|
The Outlaw Of Torn
''The Outlaw of Torn'' is a historical novel by Edgar Rice Burroughs, taking place in 13th century England. Originally published as a five-part serial in ''New Story Magazine'' from January to May 1914, and first published in book form by A. C. McClurg in 1927. It was Burroughs' second novel, his first being the science fiction work ''A Princess of Mars''. His third was ''Tarzan of the Apes''. ''The Outlaw of Torn'' is one of only two historical novels Burroughs wrote. The other, ''I Am a Barbarian'', set in the Roman Empire, Rome of Caligula, was not published until 1967, seventeen years after his death. Plot summary The story is set in 13th-century England and concerns the fictional outlaw Norman of Torn, who purportedly harried the country during the power struggle between Henry III of England, King Henry III and Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester, Simon de Montfort. Norman is the supposed son of the Frenchman de Vac, once the king's fencing master, who has a grudge aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edgar Rice Burroughs
Edgar Rice Burroughs (September 1, 1875 – March 19, 1950) was an American author, best known for his prolific output in the adventure, science fiction, and fantasy genres. Best-known for creating the characters Tarzan and John Carter, he also wrote the '' Pellucidar'' series, the ''Amtor'' series, and the '' Caspak'' trilogy. Tarzan was immediately popular, and Burroughs capitalized on it in every way possible, including a syndicated Tarzan comic strip, movies, and merchandise. Tarzan remains one of the most successful fictional characters to this day and is a cultural icon. Burroughs's California ranch is now the center of the Tarzana neighborhood in Los Angeles, named after the character. Burroughs was an explicit supporter of eugenics and scientific racism in both his fiction and nonfiction; Tarzan was meant to reflect these concepts. Biography Early life and family Burroughs was born on September 1, 1875, in Chicago (he later lived for many years in the suburb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bounty (reward)
A bounty is a payment or reward of money to locate, capture or kill an outlaw or a wanted person. Two modern examples of bounties are the ones placed for the capture of Saddam Hussein and his sons by the United States government and Microsoft's bounty for computer virus creators. Those who make a living by pursuing bounties are known as bounty hunters. Examples Historical examples Written promises of reward for the capture of or information regarding criminals go back to at least the first-century Roman Empire. Graffiti from Pompeii, a Roman city destroyed by a volcanic eruption in 79 AD, contained this message: A copper pot went missing from my shop. Anyone who returns it to me will be given 65 bronze coins ( ''sestertii''). Twenty more will be given for information leading to the capture of the thief. A bounty system was used in the American Civil War as an incentive to increase enlistments. Another bounty system was used in New South Wales to increase the number of immigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Gutenberg
Project Gutenberg (PG) is a volunteer effort to digitize and archive cultural works, as well as to "encourage the creation and distribution of eBooks." It was founded in 1971 by American writer Michael S. Hart and is the oldest digital library. Most of the items in its collection are the full texts of books or individual stories in the public domain. All files can be accessed for free under an open format layout, available on almost any computer. , Project Gutenberg had reached 50,000 items in its collection of free eBooks. The releases are available in plain text as well as other formats, such as HTML, PDF, EPUB, MOBI, and Plucker wherever possible. Most releases are in the English language, but many non-English works are also available. There are multiple affiliated projects that provide additional content, including region- and language-specific works. Project Gutenberg is closely affiliated with Distributed Proofreaders, an Internet-based community for proofreading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired, anyone can legally use or reference those works without permission. As examples, the works of William Shakespeare, Ludwig van Beethoven, Leonardo da Vinci and Georges Méliès are in the public domain either by virtue of their having been created before copyright existed, or by their copyright term having expired. Some works are not covered by a country's copyright laws, and are therefore in the public domain; for example, in the United States, items excluded from copyright include the formulae of Newtonian physics, cooking recipes,Copyright Protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, educational, or musical form. Copyright is intended to protect the original expression of an idea in the form of a creative work, but not the idea itself. A copyright is subject to limitations based on public interest considerations, such as the fair use doctrine in the United States. Some jurisdictions require "fixing" copyrighted works in a tangible form. It is often shared among multiple authors, each of whom holds a set of rights to use or license the work, and who are commonly referred to as rights holders. These rights frequently include reproduction, control over derivative works, distribution, public performance, and moral rights such as attribution. Copyrights can be granted by public law and are in that case considered "territorial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip I Of France
Philip I (23 May 1052 – 29 July 1108), called the Amorous, was King of the Franks from 1060 to 1108. His reign, like that of most of the early Capetians, was extraordinarily long for the time. The monarchy began a modest recovery from the low it reached in the reign of his father and he added to the royal demesne the Vexin and Bourges. Early life Philip was born 23 May 1052 at Champagne-et-Fontaine, the son of Henry I and his wife Anne of Kiev. Unusual for the time in Western Europe, his name was of Greek origin, being bestowed upon him by his mother. Although he was crowned king at the age of seven, until age fourteen (1066) his mother acted as regent, the first queen of France ever to do so. Baldwin V of Flanders also acted as co-regent. Personal rule Following the death of Baldwin VI of Flanders, Robert the Frisian seized Flanders. Baldwin's widow, Richilda, requested aid from Philip, who was defeated by Robert at the battle of Cassel in 1071. Philip first married Ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon I De Montfort
Simon I de Montfort ( 1025 – 25 September 1087) was a French nobleman. He was born in Montfort l'Amaury, in the Duchy of Normandy, and became its lord. He was the son of Amaury I de Montfort and Bertrade. At his death he was buried about away in Épernon, because it was the site of the fortress he was instrumental in constructing. Progeny Simon I first married Isabel de Broyes (b. 1034 in Broyes, Marne), daughter of Hugh Bardoul. Their children were: * Amaury II de Montfort (c. 1056 – 1089), lord of Montfort * Isabel (Elizabeth) de Montfort (b. 1057), who married Raoul II de Tosny, a companion of William the Conqueror. Simon I's second marriage was to Agnes d'Evreux (b. 1030), daughter of Richard, Count of Évreux. Their children were: * Bertrade de Montfort (c. 1059 – 1117), became queen of France. * Richard de Montfort (c. 1066 – 1092), lord of Montfort, slain in attack on abbey at Conches. *Simon II de Montfort (c. 1068 – 1104), lord of Montfort * Amaury II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrade De Montfort
Bertrade de Montfort (c. 1070 – 14 February 1117) was Queen of France by her marriage to Philip I of France. Initially married to Fulk IV, Count of Anjou, she left him and married Philip. Later she founded a daughter house of Fontevraud Abbey at Haute-Bruyeres. Life She was the daughter of Simon I de Montfort and Agnes of Evreux. Her brother was Amaury de Montfort. In 1089, Bertrade and Fulk, Count of Anjou were married, and they became the parents of a son, Fulk. In 1092 she left her husband to live with King Philip I of France. Philip married her on 15 May 1092, despite the fact that they both had spouses living. He was so enamoured of Bertrade that he refused to leave her even when threatened with excommunication. Pope Urban II did excommunicate him in 1095, and Philip was prevented from taking part in the First Crusade. According to Orderic Vitalis, Bertrade was anxious that one of her sons succeed Philip, and sent a letter to King Henry I of England asking him to arrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
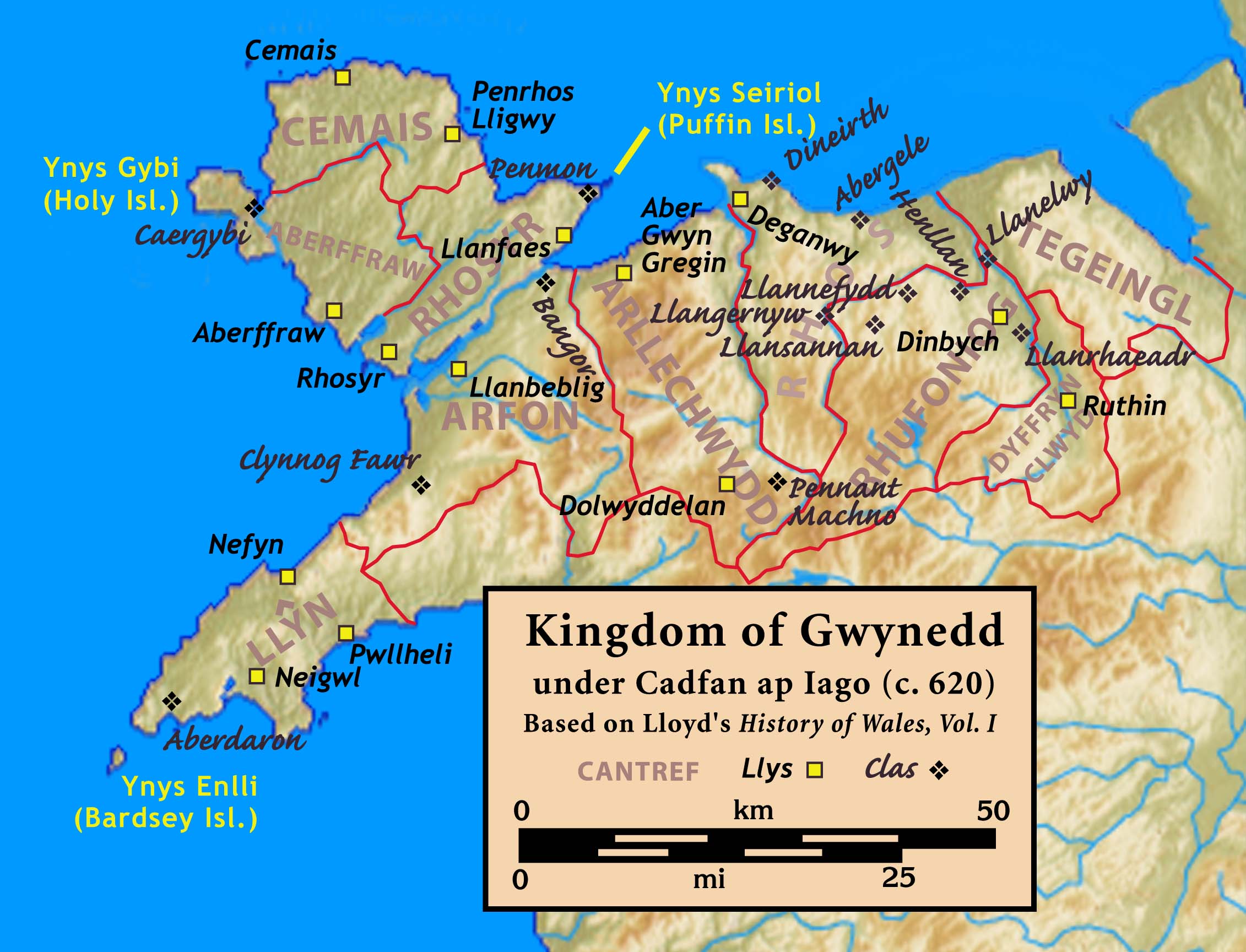
Kingdom Of Gwynedd
The Kingdom of Gwynedd (Medieval Latin: ; Middle Welsh: ) was a Welsh kingdom and a Roman Empire successor state that emerged in sub-Roman Britain in the 5th century during the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. Based in northwest Wales, the rulers of Gwynedd repeatedly rose to dominance and were acclaimed as " King of the Britons" before losing their power in civil wars or invasions. The kingdom of Gruffydd ap Llywelynthe King of Wales from 1055 to 1063was shattered by a Saxon invasion in 1063 just prior to the Norman invasion of Wales, but the House of Aberffraw restored by Gruffudd ap Cynan slowly recovered and Llywelyn the Great of Gwynedd was able to proclaim the Principality of Wales at the Aberdyfi gathering of Welsh princes in 1216. In 1277, the Treaty of Aberconwy between Edward I of England and Llewelyn's grandson Llywelyn ap Gruffudd granted peace between the two but would also guarantee that Welsh self-rule would end upon Llewelyn's death, and so it represen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Llywelyn Ap Gruffudd
Llywelyn ap Gruffudd (c. 1223 – 11 December 1282), sometimes written as Llywelyn ap Gruffydd, also known as Llywelyn the Last ( cy, Llywelyn Ein Llyw Olaf, lit=Llywelyn, Our Last Leader), was the native Prince of Wales ( la, Princeps Walliae, links=no; cy, Tywysog Cymru, links=no) from 1258 until his death at Cilmeri in 1282. Llywelyn was the son of Gruffydd ap Llywelyn Fawr and grandson of Llywelyn the Great, and he was one of the last native and independent princes of Wales before its conquest by Edward I of England and English rule in Wales that followed, until Owain Glyndŵr held the title during the Welsh Revolt of 1400–1415. Genealogy and early life Llywelyn was the second of the four sons of Gruffydd, the eldest son of Llywelyn the Great, and Senana ferch Caradog, the daughter of Caradoc ap Thomas ap Rhodri, Lord of Anglesey. The eldest was Owain Goch ap Gruffydd and Llywelyn had two younger brothers, Dafydd ap Gruffydd and Rhodri ap Gruffydd. Llywelyn is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleanor De Montfort
Eleanor de Montfort, Princess of Wales and Lady of Snowdon (1252 – 19 June 1282) was an English noble and Welsh Princess. She was the daughter of Simon de Montfort, 6th Earl of Leicester and Eleanor of England. She was also the second woman who can be shown to have used the title Princess of Wales. Early life Eleanor's maternal grandparents were King John of England and his Queen consort, Isabella of Angoulême. Her maternal uncles included the King of England, Henry of Winchester, and the King of the Romans, Richard of Cornwall. Her maternal aunts included the Queen of Scotland, Joan of England; the Holy Roman Empress, Queen of Germany and Queen of Sicily, Isabella of England; and the wife of the Prince of Wales, Joan, Lady of Wales. When Eleanor was thirteen years old, her father Simon de Montfort, and brother Lord Henry were killed at the Battle of Evesham (4 August 1265). According to the chroniclers, Nicholas Trivet, William Rishanger and others, Earl Simon had earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flores Historiarum
The ''Flores Historiarum'' (Flowers of History) is the name of two different (though related) Latin chronicles by medieval English historians that were created in the 13th century, associated originally with the Abbey of St Albans. Wendover's ''Flores Historiarum'' The first ''Flores Historiarum'' was created by St Albans writer, Roger of Wendover, who carried his chronology from the Creation up to 1235, the year before his death. Roger claims in his preface to have selected "from the books of catholic writers worthy of credit, just as flowers of various colours are gathered from various fields." Hence he also called his work ''Flores Historiarum''. However, like most chronicles, it is now valued not so much for what was culled from previous writers, as for its full and lively narrative of contemporary events from 1215 to 1235, including the signing of Magna Carta by King John at Runnymede. The book has survived in one thirteenth-century manuscript in the Bodleian Library (Dou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |