|
Tectonic Summary Of Qinghai
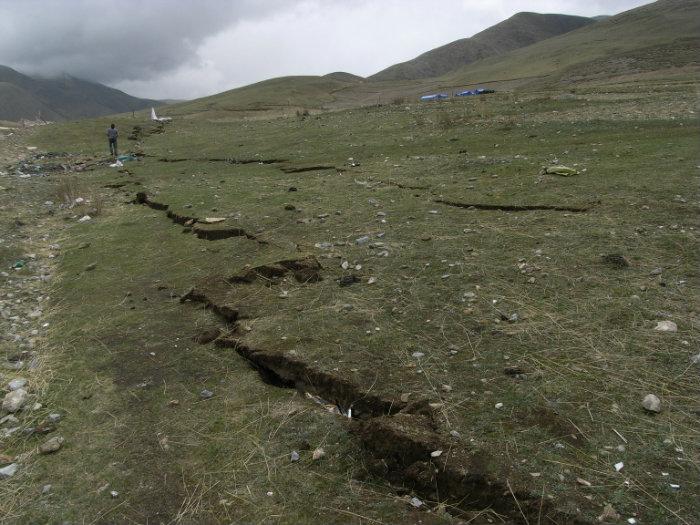
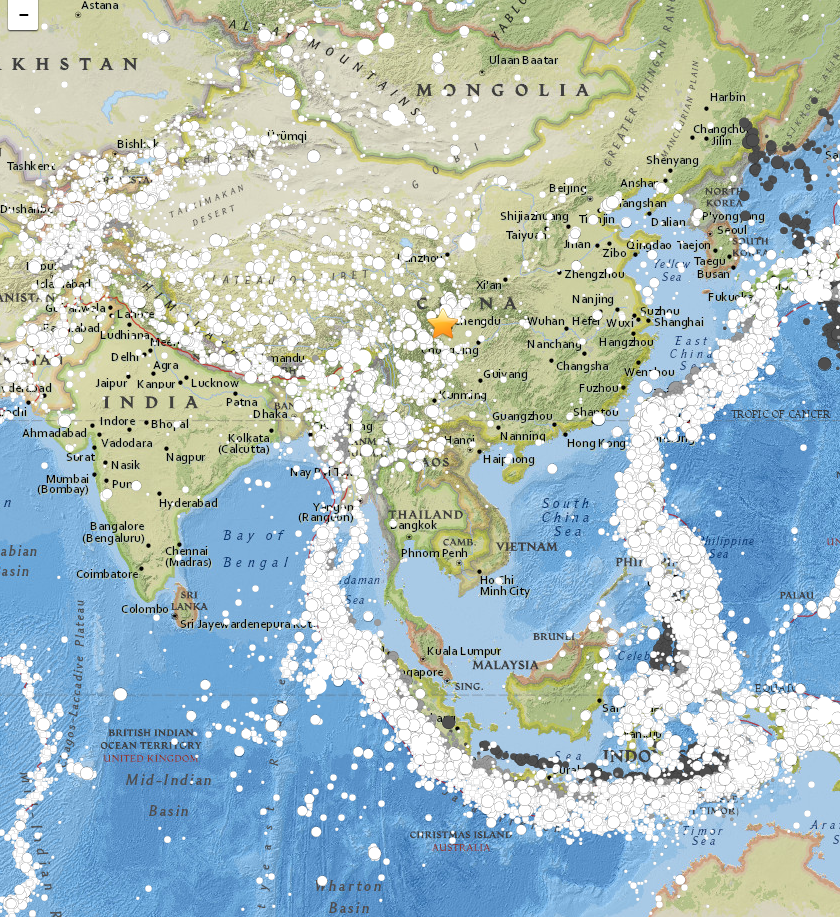
The southern Qinghai Province, China earthquake of April 13, 2010 occurred as a result of strike-slip faulting in the tectonically complex region of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. This earthquake occurred several hundred kilometers north of the convergent India:Eurasia plate boundary, where the Indian Plate is moving northwards with respect to Eurasia at a rate of approximately 46 mm/yr. This convergence drives the uplift of the Himalaya Mountains, at a rate of approximately 10 mm/yr, and the Tibetan Plateau, which is an extremely broad region of thickened and uplifted crust sitting above 4.5–5 km. In the region of the April 13 earthquake the Tibetan Plateau is extending and translating east-southeastward within a larger zone of generally north-south convergence. Based on the location, depth, and moment tensor of the event, the Qinghai Province earthquake likely reflects the interplay amongst these major tectonic forces, dominated in this location by southeastward tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai Province
Qinghai (; alternately romanized as Tsinghai, Ch'inghai), also known as Kokonor, is a landlocked province in the northwest of the People's Republic of China. It is the fourth largest province of China by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Manchu Relations in Five Phases of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Earthquake
This is a List of earthquakes in China, part of the series of lists of disasters in China. China has been the location of some of the most deadly earthquakes in history. The deadliest was the 1976 Tangshan earthquake with 300,000+ deaths. Earthquakes in the loess plateau where residents lived in yaodong caves tended to have big casualties, including the 1303 Hongdong and 1920 Haiyuan earthquakes. The most recent earthquake with a death toll of more than a thousand was the 2010 Yushu earthquake, which killed 2,698. The collision of India with the rest of Asia has led to seismic activity throughout Western China, particularly in Tibet and the Yunnan, Xinjiang, Sichuan, Gansu and Qinghai provinces. However, these regions in comparison with Eastern China have a low population density. These areas also in general have poorer transport and building codes. Throughout China, poor building codes increases the damage and loss of life from earthquakes. The northern regions of Eastern Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strike-slip Faulting
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Tibet Autonomous Region, most of Qinghai, western half of Sichuan, Southern Gansu provinces in Western China, southern Xinjiang, Bhutan, the Indian regions of Ladakh and Lahaul and Spiti (Himachal Pradesh) as well as Gilgit-Baltistan in Pakistan, northwestern Nepal, eastern Tajikistan and southern Kyrgyzstan. It stretches approximately north to south and east to west. It is the world's highest and largest plateau above sea level, with an area of (about five times the size of Metropolitan France). With an average elevation exceeding and being surrounded by imposing mountain ranges that harbor the world's two highest summits, Mount Everest and K2, the Tibetan Plateau is often referred to as "the Roof of the World". The Tibetan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago and the Russian Far East to the east. The continental landmass is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and Africa to the west, the Pacific Ocean to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and by Africa, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Indian Ocean to the south. The division between Europe and Asia as two continents is a historical social construct, as many of their borders are over land; thus, in some parts of the world, Eurasia is recognized as the largest of the six, five, or four continents on Earth. In geology, Eurasia is often considered as a single rigid megablock. However, the rigidity of Eurasia is debated based on paleomagnetic data. Eurasia covers around , or around 36.2% of the Earth's total land area. It is also home to the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began moving north and carried Insular India with it. It was once fused with the adjacent Australian Plate to form a single Indo-Australian Plate, and recent studies suggest that India and Australia have been separate plates for at least 3 million years and likely longer. The Indian Plate includes most of modern South Asia (the Indian subcontinent) and a portion of the basin under the Indian Ocean, including parts of South China and western Indonesia, and extending up to but not including Ladakh, Kohistan and Balochistan. Plate movements Until roughly , the Indian Plate formed part of the supercontinent Gondwana together with modern Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Gondwana broke up as these continents drifted apart at di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convergent Boundary
A convergent boundary (also known as a destructive boundary) is an area on Earth where two or more lithospheric plates collide. One plate eventually slides beneath the other, a process known as subduction. The subduction zone can be defined by a plane where many earthquakes occur, called the Wadati–Benioff zone. These collisions happen on scales of millions to tens of millions of years and can lead to volcanism, earthquakes, orogenesis, destruction of lithosphere, and deformation. Convergent boundaries occur between oceanic-oceanic lithosphere, oceanic-continental lithosphere, and continental-continental lithosphere. The geologic features related to convergent boundaries vary depending on crust types. Plate tectonics is driven by convection cells in the mantle. Convection cells are the result of heat generated by the radioactive decay of elements in the mantle escaping to the surface and the return of cool materials from the surface to the mantle. These convection cells bring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altyn Tagh Fault
The Altyn Tagh Fault (ATF) is a 2,000 km long, active, sinistral (left lateral) strike-slip fault that forms the northwestern boundary of the Tibetan Plateau with the Tarim Basin. It is one of the major sinistral strike-slip structures that together help to accommodate the eastward motion of this zone of thickened crust, relative to the Eurasian Plate. A total displacement of about ~475 km has been estimated for this fault zone since the middle Oligocene, although the amount of displacement, age of initiation and slip rate are disputed. Tectonic setting The Tibetan Plateau is an area of thickened continental crust, a result of the ongoing collision of the Indo-Australian Plate with the Eurasian Plate. The way in which this zone accommodates the collision remains unclear with two end-member models being proposed. The first regards the crust as being made up of a mosaic of strong blocks separated by weak fault zones, the 'microplate' model. The second regards the deformati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunlun
The Kunlun Mountains ( zh, s=昆仑山, t=崑崙山, p=Kūnlún Shān, ; ug, كۇئېنلۇن تاغ تىزمىسى / قۇرۇم تاغ تىزمىسى ) constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the broadest sense, the chain forms the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau south of the Tarim Basin. The exact definition of Kunlun Mountains varies over time. Older sources used Kunlun to mean the mountain belt that runs across the center of China, that is, Altyn Tagh along with the Qilian and Qin Mountains. Recent sources have the Kunlun range forming most of the south side of the Tarim Basin and then continuing east, south of the Altyn Tagh. Sima Qian (''Records of the Grand Historian'', scroll 123) says that Emperor Wu of Han sent men to find the source of the Yellow River and gave the name Kunlun to the mountains at its source. The name seems to have originated as a semi-mythical location in the classical Chinese text ''Classic of Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2010 Yushu Earthquake
The 2010 Yushu earthquake struck on April 14 and registered a magnitude of 6.9 Mw (USGS, EMSC) or 7.1 MsAbout 400 dead, 10,000 injured in 7.1-magnitude quake in China's Qinghai , xinhuanet.com. Retrieved 14 April 2010. ( CEA, CENC). It had a maximum felt intensity of IX (''Violent'') on the Mercalli intensity scale. It originated in Yushu, |
Geology Of China
The geology of China (or the geological structure of the People's Republic of China) consists of three Precambrian cratons surrounded by a number of orogenic belts. The modern tectonic environment is dominated by the continued collision of India with the rest of Asia starting 40–50 million years ago. This has formed the Himalaya and continues to deform most of China. China has vast mineral reserves, a significant earthquake risk in its Western regions and rare isolated active volcanoes throughout the country. Many geological concepts were discovered very early in China's history. However, it was not until the adoption of European natural science in the late 19th century that geology became a science in China. Landscape evolution The geomorphology of China can be divided into several parts. The historical centre of Chinese culture is on the loess plateau, the world's largest Quaternary loess deposit, and on the alluvial lands at the east of it. The alluvial East China plain e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

