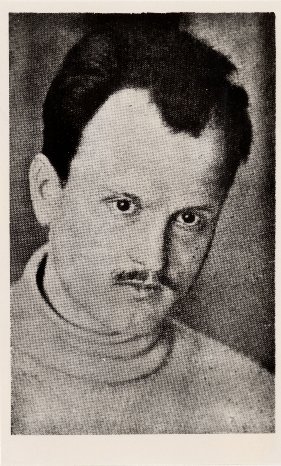|
The Declaration Of 46
The Declaration of 46 was a secret letter sent by a group of 46 leading Soviet communists to the Politburo of the Central Committee of the Soviet Communist Party on 15 October 1923. The declaration followed Leon Trotsky's letter sent to the Politburo on 8 October and expressed similar concerns, thus laying the foundation for the Left Opposition within the Soviet Communist Party later that year. The vast majority of the signatories were executed during the Great Purge. Background Starting in mid-summer 1923, the Soviet economy ran into significant difficulties arising from the scissor crisis. This led to numerous strikes countrywide. Two secret groups within the Communist Party, '' Workers' Truth'' and '' Workers' Group'', were uncovered and suppressed by the Soviet secret police. In September–October 1923, the much anticipated Communist revolution in Germany ended in defeat. On 8 October 1923, Trotsky sent a letter to the Central Committee and the Central Control Commission w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yevgeni Preobrazhensky
Yevgeni Alekseyevich Preobrazhensky ( rus, Евге́ний Алексе́евич Преображе́нский, p=jɪvˈɡʲenʲɪj ɐlʲɪˈksʲejɪvʲɪt͡ɕ prʲɪəbrɐˈʐɛnskʲɪj; 1886–1937) was a Russian revolutionary, Soviet economist and sociologist. A member of the governing Central Committee of the Bolshevik faction and its successor, the All-Union Communist Party, Preobrazhensky is remembered as a leading voice for the rapid industrialisation of peasant Russia through a concentration on state-owned heavy industry. Closely associated with Leon Trotsky and the Left Opposition movement of the 1920s, Preobrazhensky fell afoul of Stalin. He recanted Trotskyism in 1929, but eventually joined a secret alliance with Trotsky in 1932. He was arrested in 1933 and shot in 1937 during the Great Purge. Early years Yevgeni Alekseyevich Preobrazhensky was born in Bolkhov, Oryol Governorate, Russia Empire on 15 February 1886 (Old Style). His father was the son of an Orthodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleksandr Voronsky
Aleksandr Konstantinovich Voronsky (russian: Алекса́ндр Константи́нович Воро́нский) ( – 13 August 1937) was a prominent humanist Marxist literary critic, theorist and editor of the 1920s, disfavored and purged in 1937 for his work with the Left Opposition and Leon Trotsky during and after the October Revolution. Voronsky's writings were hidden away in the Soviet Union, until his autobiography, ''Waters of Life and Death'', and anthology, ''Art as the Cognition of Life'' were translated and published in English. Early life Voronsky was born in the village of Khoroshavka in Tambov Governorate; his father was the village priest, Konstantin Osipovich Voronsky, who died when Aleksandr was a few years old. After attending a Tambov religious school, in 1900 he enrolled in the Tambov Seminary, where he helped organize an illegal library for the seminary students. In 1904 he joined the Bolshevik faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labor Party, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Bubnov
Andrei Sergeyevich Bubnov (russian: Андре́й Серге́евич Бу́бнов; 23 March 1883 – 1 August 1938) was a Russian Bolshevik revolutionary leader, one of Bolshevik leaders in Ukraine, Soviet politician and military leader and member of the Left Opposition. Life Early career Bubnov was born in Ivanovo-Voznesensk in Vladimir Governorate (now Ivanovo, Ivanovo Oblast, Russia) on 23 March 1883. into a local Russian merchant's family. He was expelled from Moscow University for revolutionary activities. He studied at the Moscow Agricultural Institute and while a student joined the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) in 1903. He was a supporter of the Bolshevik faction of the party. In summer 1905, he joined the Ivanono-Voznesensk party committee, and was their delegate to the 4th (1906) and 5th (1907) Party Conferences in Stockholm and London. In 1907–08, he was a member of the RSDLP's Moscow committee, and of the Bolshevik committee for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jūlijs Daniševskis
Jūlijs Kārlis Daniševskis (russian: Карл Юлий Христианович Данишевский, Karl Yuri Hristianovich Danishevsky; 15 May 1884, Doblen County – 8 January 1938, Kommunarka shooting ground, Moscow Oblast), alias Hermanis, was a Latvian Marxist and professional revolutionary. Early life Daniševskis was born into a prosperous peasant family in Latvia. Having becoming involved in revolutionary circles as a teenager, he took an active part in the 1905 Revolution, after which he had to flee to Russia to escape the punitive expedition sent to reconquer Latvia for the Tsar. In June 1907, he was elected the sole Latvian representative on the Central Committee of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP)). in 1907–1914, he based at different times in St Petersburg, Baku, Tiflis, Warsaw, Riga, Latvia, and Moscow. In 1914, he was sentenced to exile for life in Narym, but escaped in January 1917. After the February Revolution, Daniševskis was a mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lev Sosnovsky
Lev Semyonovich Sosnovsky (Russian: Лев Семёнович Сосновский) (1 January 18863 July 1937) was a Russian revolutionary, publicist and journalist. He was a prominent Trotskyist and member of the left opposition who was executed for his opposition to Joseph Stalin during the Great Purge. Early life Lev Sosnovsky was born in Orenburg, the son of a retired soldier who had served in the army for 25 years during the reign of Tsar Nicholas I. During military service, his Jewish father, Semyon Sosnovsky, was beaten, and threatened with drowning unless he agreed to convert to the Russian Orthodox Church, which he refused to do. After leaving the army, he worked as a lawyer, despite being barely literate. Lev Sosnovsky left school early to work in a chemist's shop in Samara, where he joined the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party as a teenager, in 1903. He joined the Bolshevik faction of the RSDLP after moving to Ekaterinburg in 1904. During the 1905 Revolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timofei Sapronov
Timofei Vladimirovich Sapronov (russian: Тимофе́й Влади́мирович Сапро́нов; 1887 – September 28, 1937) was a Russian revolutionary, Old Bolshevik and socialist militant who was one of the leaders of the Left Opposition in the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. Early life and career Sapronov was born in Mostaushka, Tula Governorate in a family of Russian peasants. According to an autobiographical essay he wrote in the 1920s for the ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' his family lived a hut with a roof that leaked, and when he started school, aged seven, his clothes were so ragged that the other children nicknamed him "the beggar". From the age of 15, he worked as a painter. He took part in street demonstrations in Moscow during the 1905 Revolution, but the revolution had been suppressed, he wrote, "my search for some kind of organisation among construction workers was in vain, and I had no choice but to work alone." In 1912, he learnt about the Bolshevik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Muralov
Nikolay Ivanovich Muralov (russian: Николай Иванович Муралов; 7 December 1877 – 1 February 1937) was a Bolshevik revolutionary leader and military commander in Russia, who after 1923 became a member of the Left Opposition. Muralov was a direct participant in both the Revolution of 1905 and the October Revolution of 1917. A personal friend of Leon Trotsky, Muralov was arrested in 1936 during the Great Terror and was a defendant in the so-called "Trial of the Seventeen" in January 1937, after which he was executed. The official Soviet reckoning of Muralov was softened during the 1960s and he was afforded a full posthumous rehabilitation in 1986. Biography Early years Nikolay Ivanovich Muralov was born in 1877 on a farm ''(khutor)'' near Taganrog, a port city on the Sea of Azov.Nikolay Muralov, "Autobiography," in Georges Haupt and Jean-Jacques Marie, ''Makers of the Russian Revolution: Biographies of Bolshevik Leaders.'' 969C.I.P. Ferdinand and D.M. Bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerian Osinsky
Valerian Valerianovich Obolensky (Russian: Валериа́н Валериа́нович Оболе́нский; 25 March 1887 – 1 September 1938) (who worked under the pseudonym Nikolai Osinsky) was a Russian Bolshevik revolutionary, Marxist theorist, Soviet politician, economist and Professor of the Agricultural Academy of Moscow. Early life Valerian Obolensky was born in Kursk province, where his father was manager of a stud farm. While studying at the Faculty of Law of the Moscow University, Obolensky participated in the 1905 Russian Revolution and distributed revolutionary literature among students and was a reporter for the newspaper ''Izvestiya''. In 1907, he joined the Bolshevik faction of the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party. In the same year, he and Nikolai Bukharin organised a mass student demonstration. They and Vladimir Smirnov formed a trio of young economists who conducted theoretical 'raids' in which they disrupted lectures to challenge the lecturer. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgy Pyatakov
Georgy (Yury) Leonidovich Pyatakov (russian: Гео́ргий Леони́дович Пятако́в; 6 August 1890 – 30 January 1937) was a leader of the Bolsheviks and a key Soviet politician during and after the 1917 Russian Revolution. Biography Pre-revolution Pyatakov (party pseudonyms: Kievsky, Lyalin, Petro, Yaponets) was born 6 August 1890 in the town of Horodyshche in the Kiev Governorate of the Russian Empire, now modern-day Ukraine, to the large factory owning the Mariinsky or . His father, Leonid Timofeyevich Pyatakov (1847-1915), was a nobleman and chief engineer and director of the factory as well as co-owner of Musatov, Pyatakov, Sirotin, and Co. Pyatakov first became politically active as an anarchist in secondary school. He studied at the Faculty of Economics of St Petersburg University, until he was expelled in 1910. While studying at the school, he participated in a 1905-7 revolutionary movement in Kyiv. After his expulsion, he joined the Russian So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Nikitich Smirnov
Ivan Nikitich Smirnov (russian: Ива́н Ники́тич Смирно́в) (1881 – 25 August 1936) was a Russian Bolshevik revolutionary, Soviet politician and Communist Party functionary. A prominent member of the Left Opposition, he led a secret trotskyist opposition group in the Soviet Union during the Stalin period. He was arrested in 1933 and shot during the Great Purge. Political life He was born in Gorodishche, Penza Governorate in a family of Russian ethnicity. In 1899, Smirnov joined the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party and became a Bolshevik. He led Party activity in Moscow, Saint Petersburg, Vyshniy Volochok, Rostov, Kharkov, and Tomsk. Smirnov was subject to repeated arrests. In 1916, he was called up for army service in a reserve regiment in Tomsk. In 1917, he became a member of the executive committee of the Tomsk Soviet. In August of the same year, Smirnov was one of the organizers and managers of the Bolshevist publishing house ''"Volna"'' (Wave) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Antonov-Ovseenko
Vladimir Alexandrovich Antonov-Ovseenko (russian: Влади́мир Алекса́ндрович Анто́нов-Овсе́енко; ua, Володимир Антонов-Овсєєнко; 9 March 1883 – 10 February 1938), real surname Ovseenko, party aliases the 'Bayonet' (Штык) and 'Nikita' (Ники́та), a literary pseudonym A. Gal (А. Га́льский), was a prominent Bolshevik leader, Soviet statesman, military commander and diplomat. Early career He was born in Chernihiv, the son of an infantry officer and nobleman. He was of Ukrainian ethnicity. He studied at the secondary military school of Voronezh, but left the army in 1901 and joined a student Marxist circle in Warsaw. He graduated from military college in Saint Petersburg in 1904. In 1902 he secretly joined the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) and set about organising a military section of the party among graduate officers in five cities. Early in the Russian Revolution of 1905 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |