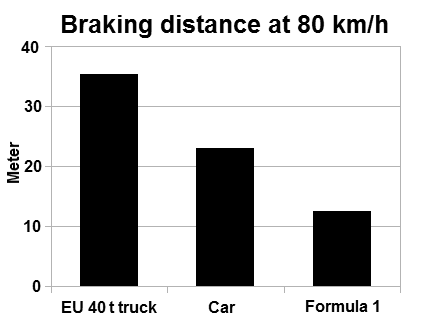
Braking Distance
Braking distance refers to the distance a vehicle will travel from the point when its brakes are fully applied to when it comes to a complete stop. It is primarily affected by the original speed of the vehicle and the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road surface, and negligibly by the tires' rolling resistance and vehicle's air drag. The type of brake system in use only affects trucks and large mass vehicles, which cannot supply enough force to match the static frictional force. The braking distance is one of two principal components of the total stopping distance. The other component is the reaction distance, which is the product of the speed and the perception-reaction time of the driver/rider. A perception-reaction time of 1.5 seconds, and a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.7 are standard for the purpose of determining a bare baseline for accident reconstruction and judicial notice; most people can stop slightly sooner under ideal conditions. Brakin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blocco Automatico A Correnti Codificate
Blocco automatico a correnti codificate (BACC or BAcc, ''automatic block with codified currents'') is a signalling block system used in Italy on railway lines using 3 kV DC electrification. The track circuits used to detect the presence of a train also transmit coded signals to the trains which are used for train protection and cab signaling. Train protection systems that use BAcc are RS4 Codici, RS9 Codici and SCMT. Codes The information is conveyed by superposition of two amplitude-modulated alternating currents in the rails (with a carrier frequency of 50 Hz and 178 Hz, respectively). Receiver coils in front of the first axle of a locomotive or control car are used to detect the signal. The frequency of the modulating signal encodes the signal aspect: {, class="wikitable" , - ! modulation frequency of 50 or 83.3 Hz carrier , , modulation frequency of 178 Hz carrier , , code , , meaning , - , (none) , , (none) , , AC(''Assenza di Codice'') , , trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Train Protection
Automatic train protection (ATP) is a type of train protection system which continually checks that the speed of a train is compatible with the permitted speed allowed by signalling, including automatic stop at certain signal aspects. If it is not, ATP activates an emergency brake to stop the train. See also * Advanced Civil Speed Enforcement System * Anti Collision Device * Automatic Warning System * Automatische treinbeïnvloeding (ATB) * British Rail's ATP system * Continuous Automatic Warning System (CAWS) * EBICAB * European Train Control System (ETCS) * Kavach * Positive Train Control (PTC) * Punktförmige Zugbeeinflussung PZB or Indusi is an intermittent cab signalling system and train protection system used in Germany, Austria, Slovenia, Croatia, Romania, Israel, Serbia, on two lines in Hungary, on the Tyne and Wear Metro in the United Kingdom, and forme ... (PZB) * Train Protection & Warning System * Train Warning System References {{ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Train Control System
An Advanced Train Control System (ATCS) is a system of railway/railroad equipment designed to ensure safety by monitoring locomotive and train locations, providing analysis and reporting, automating track warrants A track warrant is a set of instructions issued to a train crew authorizing specific train movements. The system is widely used in North America. The warrant is issued by the train dispatcher and delivered to the train crew via radio. The train cr ..., detecting blind spot and similar orders. ATCS specifications are published by the Association of American Railroads (AAR), and are designed to document the stated requirements of railway/railroad operational and technical professionals concerning ATCS hardware and software.Association of American Railroads, Washington, DC (2005)"Manual of Standards and Recommended Practices. Section K: Railway Electronics." The basic principle behind ATCS is to provide a cost efficient, safe, modular, train control system with an open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Train Control
Automatic train control (ATC) is a general class of train protection systems for railways that involves a speed control mechanism in response to external inputs. For example, a system could effect an emergency brake application if the driver does not react to a signal at danger. ATC systems tend to integrate various cab signalling technologies and they use more granular deceleration patterns in lieu of the rigid stops encountered with the older automatic train stop (ATS) technology. ATC can also be used with automatic train operation (ATO) and is usually considered to be the safety-critical part of a railway system. Over time, there have been many different safety systems labelled as "automatic train control". The first experimental apparatus was installed on the Henley branch line in January 1906 by the Great Western Railway, although it would now be referred to as an automatic warning system (AWS) because the driver retained full command of braking. The term is especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatische Treinbeïnvloeding
Automatische TreinBeïnvloeding or ATB (English: Automatic Train Control) is a Dutch train protection system first developed in the 1950s. Its installation was spurred by the Harmelen train disaster of 1962. ATB operates by the train collecting electrical signals from line-side apparatus and will override the driver's controls in the following situations: * a) failure to reduce speed at a caution signal (ATB will slow the train sufficiently to stop at the next signal). * b) failure to observe speed limit (ATB makes an immediate emergency brake application) ATB-EG ATB-EG ''(''ATB Eerste Generatie ''English: ATB First Generation'') is based on the American Pulse Code Cab Signaling system. It is installed on all major Dutch rail lines Technical overview ATB-EG controls 5 speeds: 40 km/h, 60 km/h, 80 km/h, 130 km/h and 140 km/h. Just like Pulse Code Cab Signaling the system works by sending pulses along the AC track circuit. When the circuit is closed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anuncio De Señales Y Frenado Automático
Anuncio de Señales y Frenado Automático (ASFA; "Announcement of Signals and Automatic Braking") is an Automatic Train Protection system widely deployed on the Spanish rail network. It consists of a mechanism that stops a train if the driver does not properly heed signals. Operation ASFA makes use of inductive coupling between a transceiver on the rolling stock and a balise (tuned electronic beacon) that oscillates at one of nine preset frequencies when activated by a magnetic field emanating from said transceiver. The balise requires no external power, however, there is a cable for controlling small relays inside the transponder which switch capacitors in/out of the coil circuit and determine which frequency is detected by the passing train. The nine frequencies lie in the 60-100 kHz range (although only five frequencies are used in ASFA) and the wayside balises are mounted between the rails offset from the track centerline to provide directionality. Each balise is protected f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALSN
ALSN (Автоматическая локомотивная сигнализация непрерывная, in Latin - Avtomaticheskaya Lokomotivnaya Signalizatsiya Nepreryvnaya, meaning ''Continuous Automatic Train Signalling'') is a train control system used widely on the main lines of the ex-Soviet states (Russian Federation, Ukraine, Belarus, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia). It uses modulated pulses inducted into rails similar to the Italian RS4 Codici and American Pulse Code Cab Signaling. On high-speed lines the variant ALS-EN (АЛС-ЕН) is used which takes advantage of a double phase difference modulation of the carrier wave. The name ALSN (АЛСН - автоматическая локомотивная сигнализация непрерывного действия) is composed of ALS, literally "Automatic Locomotive Signalling" (АЛС - автоматическая локомотивная сигнализация) and the variant designation N "Continuous Effect" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Civil Speed Enforcement System
Advanced Civil Speed Enforcement System (ACSES) is a positive train control cab signaling system developed by Alstom. The system is designed to prevent train-to-train collisions, protect against overspeed, and protect work crews with temporary speed restrictions. The information about permanent and temporary speed restrictions is transmitted to the train by transponders ( Balises) lying in the track, coded track circuits and digital radio. It was installed beginning in 2000 on all of Amtrak's Northeast Corridor (except MTA territory) between Washington and Boston, and has been fully active since December 2015, a few months after the 2015 Philadelphia train derailment which it would have prevented. General system design ACSES provides railway trains with positive enforcement of "civil" speed restrictions (those based on the physical characteristics of the line). The on-board components keep track of a train's position and continuously calculates a maximum safe braking curve fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communications-based Train Control
Communications-based train control (CBTC) is a railway signaling system that uses telecommunications between the train and track equipment for traffic management and infrastructure control. CBTC allows a train's position to be known more accurately than with traditional signaling systems. This makes railway traffic management safer and more efficient. Metros (and other railway systems) are able to reduce headways while maintaining or even improving safety. A CBTC system is a "continuous, automatic train control system utilizing high-resolution train location determination, independent from track circuits; continuous, high-capacity, bidirectional train-to-wayside data communications; and trainborne and wayside processors capable of implementing automatic train protection (ATP) functions, as well as optional automatic train operation (ATO) and automatic train supervision (ATS) functions," as defined in the IEEE 1474 standard.1474.1–1999 – IEEE Standard for Communications-Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north toward the East China Sea, Philippine Sea, and Taiwan in the south. Japan is a part of the Ring of Fire, and spans Japanese archipelago, an archipelago of List of islands of Japan, 6852 islands covering ; the five main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the "mainland"), Shikoku, Kyushu, and Okinawa Island, Okinawa. Tokyo is the Capital of Japan, nation's capital and largest city, followed by Yokohama, Osaka, Nagoya, Sapporo, Fukuoka, Kobe, and Kyoto. Japan is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh most populous country in the world, as well as one of the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated and Urbanization by country, urbanized. About three-fourths of Geography of Japan, the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |