|
Transcription Factor Jun
Transcription factor Jun is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''JUN'' gene. c-Jun, in combination with protein c-Fos, forms the AP-1 early response transcription factor. It was first identified as the Fos-binding protein p39 and only later rediscovered as the product of the JUN gene. c-jun was the first oncogenic transcription factor discovered. The proto-oncogene c-Jun is the cellular homolog of the viral oncoprotein v-jun (). The viral homolog v-jun was discovered in avian sarcoma virus 17 and was named for ''ju-nana'', the Japanese word for 17. The human JUN encodes a protein that is highly similar to the viral protein, which interacts directly with specific target DNA sequences to regulate gene expression. This gene is intronless and is mapped to 1p32-p31, a chromosomal region involved in both translocations and deletions in human malignancies. Function Regulation Both Jun and its dimerization partners in AP-1 formation are subject to regulation by diverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In eukaryotic cells (having a cell nucleus) including animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells, the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase, and the M phase that includes mitosis and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the M phase, the replicated Chromosome, chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angiogenesis
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature mainly by processes of sprouting and splitting, but processes such as coalescent angiogenesis, vessel elongation and vessel cooption also play a role. Vasculogenesis is the embryonic formation of endothelial cells from mesoderm cell precursors, and from neovascularization, although discussions are not always precise (especially in older texts). The first vessels in the developing embryo form through vasculogenesis, after which angiogenesis is responsible for most, if not all, blood vessel growth during development and in disease. Angiogenesis is a normal and vital process in growth and development, as well as in wound healing and in the formation of granulation tissue. However, it is also a fundamental step in the transition of tumors from a benign state to a malign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), or non-small-cell lung carcinoma, is any type of epithelial lung cancer other than small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC accounts for about 85% of all lung cancers. As a class, NSCLCs are relatively insensitive to chemotherapy, compared to small-cell carcinoma. When possible, they are primarily treated by surgical resection with curative intent, although chemotherapy has been used increasingly both preoperatively ( neoadjuvant chemotherapy) and postoperatively ( adjuvant chemotherapy). Types The most common types of NSCLC are squamous-cell carcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma, but several other types occur less frequently. A few of the less common types are pleomorphic, carcinoid tumor, salivary gland carcinoma, and unclassified carcinoma. All types can occur in unusual histologic variants and as mixed cell-type combinations. Non-squamous-cell carcinoma almost occupies the half of NSCLC. In the tissue classification, the cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stromal Cell
Stromal cells, or mesenchymal stromal cells, are differentiating cells found in abundance within bone marrow but can also be seen all around the body. Stromal cells can become connective tissue cells of any organ, for example in the uterine mucosa (endometrium), prostate, bone marrow, lymph node and the ovary. They are cells that support the function of the parenchymal cells of that organ. The most common stromal cells include fibroblasts and pericytes. The term ''stromal'' comes from Latin , "bed covering", and Ancient Greek , , "bed". Stromal cells are an important part of the body's immune response and modulate inflammation through multiple pathways. They also aid in differentiation of hematopoietic cells and forming necessary blood elements. The interaction between stromal cells and tumor cells is known to play a major role in cancer growth and progression. In addition, by regulating local cytokine networks (e.g. M-CSF, LIF), bone marrow stromal cells have been describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is a series of natural changes in hormone production and the structures of the uterus and ovaries of the female reproductive system that makes pregnancy possible. The ovarian cycle controls the production and release of eggs and the cyclic release of estrogen and progesterone. The uterine cycle governs the preparation and maintenance of the lining of the uterus (womb) to receive an embryo. These cycles are concurrent and coordinated, normally last between 21 and 35 days, with a median length of 28 days. Menarche (the onset of the first period) usually occurs around the age of 12 years; menstrual cycles continue for about 30–45 years. Naturally occurring hormones drive the cycles; the cyclical rise and fall of the follicle stimulating hormone prompts the production and growth of oocytes (immature egg cells). The hormone estrogen stimulates the uterus lining ( endometrium) to thicken to accommodate an embryo should fertilization occur. The blood suppl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
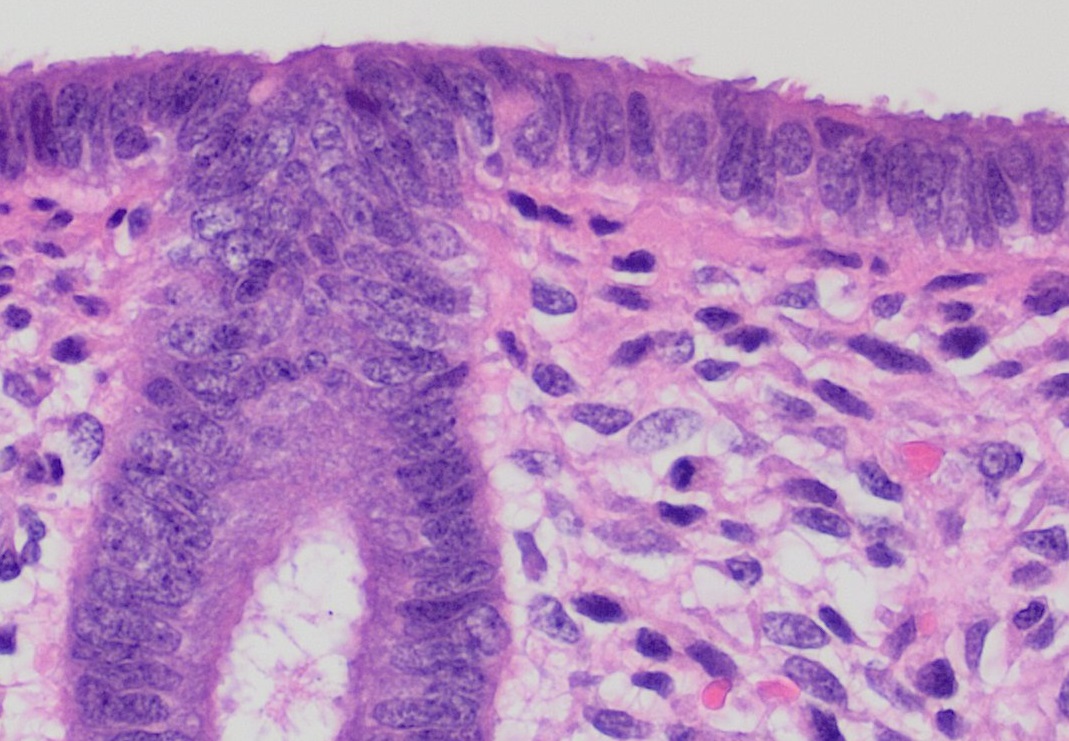
Endometrium
The endometrium is the inner epithelium, epithelial layer, along with its mucous membrane, of the mammalian uterus. It has a basal layer and a functional layer: the basal layer contains stem cells which regenerate the functional layer. The functional layer thickens and then is shed during menstruation in humans and some other mammals, including other apes, Old World monkeys, some species of bat, the elephant shrew and the Cairo spiny mouse. In most other mammals, the endometrium is reabsorbed in the estrous cycle. During pregnancy, the glands and blood vessels in the endometrium further increase in size and number. Vascular spaces fuse and become interconnected, forming the placenta, which supplies oxygen and nutrition to the embryo and fetus.Blue Histology - Female Reproductive System ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life * Cellphone, a phone connected to a cellular network * Clandestine cell, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Electrochemical cell, a device used to convert chemical energy to electrical energy * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Cell may also refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities * Cell (comics), a Marvel comic book character * Cell (Dragon Ball), Cell (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the manga series ''Dragon Ball'' Literature * Cell (novel), ''Cell'' (novel), a 2006 horror novel by Stephen King * "Cells", poem, about a hungover soldier in gaol, by Rudyard Kipling *The Cell (play), ''The Cell'' (play), an Australian play by Robert Wales Music * Cell (music), a small rhythmic and melodic design that can be isolated, or can make up one part of a thematic context * Cell (American band) * Cell (Japanese band) * Cell (album), ''Cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in: * Protein synthesis * Protein storage * Transformation of carbohydrates * Synthesis of cholesterol, bile salts and phospholipids * Detoxification, modification, and excretion of exogenous and endogenous substances * Initiation of formation and secretion of bile Structure The typical hepatocyte is cubical with sides of 20-30 μm, (in comparison, a human hair has a diameter of 17 to 180 μm).The diameter of human hair ranges from 17 to 181 μm. The typical volume of a hepatocyte is 3.4 x 10−9 cm3. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in hepatocytes, in contrast to most other cell types. Microanatomy Hepatocytes display an eosinophilic cytoplasm, reflecting numerous mitochondria, and basophilic stippling due to large amounts of rough endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. Brown lipofuscin granules are also observed (wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF), formerly known as TNF-α, is a chemical messenger produced by the immune system that induces inflammation. TNF is produced primarily by activated macrophages, and induces inflammation by binding to its receptors on other cells. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily, a family of transmembrane proteins that are cytokines, chemical messengers of the immune system. Excessive production of TNF plays a critical role in several inflammatory diseases, and TNF-blocking drugs are often employed to treat these diseases. TNF is produced primarily by macrophages but is also produced in several other cell types, such as T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and mast cells. It is produced rapidly in response to pathogens, cytokines, and environmental stressors. TNF is initially produced as a type II transmembrane protein (tmTNF), which is then cleaved by TNF alpha converting enzyme (TACE) into a soluble form (sTNF) and secreted from the cell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a family of transcription factor protein complexes that controls transcription (genetics), transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found in almost all animal cell types and is involved in cellular responses to stimuli such as stress, cytokines, free radicals, heavy metals, ultraviolet irradiation, oxidized LDL, and bacterial or viral antigens. NF-κB plays a key role in regulating the immune response to infection. Incorrect regulation of NF-κB has been linked to cancer, inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, septic shock, viral infection, and improper immune development. NF-κB has also been implicated in processes of synaptic plasticity and memory. Discovery NF-κB was discovered by Ranjan Sen in the lab of Nobel laureate David Baltimore via its interaction with an 11-base pair sequence in the immunoglobulin light-chain Enhancer (genetics), enhancer in B cells. Later work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |