|
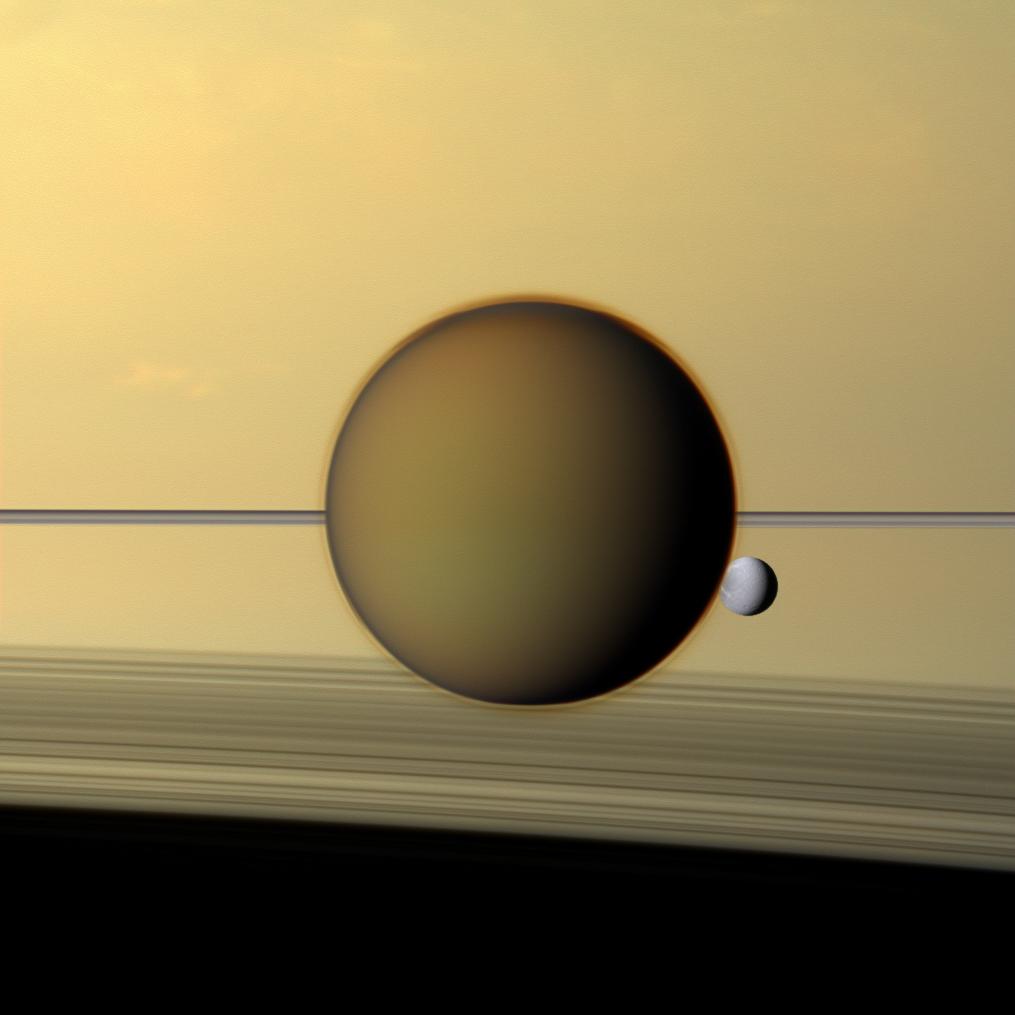
Titan Mare Explorer
Titan Mare Explorer (TiME) is a proposed design for a lander for Saturn's moon Titan. TiME is a relatively low-cost, outer-planet mission designed to measure the organic constituents on Titan and would have performed the first nautical exploration of an extraterrestrial sea, analyze its nature and, possibly, observe its shoreline. As a Discovery-class mission it was designed to be cost-capped at US$425 million, not counting launch vehicle funding. It was proposed to NASA in 2009 by Proxemy Research as a scout-like pioneering mission, originally as part of NASA's Discovery Program. The TiME mission design reached the finalist stage during that Discovery mission selection, but was not selected, and despite attempts in the U.S. Senate failed to get earmark funding in 2013. A related Titan Submarine has also been proposed. Discovery-class finalist TiME was one of three Discovery Mission finalists that received US$3 million in May 2011 to develop a detailed concept study. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are examples of group 14 hydrides. Hydrocarbons are generally colourless and Hydrophobe, hydrophobic; their odor is usually faint, and may be similar to that of gasoline or Naphtha, lighter fluid. They occur in a diverse range of molecular structures and phases: they can be gases (such as methane and propane), liquids (such as hexane and benzene), low melting solids (such as paraffin wax and naphthalene) or polymers (such as polyethylene and polystyrene). In the fossil fuel industries, ''hydrocarbon'' refers to naturally occurring petroleum, natural gas and coal, or their hydrocarbon derivatives and purified forms. Combustion of hydrocarbons is the main source of the world's energy. Petroleum is the dominant raw-material source for organic commodity chemicals such as solvents and polymers. Most anthropogenic (human-generated) emissions of greenhouse gases are eithe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Titan
Lakes of liquid ethane and methane exist on the surface of Titan, Saturn's largest moon. This was confirmed by the ''Cassini–Huygens'' space probe, as had been suspected since the 1980s. The large bodies of liquid are known as (seas) and the small ones as (lakes). History and discovery The possibility that there are seas on Titan was first suggested based on data from the Voyager 1 and 2 space probes, which flew past Titan in 1980. The data showed Titan to have a thick atmosphere of approximately the correct temperature and composition to support liquid hydrocarbons. Direct evidence was obtained in 1995 when data from the Hubble Space Telescope and other observations suggested the existence of liquid methane on Titan, either in disconnected pockets or on the scale of satellite-wide oceans, similar to water on Earth. The ''Cassini'' mission affirmed the former hypothesis, although not immediately. When the probe arrived in the Saturnian system in 2004, it was hoped that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligeia Mare
Ligeia Mare is a lake in the north polar region of Titan, the planet Saturn's largest moon. It is the second largest body of liquid on the surface of Titan, after Kraken Mare. Larger than Lake Superior on Earth, it is mostly composed of liquid methane, with unknown but lesser components of dissolved nitrogen and ethane, as well as other organic compounds. It is located at 78° N, 249° W, and has been fully imaged by the '' Cassini'' spacecraft. Measuring roughly 420 km (260 mi) by 350 km (217 mi) across, it has a surface area of about 126,000 km2, and a shoreline over 2,000 km (1,240 mi) in length. The lake may be hydrologically connected to the larger Kraken Mare. Its namesake is Ligeia, one of the sirens in Greek mythology. Description Ligeia Mare has two predominant types of coastline, "crenulated" and "subdued". The former is characterized by hummocky, eroded terrain, the latter by lower, smoother topography and the presence of more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malin Space Science Systems
Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) is a San Diego, California-based private technology company that designs, develops, and operates instruments and technical equipment to fly on uncrewed spacecraft. MSSS is headed by chief scientist and CEO Michael C. Malin. Founded in 1990, their first mission was the failed 1993 Mars Observer for which they developed and operated the Mars Observer Camera Ground Data System. After this mission they were selected to provide the main camera for Mars Global Surveyor. They also developed the cameras that were carried on Mars Polar Lander, Mars Climate Orbiter, 2001 Mars Odyssey, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and ''Phoenix lander''. One of the most successful of their instruments to date was the Mars Observer Camera (MOC), on board the Mars Global Surveyor placed into orbit around Mars in September 1997. From that date until November 2006, the MOC took more than 243,000 images of Mars, some at very high resolution. Among the MOCs notable successes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American Arms industry, defense and aerospace manufacturer with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta on March 15, 1995. It is headquartered in North Bethesda, Maryland, United States. As of January 2022, Lockheed Martin employs approximately 121,000 employees worldwide, including about 60,000 engineers and scientists. Reports from 2024 estimate that Lockheed Martin Corporation (LMT) holds a market cap of around $139.7 billion. Lockheed Martin is one of the largest companies in the aerospace, military support, security, and technologies industry. It was the world's largest defense contractor by revenue for fiscal year 2014.POC Top 20 Defence Contractors of 2014 . Retrieved: July 2015 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Physics Laboratory
The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (or simply Applied Physics Laboratory, or APL) is a not-for-profit university-affiliated research center (UARC) in Howard County, Maryland. It is affiliated with Johns Hopkins University and employs 8,700 people as of 2024. APL is the nation's largest UARC. The lab serves as a technical resource for the Department of Defense, NASA, and other government agencies. APL has developed numerous systems and technologies in the areas of air and missile defense, surface and undersea naval warfare, computer security, and space science and spacecraft construction. While APL provides research and engineering services to the government, it is not a traditional defense contractor, as it is a UARC and a division of Johns Hopkins University. APL is a scientific and engineering research and development division, rather than an academic division, of Johns Hopkins. Hopkins' Whiting School of Engineering offers part-time graduate programs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Chief Scientist
Chief Scientist is the most senior science position at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the United States's civil space program, aeronautics research and space research. Established in 1958, it su ... (NASA). The chief scientist serves as the principal advisor to the NASA Administrator in science issues and as interface to the national and international science community, ensuring that NASA research programs are scientifically and technologically well founded and are appropriate for their intended applications. History The Chief Scientist position was created to advise the NASA Administrator on budget, strategic objectives, and current content of NASA's science programs. The Chief Scientist works closely with appropriate representatives of the NASA Strategic Enterprises and the Field Centers, as well as advisory committees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, including its Rings of Saturn, rings and Moons of Saturn, natural satellites. The Large Strategic Science Missions, Flagship-class robotic spacecraft comprised both NASA's ''Cassini'' space probe and ESA's Huygens (spacecraft), ''Huygens'' lander (spacecraft), lander, which landed on Saturn's largest moon, Titan (moon), Titan. ''Cassini'' was the fourth space probe to visit Saturn and the first to enter its orbit, where it stayed from 2004 to 2017. The two craft took their names from the astronomers Giovanni Cassini and Christiaan Huygens. Launched aboard a Titan IV, Titan IVB/Centaur on October 15, 1997, ''Cassini'' was active in space for nearly 20 years, spending its final 13 years orbiting Saturn and studying the planet and its system a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellen Stofan
Ellen Renee Stofan (born February 24, 1961) is Under Secretary for Science and Research at The Smithsonian and was previously the Director of the National Air and Space Museum. As a planetary geologist, Stofan served as Chief Scientist of NASA and as principal advisor to NASA Administrator Charles Bolden on the agency's science programs, planning and investments. Previously, she was vice president of Proxemy Research in Laytonsville, Maryland, and as an honorary professor in the Earth sciences department at the University College London. Early life and education Ellen Stofan is the daughter of Andrew J. Stofan, a rocket engineer who worked for NASA in a number of roles including director of the NASA Lewis Research Center and associate administrator for NASA's Space Station Office. Ellen Stofan received her Bachelor of Science degree in geology from the College of William & Mary in 1983 and went on to earn masters and doctorate degrees from Brown University. Her doctoral thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane Cycle
Atmospheric methane is the methane present in Earth's atmosphere. The concentration of atmospheric methane is increasing due to methane emissions, and is causing climate change. Methane is one of the most potent greenhouse gases. Methane's radiative forcing (RF) of climate is direct, and it is the second largest contributor to human-caused climate forcing in the historical period. Methane is a major source of water vapour in the stratosphere through oxidation; and water vapour adds about 15% to methane's radiative forcing effect. The global warming potential (GWP) for methane is about 84 in terms of its impact over a 20-year timeframe, and 28 in terms of its impact over a 100-year timeframe. See Table 8.7. Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (around 1750), the methane concentration in the atmosphere has increased by about 160%, and human activities almost entirely caused this increase. Since 1750 methane has contributed 3% of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in terms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |