|
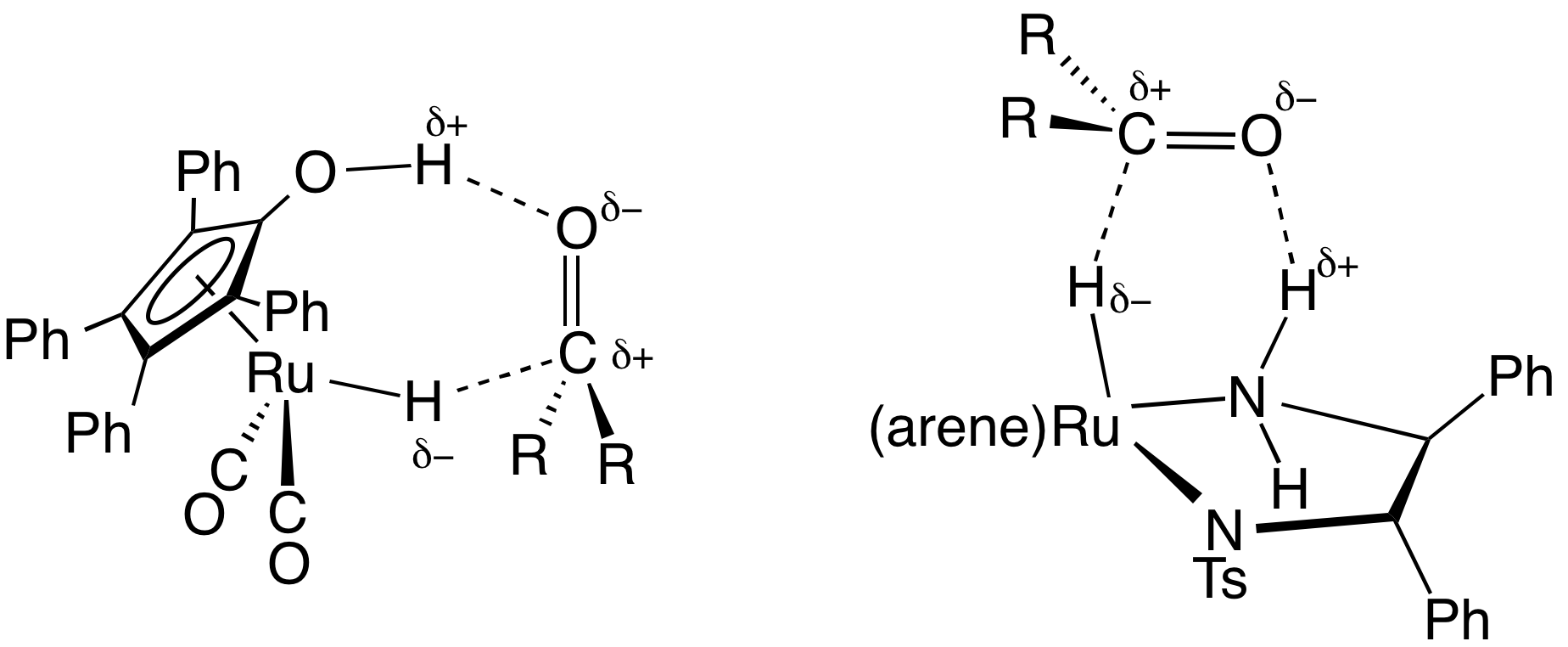
Transfer Hydrogenation
In chemistry, transfer hydrogenation is a chemical reaction involving the addition of hydrogen to a compound from a source other than molecular . It is applied in laboratory and industrial organic synthesis to saturate organic compounds and reduce ketones to alcohols, and imines to amines. It avoids the need for high-pressure molecular used in conventional hydrogenation. Transfer hydrogenation usually occurs at mild temperature and pressure conditions using organic or organometallic catalysts, many of which are chiral, allowing efficient asymmetric synthesis. It uses hydrogen donor compounds such as formic acid, isopropanol or dihydroanthracene, dehydrogenating them to , acetone, or anthracene respectively. Often, the donor molecules also function as solvents for the reaction. A large scale application of transfer hydrogenation is coal liquefaction using "donor solvents" such as tetralin. Organometallic catalysts In the area of organic synthesis, a useful family of hydrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during chemical reaction, reactions with other chemical substance, substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both Basic research, basic and Applied science, applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth (botany), the formation of igneous rocks (geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded (ecology), the prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropanol
Isopropyl alcohol (IUPAC name propan-2-ol and also called isopropanol or 2-propanol) is a colorless, flammable, organic compound with a pungent alcoholic odor. Isopropyl alcohol, an organic polar molecule, is miscible in water, ethanol, and chloroform, demonstrating its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances including ethyl cellulose, polyvinyl butyral, oils, alkaloids, and natural resins. Notably, it is not miscible with salt solutions and can be separated by adding sodium chloride in a process known as salting out. It forms an azeotrope with water, resulting in a boiling point of 80.37 °C and is characterized by its slightly bitter taste. Isopropyl alcohol becomes viscous at lower temperatures, freezing at −89.5 °C, and has significant ultraviolet-visible absorbance at 205 nm. Chemically, it can be oxidized to acetone or undergo various reactions to form compounds like isopropoxides or aluminium isopropoxide. As an isopropyl group linked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol (), is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a Saturated and unsaturated compounds, saturated carbon atom. Alcohols range from the simple, like methanol and ethanol, to complex, like sugar alcohols and cholesterol. The presence of an OH group strongly modifies the properties of Hydrocarbon, hydrocarbons, conferring Hydrophile, hydrophilic (water-loving) properties. The OH group provides a site at which many reactions can occur. History The flammable nature of the exhalations of wine was already known to ancient natural philosophers such as Aristotle (384–322 BCE), Theophrastus (–287 BCE), and Pliny the Elder (23/24–79 CE). However, this did not immediately lead to the isolation of alcohol, even despite the development of more advanced distillation techniques in second- and third-century Roman Egypt. An important recognition, first found in one of the writings attributed to Jabir ibn Hayyan, J� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysts
Catalysis () is the increase in reaction rate, rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form reaction intermediate, intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous catalysis, homogeneou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylethylenediamine
1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethylenediamine, DPEN, is an organic compound with the formula H2NCHPhCHPhNH2, where Ph is phenyl (C6H5). DPEN exists as three stereoisomers: meso and two enantiomers S,S- and R,R-. The chiral diastereomers are used in asymmetric hydrogenation. Both diastereomers are bidentate ligands. Preparation and optical resolution 1,2-Diphenyl-1,2-ethylenediamine can be prepared from benzil by reductive amination. DPEN can be obtained as both the chiral and meso diastereomers, depending on the relative stereochemistry of the two CHPhNH2 subunits. The chiral diastereomer, which is of greater value, can be resolved into the R,R- and S,S- enantiomers using tartaric acid as the resolving agent. In methanol, the R,R enantiomer has a specific rotation of �sub>23 +106±1°. Asymmetric catalysis N-tosylated derivative, TsDPEN, is a ligand precursor for catalysts for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. For example, (cymene)Ru(''S'',''S''-TsDPEN) catalyzes the hydrogenation of ben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(cymene)ruthenium Dichloride Dimer
(Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer is the organometallic compound with the formula cymene)RuCl This red-coloured, diamagnetic solid is a reagent in organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. The complex is structurally similar to (benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer. Preparation and reactions The dimer is prepared by the reaction of the phellandrene with hydrated ruthenium trichloride. At high temperatures, cymene)RuClexchanges with other arenes: : cymene)RuCl+ 2 CMe → CMe)RuCl+ 2 cymene (Cymene)ruthenium dichloride dimer reacts with Lewis bases to give monometallic adducts: : cymene)RuCl+ 2 PPh → 2 (cymene)RuCl(PPh) Such monomers adopt pseudo-octahedral piano-stool structures. Precursor to catalysts Treatment of cymene)RuClwith the chelating ligand Ts DPENH gives (cymene)Ru(TsDPEN-H), a catalyst for asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. cymene)RuClis also used to prepare catalysts (by monomerization with dppf) used in borrowing hydrogen catalysis, a cataly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphine
Phosphine (IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotting fish, due to the presence of substituted phosphine and diphosphane (). With traces of present, is spontaneously flammable in air ( pyrophoric), burning with a luminous flame. Phosphine is a highly toxic respiratory poison, and is immediately dangerous to life or health at 50 ppm. Phosphine has a trigonal pyramidal structure. Phosphines are compounds that include and the organophosphines, which are derived from by substituting one or more hydrogen atoms with organic groups. They have the general formula . Phosphanes are saturated phosphorus hydrides of the form , such as triphosphane. Phosphine () is the smallest of the phosphines and the smallest of the phosphanes. History Philippe Gengembre (1764–1838), a student of Lavoisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamine
A diamine is an amine with two amino groups. Diamines are used as monomers to prepare polyamides, polyimides, and polyureas. The term ''diamine'' refers mostly to Primary (chemistry), primary diamines, as those are the most reactive. In terms of quantities produced, 1,6-diaminohexane (a precursor to Nylon 6-6) is most important, followed by ethylenediamine. Vicinal (chemistry), Vicinal diamines (1,2-diamines) are a structural motif in many biological compounds and are used as ligands in coordination chemistry. Aliphatic diamines Linear * 2 carbon backbone: ethylenediamine (1,2-diaminoethane). Related derivatives include the N-alkylated compounds, 1,1-dimethylethylenediamine, 1,2-dimethylethylenediamine, ethambutol, tetrakis(dimethylamino)ethylene, TMEDA. Many 1,2-diamine derivatives are of practical interest such as penicillin. * 3 carbon backbone: 1,3-diaminopropane (propane-1,3-diamine) * 4 carbon backbone: putrescine (butane-1,4-diamine) * 5 carbon backbone: cadaverine (pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhodium
Rhodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isotope, which is 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is usually found as a free metal or as an alloy with similar metals and rarely as a chemical compound in minerals such as bowieite and rhodplumsite. It is one of the rarest and most valuable precious metals. Rhodium is a group 9 element (cobalt group). Rhodium is found in platinum or nickel ores with the other members of the platinum group metals. It was discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston in one such ore, and named for the rose color of one of its chlorine compounds. The element's major use (consuming about 80% of world rhodium production) is as one of the catalysts in the three-way catalytic converters in automobiles. Because rhodium metal is inert against corrosion and mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruthenium
Ruthenium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is unreactive to most chemicals. Karl Ernst Claus, a Russian scientist of Baltic-German ancestry, discovered the element in 1844 at Kazan State University and named it in honor of Russia. (He used the Latin name '' Ruthenia'', which can have other meanings, but specifically stated that the element was named in honor of his "motherland".) Ruthenium is usually found as a minor component of platinum ores; the annual production has risen from about 19 tonnes in 2009 to some 35.5 tonnes in 2017. Most ruthenium produced is used in wear-resistant electrical contacts and thick-film resistors. A minor application for ruthenium is in platinum alloys and as a chemical catalyst. A new application of ruthenium is as the capping layer for extreme ultraviolet photoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetralin
Tetralin (1,2,3,4-tetrahydronaphthalene) is a hydrocarbon having the chemical formula C10H12. It is a partially hydrogenated derivative of naphthalene. It is a colorless liquid that is used as a hydrogen-donor solvent. Production Tetralin is produced by the catalytic hydrogenation of naphthalene. Although nickel catalysts are traditionally employed, many variations have been evaluated. Over-hydrogenation converts tetralin into decahydronaphthalene ( decalin). Rarely encountered is dihydronaphthalene ( dialin). Laboratory methods In a classic named reaction called the Darzens tetralin synthesis, named for Auguste Georges Darzens (1926), derivatives can be prepared by intramolecular electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of a 1-aryl-pent-4-ene using concentrated sulfuric acid, Uses Tetralin is used as a hydrogen-donor solvent, for example in coal liquifaction. It functions as a source of H2, which is transferred to the coal. The partially hydrogenated coal is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Liquefaction
Coal liquefaction is a process of converting coal into liquid hydrocarbons: liquid fuels and petrochemicals. This process is often known as "coal to X" or "carbon to X", where X can be many different hydrocarbon-based products. However, the most common process chain is "coal to liquid fuels" (CTL). Historical background Coal liquefactions originally was developed at the beginning of the 20th century. The best-known CTL process is Fischer–Tropsch synthesis (FT), named after the inventors Franz Joseph Emil Fischer, Franz Fischer and Hans Tropsch from the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute in the 1920s. The FT synthesis is the basis for indirect coal liquefaction (ICL) technology. Friedrich Bergius, also a German chemist, invented direct coal liquefaction (DCL) as a way to convert lignite into synthetic oil in 1913. Coal liquefaction was an important part of Adolf Hitler's four-year plan of 1936, and became an integral part of German industry during World War II. During the mid-1930s, compan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |