|
Timeline Of Hindu Texts
Hindu scriptures are traditionally classified into two parts: ''śruti'', meaning "what has been heard" (originally transmitted orally) and ''Smriti'', meaning "what has been retained or remembered" (originally written, and attributed to individual authors). The Vedas are classified under ''śruti''. The following list provides a somewhat common set of reconstructed dates for the ''terminus ante quem'' of Hindu texts, by title and genre. It is notable that Hinduism largely followed an oral tradition to pass on knowledge, for which there is no record of historical dates. All dates here given ought to be regarded as roughly approximate, subject to further revision, and generally as relying for their validity on highly inferential methods and standards of evidence. Samhita, Brahmana layers of the Vedas *''Rigveda'', 1500 – 1100 BCEOberlies, Thomas (''Die Religion des Rgveda'', Wien, 1998, p. 155) gives an estimate of 1100 BCE for the youngest hymns in book 10. Estimates for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
śruti
''Shruti'' ( sa, श्रुति, , ) in Sanskrit means "that which is heard" and refers to the body of most authoritative, ancient religious texts comprising the central canon of Hinduism. Manusmriti states: ''Śrutistu vedo vijñeyaḥ'' (Sanskrit: श्रुतिस्तु वेदो विज्ञेय:) meaning, "Know that Vedas are Śruti". Thus, it includes the four Vedas including its four types of embedded texts—the Samhitas, the Upanishads, the Brahmanas and the Aranyakas.Wendy Doniger O'Flaherty (1988), Textual Sources for the Study of Hinduism, Manchester University Press, , pages 2-3 ''Śruti''s have been variously described as a revelation through ''anubhava'' (direct experience), or of primordial origins realized by ancient Rishis.James Lochtefeld (2002), "Shruti", The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 2: N–Z, Rosen Publishing. , page 645 In Hindu tradition, they have been referred to as ''apauruṣeya'' (not created by humans). The ''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
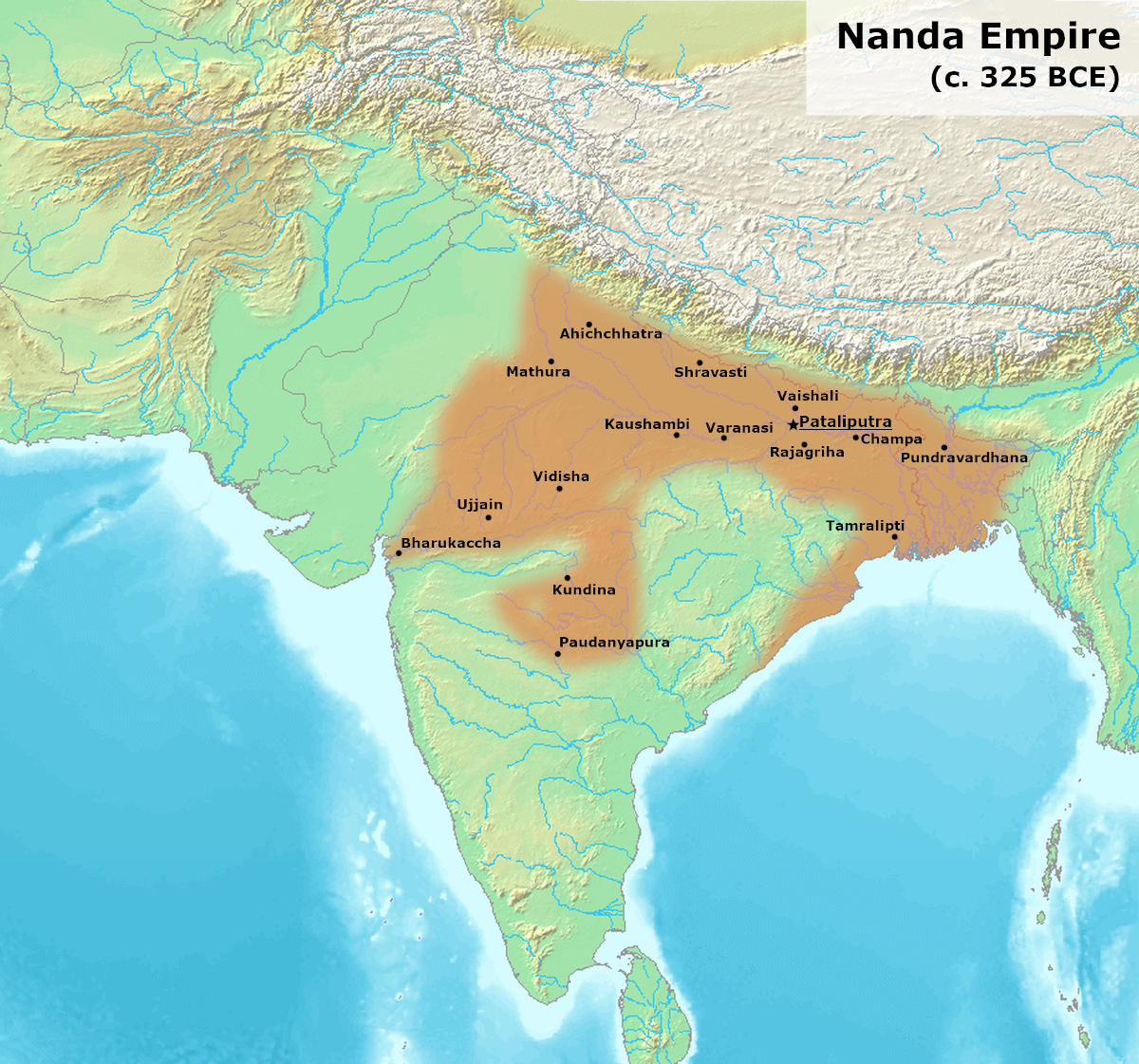
Chanakya
Chanakya (Sanskrit: चाणक्य; IAST: ', ; 375–283 BCE) was an ancient Indian polymath who was active as a teacher, author, strategist, philosopher, economist, jurist, and royal advisor. He is traditionally identified as Kauṭilya or Vishnugupta, who authored the ancient Indian political treatise, the '' Arthashastra'', a text dated to roughly between the fourth century BCE and the third century CE. As such, he is considered the pioneer of the field of political science and economics in India, and his work is thought of as an important precursor to classical economics.Waldauer, C., Zahka, W.J. and Pal, S. 1996Kauṭilya's Arthashastra: A neglected precursor to classical economics ''Indian Economic Review'', Vol. XXXI, No. 1, pp. 101–108. His works were lost near the end of the Gupta Empire in the sixth century CE and not rediscovered until the early 20th century. Around 321 BCE, Chanakya assisted the first Mauryan emperor Chandragupta in his rise to power and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manusmriti
The ''Manusmṛiti'' ( sa, मनुस्मृति), also known as the ''Mānava-Dharmaśāstra'' or Laws of Manu, is one of the many legal texts and constitution among the many ' of Hinduism. In ancient India, the sages often wrote their ideas on how society should run in the manuscripts. It is believed that the original form of ''Manusmriti'' was changed as many things written in the manuscript contradict each other. Over fifty manuscripts of the ''Manusmriti'' are now known, but the earliest discovered, most translated and presumed authentic version since the 18th century has been the "Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) manuscript with Kulluka Bhatta commentary". Modern scholarship states this presumed authenticity is false, and the various manuscripts of ''Manusmriti'' discovered in India are inconsistent with each other, and within themselves, raising concerns of its authenticity, insertions and interpolations made into the text in later times. The metrical text is in Sans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sangam Literature
The Sangam literature (Tamil: சங்க இலக்கியம், ''caṅka ilakkiyam'';) historically known as 'the poetry of the noble ones' (Tamil: சான்றோர் செய்யுள், ''Cāṉṟōr ceyyuḷ'') connotes the ancient Tamil literature and is the earliest known literature of South India. The Tamil tradition and legends link it to three literary gatherings around Madurai and Kapāṭapuram ( Pandyan capitals): the first over 4,440 years, the second over 3,700 years, and the third over 1,850 years before the start of the common era. Scholars consider this Tamil tradition-based chronology as ahistorical and mythical. Most scholars suggest the historical Sangam literature era spanned from c. 300 BCE to 300 CE, while others variously place this early classical Tamil literature period a bit later and more narrowly but all before 300 CE. According to Kamil Zvelebil – a Tamil literature and history scholar, the most acceptable range for the Sangam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Historic Indian Texts
This article attempts to capture in one place the names of books and other works written in ancient India. For the purpose of this list, we consider all books written in India up to and including the Mughal era as being 'ancient books'. Collections Each collection represents a set of books that are collectively known by the collection's name. In the list of books (shown below the table of collections), each book also refers to the collection it belongs to (if it does). Books Key * Subject Area - subject area of the book * Topic - topic (within the subject area) * Collection - belongs to a collection listed in the table above * Date - date (year range) book was written/composed * Reign of - king/ruler in whose reign this book was written (occasionally a book could span reigns) * Reign Age - extent of the reign * Geographic Region - as it was known at the time of writing See also * Indian literature * Timeline of Hindu texts * Sanskrit Buddhist literature * Sansk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swami Venkatesananda
Venkatesananda Saraswati (or Swami Venkatesananda) 29 December 1921 in Tanjore, South India–2 December 1982 in Johannesburg, South Africa), known previously as Parthasarathy, was a disciple of Sivananda Saraswati. He received his spiritual training at the Divine Life Society in Rishikesh, India, and disseminated his master's teachings in South Africa, Mauritius, Australia, and New Zealand. Venkatesananda said that he had been specially commissioned by his master, Sivananda Sivananda Saraswati (or Swami Sivananda; 8 September 1887 – 14 July 1963) was a yoga guru, a Hindu spiritual teacher, and a proponent of Vedanta. Sivananda was born Kuppuswami in Pattamadai, in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu. He stu ..., to spread the gospel of goodness – the four words: "Be good, do Good". Swami Venkatesananda is also referred to as Siva-Pada-Renu (dust of Siva's feet), a title conferred to him by Swami Sivananda, his guru. Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abhinavabharati
''Abhinavabharati'' is a commentary on ancient Indian author Bharata Muni's work of dramatic theory, the '' Natyasastra''. It is the oldest commentary available on the treatise. The ''Abhinavabharati'' was written by Abhinavagupta (c. 950–1020), the great Kashmiri Saivite spiritual leader and a yogi. In this monumental work, Abhinavagupta explains the ''rasasutra'' of Bharata in consonance with the theory of ''abhivyakti'' (expression) propounded in Anandavardhana's (820–890) work ''Dhvanyaloka'' ("aesthetic suggestion"), as well as the tenets of the Pratyabhijna philosophy of Kashmir. According to Abhinavagupta, the aesthetic experience is the manifestation of the innate dispositions of the self The self is an individual as the object of that individual’s own reflective consciousness. Since the ''self'' is a reference by a subject to the same subject, this reference is necessarily subjective. The sense of having a self—or ''selfhoo ..., such as love and sorrow, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiva Sutras Of Vasugupta
Shiva Sutras are a collection of seventy seven aphorisms that form the foundation of the tradition of spiritual mysticism known as Kashmir Shaivism. They are attributed to the sage Vasugupta of the 9th century C.E. Vasugupta is said to have lived near Mahadeva Mountain in the valley of the Harvan stream behind what are now the Shalimar Gardens near Srinagar. One myth is that he received the aphorisms in a dream visitation of a Siddha or semi-divine being. Another is that Lord Shiva came to him in a dream and instructed him to go to a certain rock on which he would find the teachings inscribed. This rock called Shankaropala is still visited by devotees. The other theory is that Lord Shiva taught the Siva-Sutras to Vasugupta in a dream. Whatever the truth is these myths point to the traditional belief that the Shiva sutras are of Philosophical origin or revelation and are surely a very great product of Sanatana Dharma. Historically the Shiva Sutras and the ensuing school ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puranas
Purana (; sa, , '; literally meaning "ancient, old"Merriam-Webster's Encyclopedia of Literature (1995 Edition), Article on Puranas, , page 915) is a vast genre of Indian literature about a wide range of topics, particularly about legends and other traditional lore. The Puranas are known for the intricate layers of symbolism depicted within their stories. Composed originally in Sanskrit and in other Indian languages,John Cort (1993), Purana Perennis: Reciprocity and Transformation in Hindu and Jaina Texts (Editor: Wendy Doniger), State University of New York Press, , pages 185-204 several of these texts are named after major Hindu gods such as Vishnu, Shiva, Brahma, and Adi Shakti. The Puranic genre of literature is found in both Hinduism and Jainism. The Puranic literature is encyclopedic, and it includes diverse topics such as cosmogony, cosmology, genealogies of gods, goddesses, kings, heroes, sages, and demigods, folk tales, pilgrimages, temples, medicine, astronomy, gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahma Sutras
The ''Brahma Sūtras'' ( sa, ब्रह्मसूत्राणि) is a Sanskrit text, attributed to the sage bādarāyaṇa or sage Vyāsa, estimated to have been completed in its surviving form in approx. 400–450 CE,, Quote: "...we can take it that 400–450 is the period during which the ''Brahma Sūtras'' was compiled in its extant form." while the original version might be ancient and composed between 600 BCE and 200 BCE.James Lochtefeld, Brahman, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , p. 746. The text systematizes and summarizes the philosophical and spiritual ideas in the Upanishads.James Lochtefeld, Brahman, The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A–M, Rosen Publishing, , p. 124. The scholar Adi Shankara's interpretation of the Brahmasutra attempted to synthesize diverse and sometimes apparently conflicting teachings of the Upanishads by arguing, as John Koller states: "that Brahman and Atman are, in some respects ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoga Sutras Of Patanjali
The ''Yoga Sutras of Patañjali'' is a collection of Sanskrit sutras ( aphorisms) on the theory and practice of yoga – 195 sutras (according to Vyāsa and Krishnamacharya) and 196 sutras (according to others, including BKS Iyengar). The ''Yoga Sutras'' was compiled in the early centuries CE, by the sage Patanjali in India who synthesized and organized knowledge about yoga from much older traditions. The ''Yoga Sutras'' is best known for its reference to '' ashtanga'', eight elements of practice culminating in ''samadhi''. The eight elements are ''yama'' (abstinences), '' niyama'' (observances), '' asana'' (yoga postures), ''pranayama'' (breath control), '' pratyahara'' (withdrawal of the senses), '' dharana'' (concentration of the mind), '' dhyana'' (meditation) and ''samadhi'' (absorption). The main aim of practice is '' kaivalya'', discernment of '' purusha'', the witness-consciousness, as distinct from '' prakriti'', the cognitive apparatus, and disentanglement of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |