|
Theophylact I Of Tusculum
Theophylact I (before 864 – 924/925) was a medieval count of Tusculum who was the effective ruler of Rome from around 905 through to his death in 924. His descendants controlled the papacy for the next 100 years. Biography Theophylact was the hereditary count of Tusculum, a small hill town near the vicinity of Rome. He is mentioned for the first time in a document of 901 as '' palatine iudex'' (''palace judge'', or leader of the militia) of Emperor Louis the Blind. He remained in Rome, commanding a group of soldiers after the emperor's return to Provence in 902, and was prominent in the overthrow of Antipope Christopher in January 904, whom he very likely ordered to be killed whilst in prison later that year. Theophylact formed an alliance with Duke Alberic I of Spoleto, and with their combined backing, Pope Sergius III was elected in Christopher's place. During his pontificate, Theophylact became Sergius’ '' sacri palatii vestararius'' and ''magister militum'', effectively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Tusculum
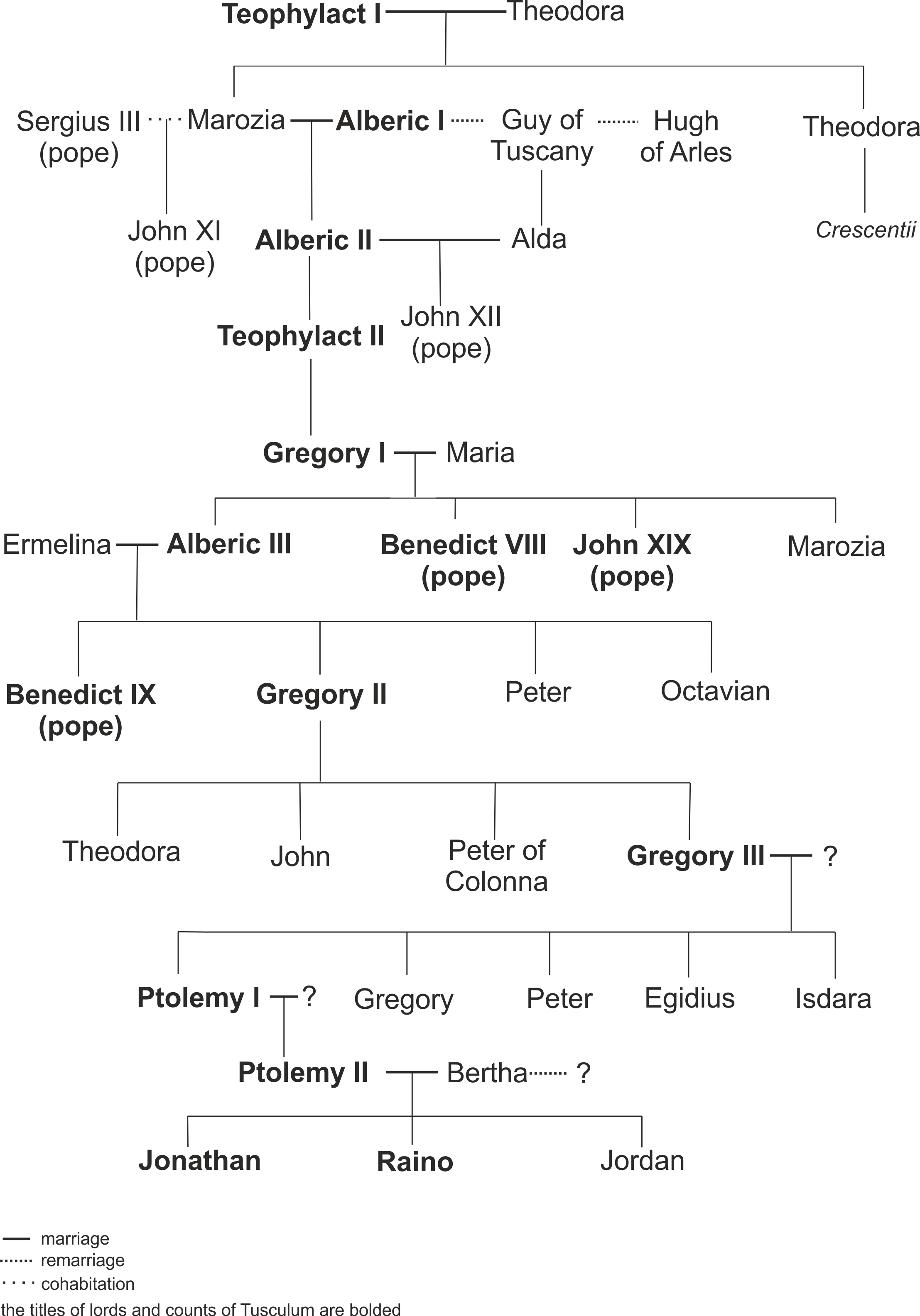
The counts of Tusculum, also known as the Theophylacti, were a family of secular noblemen from Latium that maintained a powerful position in Rome between the 10th and 12th centuries. Several popes and an antipope during the 11th century came from their ranks. They created and perfected the political formula of noble-papacy, wherein the pope was arranged to be elected only from the ranks of the Roman nobles. The Pornocracy, the period of influence by powerful female courtesans of the family, also influenced papal history. The counts of Tusculum remained arbiters of Roman politics and religion for more than a century. In addition to the papal influence, they held lay power through consulships and senatorial membership. Traditionally they were pro-Byzantine and anti-Germanic in their political affiliation. After 1049, the Tusculan Papacy came to an end with the appointment of Pope Leo IX. In fact, the Tusculan papacy was largely responsible for the reaction known as the Gregorian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodora (senatrix)
Theodora (c. 870 – 916) was a senatrix and ''serenissima vestaratrix'' of Rome. She was the mother of Marozia, alleged concubine to Pope Sergius III, and the mother of Pope John XI, fathered by—according to Liutprand of Cremona and the '' Liber Pontificalis''—Sergius. A third contemporary source, however—the annalist Flodoard (c. 894–966)—says John XI was the brother of Count Alberic II of Spoleto, the latter being the offspring of Marozia and her husband Count Alberic I of Spoleto. Hence John too was probably the son of Marozia and Alberic I. Theodora was characterized by the aforementioned Liutprand as a "shameless whore ... hoexercised power on the Roman citizenry like a man". Liutprand, a bishop of Cremona, was described by the as frequently being unfair to adversaries and could be partial in his judgments. General bibliography * E. Dümmler, ''Auxilius u. Vulgarius. Quellen und Forschungen zur Geschichte des Papsttums im Anfange des zehnten Jahrhunde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saeculum Obscurum
''Saeculum obscurum'' (, "the dark age/century"), also known as the Pornocracy or the Rule of the Harlots, was a period in the history of the Papacy during the first two-thirds of the 10th century, following the chaos after the death of Formosus in 896 which saw seven or eight papal elections in as many years. It began with the installation of Pope Sergius III in 904 and lasted for sixty years until the death of Pope John XII in 964. During this period, the popes were influenced strongly by a powerful and allegedly corrupt aristocratic family, the Theophylacti, and their relatives and allies. The era is seen as one of the lowest points of the history of the Papal office. Periodisation The ''saeculum obscurum'' was first named and identified as a period of papal immorality by the Italian cardinal and historian Caesar Baronius in his '' Annales Ecclesiastici'' in the sixteenth century. Baronius's primary source for his history of this period was a contemporaneous writer, Bisho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of Henry the Fowler and Matilda of Ringelheim. Otto inherited the Duchy of Saxony and the kingship of the Germans upon his father's death in 936. He continued his father's work of unifying all German tribes into a single kingdom and greatly expanded the king's powers at the expense of the aristocracy. Through strategic marriages and personal appointments, Otto installed members of his family in the kingdom's most important duchies. This reduced the various dukes, who had previously been co-equals with the king, to royal subjects under his authority. Otto transformed the church in Germany to strengthen royal authority and subjected its clergy to his personal control. After putting down a brief civil war among the rebellious duchies, Otto def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liutprand Of Cremona
Liutprand, also Liudprand, Liuprand, Lioutio, Liucius, Liuzo, and Lioutsios (c. 920 – 972),"LIUTPRAND OF CREMONA" in '' The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium'', Oxford University Press, New York & Oxford, 1991, p. 1241. was a historian, diplomat, and Bishop of Cremona born in northern Italy, whose works are an important source for the politics of the 10th century Byzantine court. Early life and career Liutprand was born into a prominent family from Pavia, of Lombard origins, around 920. In 931 he entered service as page to Hugh of Arles, who kept court at Pavia as King of Italy and who married the notorious and powerful Marozia of Rome. Liutprand was educated at the court and became a Deacon at the Cathedral of Pavia. After Hugh died in 947, leaving his son and co-ruler Lothair on the throne as King of Italy, Liutprand became confidential secretary to the actual ruler of Italy, Berengar II, marchese d'Ivrea, for whom he became chancellor. Mission to Constantinople In 949, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonna Family
The House of Colonna, also known as ''Sciarrillo'' or ''Sciarra'', is an Italian noble family, forming part of the papal nobility. It was powerful in medieval and Renaissance Rome, supplying one pope ( Martin V) and many other church and political leaders. The family is notable for its bitter feud with the Orsini family over influence in Rome, until it was stopped by papal bull in 1511. In 1571, the heads of both families married nieces of Pope Sixtus V. Thereafter, historians recorded that "no peace had been concluded between the princes of Christendom, in which they had not been included by name". History Origins According to tradition, the Colonna family is a branch of the Counts of Tusculum — by Peter (1099–1151) son of Gregory III, called Peter "de Columna" from his property the Columna Castle in Colonna, in the Alban Hills. Further back, they trace their lineage past the Counts of Tusculum via Lombard and Italo-Roman nobles, merchants, and clergy through the Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crescentii
The Crescentii (in modern Italian Crescenzi) were a baronial family, attested in Rome from the beginning of the 10th century and which in fact ruled the city and the election of the popes until the beginning of the 11th century. History Several individuals named ''Crescentius'' who appear in the very scanty documentation of the period have been grouped together by historians as the "Crescentii." Some do seem to bear family relationships, falling into two main branches, the Ottaviani and the Stefaniani, and their policies were consistent enough, especially as regards confronting the rival gang of aristocratic thugs, the Tusculani, who were descended from the influential curial official Theophylact, Count of Tusculum, ruler of Rome at the beginning of the 10th century. Their territorial strongholds were situated mainly in the Sabine Hills. The Crescentii had another formidable enemy, whose power did not always extend to Rome, in the German kings and emperors of the Ottonian Saxo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tusculani
The counts of Tusculum, also known as the Theophylacti, were a family of secular noblemen from Latium that maintained a powerful position in Rome between the 10th and 12th centuries. Several popes and an antipope during the 11th century came from their ranks. They created and perfected the political formula of noble-papacy, wherein the pope was arranged to be elected only from the ranks of the Roman nobles. The Pornocracy, the period of influence by powerful female courtesans of the family, also influenced papal history. The counts of Tusculum remained arbiters of Roman politics and religion for more than a century. In addition to the papal influence, they held lay power through consulships and senatorial membership. Traditionally they were pro-Byzantine and anti-Germanic in their political affiliation. After 1049, the Tusculan Papacy came to an end with the appointment of Pope Leo IX. In fact, the Tusculan papacy was largely responsible for the reaction known as the Gregorian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marozia
Marozia, born Maria and also known as Mariuccia or Mariozza ( 890 – 937), was a Roman noblewoman who was the alleged mistress of Pope Sergius III and was given the unprecedented titles ''senatrix'' ("senatoress") and ''patricia'' of Rome by Pope John X. Edward Gibbon wrote of her that the "influence of two sister prostitutes, Marozia and TheodoraHere Gibbon (the author of the famous ''The History of the Decline of the Roman Empire'') confused Theodora (the mother of Marozia) with Theodora (the sister of Marozia) was founded on their wealth and beauty, their political and amorous intrigues: the most strenuous of their lovers were rewarded with the Roman tiara, and their reign may have suggested to darker ages the fable of a female pope. The bastard son, two grandsons, two great grandsons, and one great great grandson of Marozia—a rare genealogy—were seated in the Chair of St. Peter." Pope John XIII was her nephew, the offspring of her younger sister Theodora. From th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Garigliano
The Battle of Garigliano was fought in 915 between Christian forces and the Saracens. Pope John X personally led the Christian forces into battle. The aim was to destroy the Arab fortress on the Garigliano River, which had threatened central Italy and the outskirts of Rome for nearly 30 years. Background After a series of ravaging attacks against the main sites of the Lazio in the second half of the 9th century, the Aghlabids established a colony next to the ancient city of Minturnae, near the Garigliano River. Here they even formed alliances with the nearby Christian princes (notably the hypati of Gaeta), taking advantage of the division between them. In 909, the Aghlabid Dynasty had been overthrown and replaced by the Fatimids, who assumed control over their territories in North Africa and southern Italy. Pope John X, however, managed to reunite these princes in an alliance in order to oust the Fatimids from their dangerous strongpoint. The Christian armies united the pope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saracens
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia Petraea and Arabia Deserta. The term's meaning evolved during its history of usage. During the Early Middle Ages, the term came to be associated with the tribes of Arabia. The oldest known source mentioning "Saracens" in relation to Islam dates back to the 7th century, in the Greek-language Christian tract ''Doctrina Jacobi''. Among other major events, the tract discusses the Muslim conquest of the Levant, which occurred after the rise of the Rashidun Caliphate following the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Roman-Catholic church and European Christian leaders used the term during the Middle Ages to refer to Muslims—usually Arabs, Turks, and Iranians. By the 12th century, "Saracen" had become synonymous with "Muslim" in M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berengar I Of Italy
Berengar I ( la, Berengarius, Perngarius; it, Berengario; – 7 April 924) was the king of Italy from 887. He was Holy Roman Emperor between 915 and his death in 924. He is usually known as Berengar of Friuli, since he ruled the March of Friuli from 874 until at least 890, but he had lost control of the region by 896. Berengar rose to become one of the most influential laymen in the empire of Charles the Fat, and he was elected to replace Charles in Italy after the latter's deposition in November 887. His long reign of 36 years saw him opposed by no less than seven other claimants to the Italian throne. His reign is usually characterised as ''troubled'' because of the many competitors for the crown and because of the arrival of Magyar raiders in Western Europe. His death was followed by an imperial interregnum that lasted 38 years until Otto I was crowned emperor in 962. Margrave of Friuli, 874–887 His family was called the Unruochings after his grandfather, Unruoch II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




